March/April 2015
... damaging our eyes, from our solar telescopes with filters, to the more sophisticated spectrograph that can channel and isolate specific colours (or wavelengths) of light. This is done by splitting the white light coming from the Sun into a spectrum of colour and looking for what are called spectral ...
... damaging our eyes, from our solar telescopes with filters, to the more sophisticated spectrograph that can channel and isolate specific colours (or wavelengths) of light. This is done by splitting the white light coming from the Sun into a spectrum of colour and looking for what are called spectral ...
Black Holes and Cosmic Roles: Understanding the Center of the
... • Black Hole: A region of space with a force of gravity that is so intense that nothing, including light, can escape. They are formed by the collapse of massive stars. • Escape Velocity: The speed at which an object needs to travel to overcome the Earth’s force p of gravity. Mathematically, it is ex ...
... • Black Hole: A region of space with a force of gravity that is so intense that nothing, including light, can escape. They are formed by the collapse of massive stars. • Escape Velocity: The speed at which an object needs to travel to overcome the Earth’s force p of gravity. Mathematically, it is ex ...
Galaxies - science1d
... •The most distant galaxies are 15 million ly away •When light left them, the ...
... •The most distant galaxies are 15 million ly away •When light left them, the ...
I. Stars - SharpSchool
... • Galaxy: A large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. • Milky Way: Our galaxy which contains about 200 billion stars and many nebulas ...
... • Galaxy: A large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. • Milky Way: Our galaxy which contains about 200 billion stars and many nebulas ...
Document
... We are orbiting one of Many stars in many Galaxies We locate everything in Space based on the types of radiation or light it gives off. ...
... We are orbiting one of Many stars in many Galaxies We locate everything in Space based on the types of radiation or light it gives off. ...
TTh HW05 key
... Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures thus far. Choose the correct response from those listed, along with at least a one (1) sentence justification for your answer. Alternate justification techniques include math calculations ...
... Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures thus far. Choose the correct response from those listed, along with at least a one (1) sentence justification for your answer. Alternate justification techniques include math calculations ...
fall semester review
... 35. If a star is 17 light years away from us, how long does it take light from that star to reach Earth? 17 years 36. What is the importance of using different units of measurement for different lengths? Some distances are much shorter or longer than others so we use different measurements to make ...
... 35. If a star is 17 light years away from us, how long does it take light from that star to reach Earth? 17 years 36. What is the importance of using different units of measurement for different lengths? Some distances are much shorter or longer than others so we use different measurements to make ...
the free PDF resource
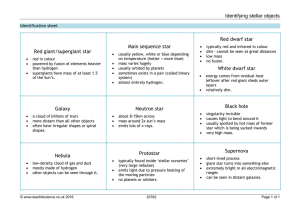
... usually yellow, white or blue depending on temperature (hotter = more blue) mass varies hugely usually orbited by planets sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
... usually yellow, white or blue depending on temperature (hotter = more blue) mass varies hugely usually orbited by planets sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 77 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 3 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 77 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 3 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE Objectives
... The force of gravity depends on what two factors? What two factors keep moons and planets in orbit? What causes the phases of the moon? What are the eight phases of the moon? Sketch each one. What is an eclipse? What are the two types of eclipses? What causes each one? What is the difference between ...
... The force of gravity depends on what two factors? What two factors keep moons and planets in orbit? What causes the phases of the moon? What are the eight phases of the moon? Sketch each one. What is an eclipse? What are the two types of eclipses? What causes each one? What is the difference between ...
The Earth and Beyond
... If the light source is moving ___ from us we would find that the absorption lines are all _______ towards the ___ end of the spectrum (the longer wavelength end). The ________ the light source is moving the further its pattern is shifted. Light from the edge of the ______ also shows this pattern, so ...
... If the light source is moving ___ from us we would find that the absorption lines are all _______ towards the ___ end of the spectrum (the longer wavelength end). The ________ the light source is moving the further its pattern is shifted. Light from the edge of the ______ also shows this pattern, so ...
Atomic_spectra
... Fraunhofer also completed an important theoretical work on diffraction and established the laws of diffraction. One important innovation that Fraunhofer made was to place a diffraction slit in front of the objective of a measuring telescope in order to study the solar spectrum. He later made and use ...
... Fraunhofer also completed an important theoretical work on diffraction and established the laws of diffraction. One important innovation that Fraunhofer made was to place a diffraction slit in front of the objective of a measuring telescope in order to study the solar spectrum. He later made and use ...
1 PS 3.9 Grade 9 Review
... Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ supernova □ nebula ...
... Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ supernova □ nebula ...
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels thru space Electromagnetic Spectrum - all of the forms of electromagnetic radiation (visible light, x-rays, uv and infrared light, micro and radio waves) ...
... that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels thru space Electromagnetic Spectrum - all of the forms of electromagnetic radiation (visible light, x-rays, uv and infrared light, micro and radio waves) ...
Back ground information
... of evidence is that the universe is still expanding. When scientists use telescopes to look at the night sky, they can see galaxies moving away from our galaxy and each other all over the universe at very high speeds. Using telescopes, they can take pictures of these galaxies moving away from us. Sp ...
... of evidence is that the universe is still expanding. When scientists use telescopes to look at the night sky, they can see galaxies moving away from our galaxy and each other all over the universe at very high speeds. Using telescopes, they can take pictures of these galaxies moving away from us. Sp ...
IL CIELO COME LABORATORIO – 2010/2011 STAR FORMATION
... and the theoretical number of stars necessary to heat the ionized gas if all the stars belong to spectral class O5 or B1. The Star Formation Rate of the galaxy results 7 solar masses per year, that means that in the warmest regions of the arms and in the bulge, every year could be created on average ...
... and the theoretical number of stars necessary to heat the ionized gas if all the stars belong to spectral class O5 or B1. The Star Formation Rate of the galaxy results 7 solar masses per year, that means that in the warmest regions of the arms and in the bulge, every year could be created on average ...
Lecture 1 outline handout
... Lecture: Deep Space & Deep Time 1. Range of space and time A. electrons to Universe B. microseconds (1/1,000,000 sec. ) to age of Universe (~14,000,000,000 years) 2. Units of measure A. metric system B. units of mass (M), length (L), time (T) C. converting english to metric (1 km = 0.6 mi; 1 mi = 1. ...
... Lecture: Deep Space & Deep Time 1. Range of space and time A. electrons to Universe B. microseconds (1/1,000,000 sec. ) to age of Universe (~14,000,000,000 years) 2. Units of measure A. metric system B. units of mass (M), length (L), time (T) C. converting english to metric (1 km = 0.6 mi; 1 mi = 1. ...
Slide 1
... picture taken by the Hubble telescope. The dimensions of the galaxy, officially called M104, are as spectacular as its appearance It has 800 billion suns and is 50,000 light years across. ...
... picture taken by the Hubble telescope. The dimensions of the galaxy, officially called M104, are as spectacular as its appearance It has 800 billion suns and is 50,000 light years across. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.