Advantages of FTIR spectroscopy
... and combination vibrations are excited. The far infrared’, or FIR, spectral range is between 400 and about 5 cm-1 wavenumbers. This range covers the vibrational frequencies of both backbone vibrations of large molecules, as well as fundamental vibrations of molecules that include heavy atoms (e.g. i ...
... and combination vibrations are excited. The far infrared’, or FIR, spectral range is between 400 and about 5 cm-1 wavenumbers. This range covers the vibrational frequencies of both backbone vibrations of large molecules, as well as fundamental vibrations of molecules that include heavy atoms (e.g. i ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Apparent Magnitude – The measure of how bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
... Apparent Magnitude – The measure of how bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
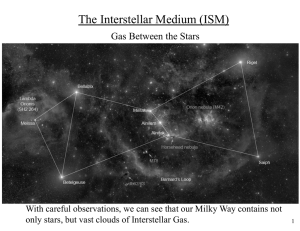
The Interstellar Medium (ISM)
... Why is the gas ionized and why does it trace star-forming regions? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star f ...
... Why is the gas ionized and why does it trace star-forming regions? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star f ...
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... 22. A ____________ is a huge collection of gas, dust, and hundreds of billions of stars. Our galaxy is called the _________ _________ and is ____________ shaped. 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the ...
... 22. A ____________ is a huge collection of gas, dust, and hundreds of billions of stars. Our galaxy is called the _________ _________ and is ____________ shaped. 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the ...
P1 The Earth in the Universe
... The heat and light is caused by nuclear fusion when hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium. All elements larger than helium were created in earlier stars. All stars have a life cycle. The information we get about other stars comes from radiation that we can detect. ...
... The heat and light is caused by nuclear fusion when hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium. All elements larger than helium were created in earlier stars. All stars have a life cycle. The information we get about other stars comes from radiation that we can detect. ...
Chapter 18 Notes Astronomy: The Original Science People in
... sun revolved around the Earth. b. Ptolemy i. Greek astronomer who published a book in 140 AD that combined all of the ancient knowledge of astronomy. ii. Ptolemy agreed with Aristotle that the Earth was the center of the universe. c. Copernicus i. Polish Astronomer who was trained as a medical docto ...
... sun revolved around the Earth. b. Ptolemy i. Greek astronomer who published a book in 140 AD that combined all of the ancient knowledge of astronomy. ii. Ptolemy agreed with Aristotle that the Earth was the center of the universe. c. Copernicus i. Polish Astronomer who was trained as a medical docto ...
Evolution phototrophic microorganism has resulted in a diversity of
... Groote Moost (51o18’N, 5o51 E’) were sampled from small rowing boats on 16 September 2005 and 16 September 2006, respectively. Water samples were taken at 1 m depth with a Ruttner water sampler (Hydro-Bios Apparatebau GmbH, Kiel, Germany). Measurement of light spectra At each sampling station, the i ...
... Groote Moost (51o18’N, 5o51 E’) were sampled from small rowing boats on 16 September 2005 and 16 September 2006, respectively. Water samples were taken at 1 m depth with a Ruttner water sampler (Hydro-Bios Apparatebau GmbH, Kiel, Germany). Measurement of light spectra At each sampling station, the i ...
Level :3ASS3-4 School Year: 2009/2010 English
... Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. It includes also the satellites of the planets; numerous comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. The moon is the satellite rotating around the Erath and the closest body to it. The Sun is the richest source of electromagnetic energy (mostly in the ...
... Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. It includes also the satellites of the planets; numerous comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. The moon is the satellite rotating around the Erath and the closest body to it. The Sun is the richest source of electromagnetic energy (mostly in the ...
Chapter 3 Light and Atoms
... related to its temperature • Hotter objects radiate more strongly at shorter wavelengths • Blue has a shorter •Objects can emit radiation at many different wavelengths. wavelength than red, so •The wavelength at which a star is brightest hotter objects look bluer. is related to its temperature. •Thi ...
... related to its temperature • Hotter objects radiate more strongly at shorter wavelengths • Blue has a shorter •Objects can emit radiation at many different wavelengths. wavelength than red, so •The wavelength at which a star is brightest hotter objects look bluer. is related to its temperature. •Thi ...
30-3
... c. has no particular shape, may have a low total mass, and is fairly rich in dust and gas d. has a straight bar of stars that runs through the center ...
... c. has no particular shape, may have a low total mass, and is fairly rich in dust and gas d. has a straight bar of stars that runs through the center ...
Scaling the Universe
... Match the following objects with the correct letter in front of its name. A. B. C. D. E. F. ...
... Match the following objects with the correct letter in front of its name. A. B. C. D. E. F. ...
Earth Science
... Apparent change in position of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
... Apparent change in position of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum - Introduction
... Electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of a stream of photons, which are massless particles each traveling in a wave-like pattern and moving at the speed of light. Each photon contains a certain amount (or bundle) of energy, and all electromagnetic radiation consists of these photons. T ...
... Electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of a stream of photons, which are massless particles each traveling in a wave-like pattern and moving at the speed of light. Each photon contains a certain amount (or bundle) of energy, and all electromagnetic radiation consists of these photons. T ...
The universe - Villanova University
... of atoms to form, which they do. Photons can now move large distances. Universe is “visible”. ...
... of atoms to form, which they do. Photons can now move large distances. Universe is “visible”. ...
Midterm II Jeopardy
... $200 - This planet occasionally has dust storms which obscure its ENTIRE surface. (Mars) $400 - You can only see these planets close to the horizon (45 degrees or less). (Venus & Mercury) $600 - This is how we observed the rings around Uranus. (Occultation) $800 - These two planets most closely rese ...
... $200 - This planet occasionally has dust storms which obscure its ENTIRE surface. (Mars) $400 - You can only see these planets close to the horizon (45 degrees or less). (Venus & Mercury) $600 - This is how we observed the rings around Uranus. (Occultation) $800 - These two planets most closely rese ...
The Sun
... The Moon, Tides, Eclipses, and the Seasons The Earth has seasons because the axis is tilted as it revolves around the sun. The Moon: The Moon revolves and rotates at the same rate. This is why the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth. The phase of the moon you see depends on how much of the ...
... The Moon, Tides, Eclipses, and the Seasons The Earth has seasons because the axis is tilted as it revolves around the sun. The Moon: The Moon revolves and rotates at the same rate. This is why the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth. The phase of the moon you see depends on how much of the ...
Reading Selections for ID1113, p
... a. the movement of galaxies away from the Earth I also think this is an answer b. the expanding movement of the universe best answer; see paragraph 6 c. the gravitational attraction of stars 2. This text can be seen in terms of: Perhaps the question should be, “This text presents…” a. a sugges ...
... a. the movement of galaxies away from the Earth I also think this is an answer b. the expanding movement of the universe best answer; see paragraph 6 c. the gravitational attraction of stars 2. This text can be seen in terms of: Perhaps the question should be, “This text presents…” a. a sugges ...
Document
... Photomultiplier-single channel, but very high sensitivity - Light falls on a photosensitive alloy (Cs3Sb, K2CsSb, Na2KSb) - Electrons from surface are ...
... Photomultiplier-single channel, but very high sensitivity - Light falls on a photosensitive alloy (Cs3Sb, K2CsSb, Na2KSb) - Electrons from surface are ...
The Big Bang Theory
... Red shift - as light from distant galaxies approach earth there is an increase of space between earth and the galaxy, which leads to wavelengths being stretched In 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, discovered a noise of extraterrestrial origin that came from all directions at once radiation left ...
... Red shift - as light from distant galaxies approach earth there is an increase of space between earth and the galaxy, which leads to wavelengths being stretched In 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, discovered a noise of extraterrestrial origin that came from all directions at once radiation left ...
Solar System Unit Review - Parma City School District
... What is a huge ball of very hot, glowing gases in space that can produce it’s own heat? ...
... What is a huge ball of very hot, glowing gases in space that can produce it’s own heat? ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.