Unit 1: Map Skills Vocabulary
... or south of the Equator; used to measure degrees of latitude. Global Positioning System: a group of satellites that travel around the Earth, which can be used to pinpoint an exact location on the earth. ...
... or south of the Equator; used to measure degrees of latitude. Global Positioning System: a group of satellites that travel around the Earth, which can be used to pinpoint an exact location on the earth. ...
Chapter 3 - Csulb.edu
... using parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude. Latitude is the angular distance of a point north or south of the equator. It increases from a minimum of 0° at the equator to a maximum of 90° at the north and the south poles. Lines of latitude are parallel to each other and describe circle ...
... using parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude. Latitude is the angular distance of a point north or south of the equator. It increases from a minimum of 0° at the equator to a maximum of 90° at the north and the south poles. Lines of latitude are parallel to each other and describe circle ...
The 5 Themes of Geography
... 1.____ Great Plains used to be a wide open area with no settlements or farms. Today towns and cities dot the Great Plains, and much of the land is used for farming 2. ____ Areas that receive very little rainfall are called deserts. 3._____ Texas is south of Oklahoma. 4._____ Hawaii is made up of isl ...
... 1.____ Great Plains used to be a wide open area with no settlements or farms. Today towns and cities dot the Great Plains, and much of the land is used for farming 2. ____ Areas that receive very little rainfall are called deserts. 3._____ Texas is south of Oklahoma. 4._____ Hawaii is made up of isl ...
1st Nine Weeks Geography Study Guide
... latitude run East to West. Lines of longitude run North to South. The Equator is at 0 degrees latitude and divides the Earth into northern and southern hemispheres. The Prime Meridian is at 0 degrees longitude and divides the Earth into eastern and western hemispheres. 3. What is another name for li ...
... latitude run East to West. Lines of longitude run North to South. The Equator is at 0 degrees latitude and divides the Earth into northern and southern hemispheres. The Prime Meridian is at 0 degrees longitude and divides the Earth into eastern and western hemispheres. 3. What is another name for li ...
region - Fort Bend ISD
... Chad is located south of Libya, west of Sudan, East of Niger and North of the Central African Republic ...
... Chad is located south of Libya, west of Sudan, East of Niger and North of the Central African Republic ...
Student PP on Thinking Geographically-5th block
... • Globalization: Actions or processes that involve the entire world • International Date Line: 180 Longitude. -When heading East the clock moves back 24 hours -When going west the calendar moves ...
... • Globalization: Actions or processes that involve the entire world • International Date Line: 180 Longitude. -When heading East the clock moves back 24 hours -When going west the calendar moves ...
Travel Destinations
... –First-most people travel to places where people speak the same language –Second-it may be a_________________________ to tourist, they fear going to places that do not speak their language (lack of communications and understanding) –Language barriers_____________________ the movement of tourist Food ...
... –First-most people travel to places where people speak the same language –Second-it may be a_________________________ to tourist, they fear going to places that do not speak their language (lack of communications and understanding) –Language barriers_____________________ the movement of tourist Food ...
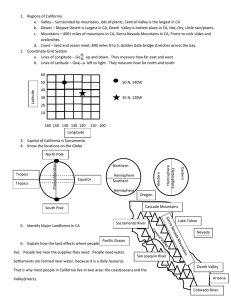
1. Regions of California a. Valley – Surrounded by mountains, lots of
... a. Lines of Longitude – Go up and down. They measure how far east and west b. Lines of Latitude – Go left to right. They measure how far north and south ...
... a. Lines of Longitude – Go up and down. They measure how far east and west b. Lines of Latitude – Go left to right. They measure how far north and south ...
geography pre-test
... 23. The parallel lines running north to south on a globe are called lines of latitude_____ 24. The parallel lines running north to south on a globe are called lines of longitude_____ 25.The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean______ ...
... 23. The parallel lines running north to south on a globe are called lines of latitude_____ 24. The parallel lines running north to south on a globe are called lines of longitude_____ 25.The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean______ ...
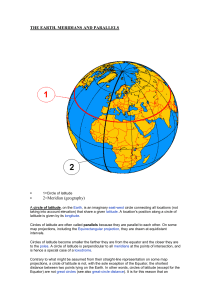
THE EARTH. MERIDIANS AND PARALLELS
... Pole to the South Pole that connects all locations running along it with a given longitude. The position of a point on the meridian is given by the latitude. Each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitudeat the intersection points. Each is also the same size, being half of a great circle ...
... Pole to the South Pole that connects all locations running along it with a given longitude. The position of a point on the meridian is given by the latitude. Each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitudeat the intersection points. Each is also the same size, being half of a great circle ...
geography - Net Texts
... lines that circle the globe from east to west and are also known as Parallels. Lines of Longitude are imaginary lines that circle the globe from north to south and are also called Meridians. ...
... lines that circle the globe from east to west and are also known as Parallels. Lines of Longitude are imaginary lines that circle the globe from north to south and are also called Meridians. ...
5 Themes of Geography
... Lines of Latitude Are used to locate places and measure distances North or South of the Equator. ...
... Lines of Latitude Are used to locate places and measure distances North or South of the Equator. ...
Unit 1 Review Game - mr. clark`s guide to geography
... Geography Quiz Show Remember to raise your hand when your team has decided on an answer. No shouting it out! ...
... Geography Quiz Show Remember to raise your hand when your team has decided on an answer. No shouting it out! ...
Chapter 3
... 2. It produces the Coriolis effect which deflects the flow of fluids (air and water) to the left in the southern hemisphere and to the right in the northern hemisphere. 3. Tides result from the moon’s gravitational pull on the side of the Earth closest to the moon, creating a rise and fall of ocean ...
... 2. It produces the Coriolis effect which deflects the flow of fluids (air and water) to the left in the southern hemisphere and to the right in the northern hemisphere. 3. Tides result from the moon’s gravitational pull on the side of the Earth closest to the moon, creating a rise and fall of ocean ...
Multiple Choice
... 4. The pattern of weather over a long period of time is called climate. 5. Geographers are most likely to study landforms and their locations. 6. Geographers study regions so that they can make comparison. 7. A globe is more accurate than a map because a globe can show the true shape of the continen ...
... 4. The pattern of weather over a long period of time is called climate. 5. Geographers are most likely to study landforms and their locations. 6. Geographers study regions so that they can make comparison. 7. A globe is more accurate than a map because a globe can show the true shape of the continen ...
Geography Skills
... C. Geographers divide the globe into 4 hemispheres to study D. An imaginary line known as the Equator divides the Globe into the Northern and Southern hemispheres ...
... C. Geographers divide the globe into 4 hemispheres to study D. An imaginary line known as the Equator divides the Globe into the Northern and Southern hemispheres ...
5 Themes of Geography Study Guide
... Map Skills and Five Themes of Geography Study Guide Key You should use this study guide as well as notes from class to help you prepare for the quiz. Spend some time studying over the weekend (half an hour each day) and you will do just fine! 1. What are the five themes of geography? LOCATION PLACE ...
... Map Skills and Five Themes of Geography Study Guide Key You should use this study guide as well as notes from class to help you prepare for the quiz. Spend some time studying over the weekend (half an hour each day) and you will do just fine! 1. What are the five themes of geography? LOCATION PLACE ...
Introduction to Geography
... How people adapt to the environment in places in which they live. Ex. People who live around the Nile River in Egypt have built irrigation ditches in order to ...
... How people adapt to the environment in places in which they live. Ex. People who live around the Nile River in Egypt have built irrigation ditches in order to ...
Chapter 6 - views of Earth PPT
... B. Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each about 15° of longitude wide and exactly one hour different from the zones on either side of it. C. Calendar dates begin and end at midnight; the International Date Line is located at the 180° meridian. ...
... B. Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each about 15° of longitude wide and exactly one hour different from the zones on either side of it. C. Calendar dates begin and end at midnight; the International Date Line is located at the 180° meridian. ...
Location of Atlantic Canada PowerPoint
... Location We often ask questions such as “Where did it happen?” and “How do you get there?” We can answer with a relative location or an absolute location ...
... Location We often ask questions such as “Where did it happen?” and “How do you get there?” We can answer with a relative location or an absolute location ...
1021 - NT - Chapter 1 Guided Notes
... Why is the Prime Meridian in Greenwich? Britain was a world leader in exploration and map making. Thus navigators of other nations often used British maps. As a result, in 1884 the meridian of Greenwich was adopted throughout most of the world as the prime meridian. There was still another reaso ...
... Why is the Prime Meridian in Greenwich? Britain was a world leader in exploration and map making. Thus navigators of other nations often used British maps. As a result, in 1884 the meridian of Greenwich was adopted throughout most of the world as the prime meridian. There was still another reaso ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.