Map scale: refers to a relationship
... earth. Can be a statement (1 inch equals 1 mile), a ration (1:100) or a graphic bar. 2. Location: where something is described as either absolute [blank] or relative [blank] 3. Cartography: the science of map making. 4. Distance: how far apart two features are 5. Distortion: this happens when trying ...
... earth. Can be a statement (1 inch equals 1 mile), a ration (1:100) or a graphic bar. 2. Location: where something is described as either absolute [blank] or relative [blank] 3. Cartography: the science of map making. 4. Distance: how far apart two features are 5. Distortion: this happens when trying ...
Illustrated Glossary File
... description of the natural environment of a place. It includes physical features (landforms and bodies of water), weather and climate, soil, vegetation, and animal life. ...
... description of the natural environment of a place. It includes physical features (landforms and bodies of water), weather and climate, soil, vegetation, and animal life. ...
Unit 3: Geography of the Western Hemisphere
... description of the natural environment of a place. It includes physical features (landforms and bodies of water), weather and climate, soil, vegetation, and animal life. ...
... description of the natural environment of a place. It includes physical features (landforms and bodies of water), weather and climate, soil, vegetation, and animal life. ...
The Earth - Valhalla High School
... • Our planet has a magnetic field as if a giant bar magnet were buried within Earth. • When you use a magnetic compass, the compass needle points toward Earth’s magnetic pole that is very close to the geographic north pole. ...
... • Our planet has a magnetic field as if a giant bar magnet were buried within Earth. • When you use a magnetic compass, the compass needle points toward Earth’s magnetic pole that is very close to the geographic north pole. ...
The Earth
... • Our planet has a magnetic field as if a giant bar magnet were buried within Earth. • When you use a magnetic compass, the compass needle points toward Earth’s magnetic pole that is very close to the geographic north pole. ...
... • Our planet has a magnetic field as if a giant bar magnet were buried within Earth. • When you use a magnetic compass, the compass needle points toward Earth’s magnetic pole that is very close to the geographic north pole. ...
General World Cultures Chapter 1
... You may have said something like “Next to the KFC” or “Across the street from Subway” or “By the railroad tracks on Vine Street”. This is called the relative location. In order to understand the relative location of a place, you must understand the location of the place(s) that you reference. * Geog ...
... You may have said something like “Next to the KFC” or “Across the street from Subway” or “By the railroad tracks on Vine Street”. This is called the relative location. In order to understand the relative location of a place, you must understand the location of the place(s) that you reference. * Geog ...
Latitude
... and west from the 0º line of longitude (also called the prime meridian). The 0º line runs through Greenwich, England. Halfway around the globe is the longitude line (in the mid-Pacific) which is both 180º east and 180º west of Greenwich. The 180 one-degree latitude lines are numbered in two 90-degre ...
... and west from the 0º line of longitude (also called the prime meridian). The 0º line runs through Greenwich, England. Halfway around the globe is the longitude line (in the mid-Pacific) which is both 180º east and 180º west of Greenwich. The 180 one-degree latitude lines are numbered in two 90-degre ...
5 Themes PowerPoint
... • An imaginary grid of lines used to find location • Can be found on most maps throughout the world • It is a uniform measurement (all countries use it) ...
... • An imaginary grid of lines used to find location • Can be found on most maps throughout the world • It is a uniform measurement (all countries use it) ...
what is geography?
... - Regions are areas that share common characteristics - These include characteristics such as land, natural resources, or population SOLAR SYSTEM • Inner planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – Small and solid planets • Outer planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune • Each planet follows an orbit ...
... - Regions are areas that share common characteristics - These include characteristics such as land, natural resources, or population SOLAR SYSTEM • Inner planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – Small and solid planets • Outer planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune • Each planet follows an orbit ...
Geography Review - Willis High School
... on the surface expressed in latitude and longitude Region-An area that is unified by on or more characteristics Grassland-An area where the natural vegetation is grass Relative location-The location of a place in location to another place Plain-A landform that is generally level ...
... on the surface expressed in latitude and longitude Region-An area that is unified by on or more characteristics Grassland-An area where the natural vegetation is grass Relative location-The location of a place in location to another place Plain-A landform that is generally level ...
Around the World - Celina City Schools
... Atlantic Ocean - the second-largest ocean in the world, covering approximately one-fifth of the Earth' s surface. The Atlantic is between the Americas on the west and Europe and Africa on the east. Pacific Ocean - the largest of the earth' s oceans. It extends from the Arctic in the north to th ...
... Atlantic Ocean - the second-largest ocean in the world, covering approximately one-fifth of the Earth' s surface. The Atlantic is between the Americas on the west and Europe and Africa on the east. Pacific Ocean - the largest of the earth' s oceans. It extends from the Arctic in the north to th ...
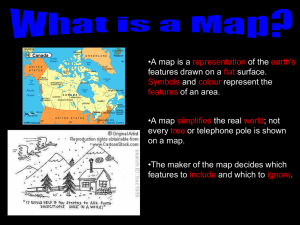
What is a Map?
... latitude and its longitude. • Who uses latitude and longitude “coordinates”? – Pilot – Captain of a Ship – GPS (Global Positioning System) ...
... latitude and its longitude. • Who uses latitude and longitude “coordinates”? – Pilot – Captain of a Ship – GPS (Global Positioning System) ...
North Carolina - River Mill Academy
... • Where a place is in relation to another place • Uses directional words to describe – Cardinal and ...
... • Where a place is in relation to another place • Uses directional words to describe – Cardinal and ...
Chapter 2: The Geographers World
... and measure distance north and south of the Equator E. Longitude Lines: imaginary lines that run between the North and South Poles and measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian ...
... and measure distance north and south of the Equator E. Longitude Lines: imaginary lines that run between the North and South Poles and measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian ...
5 Themes of Geography
... locate places northsouth (N/S) on the globe. Equator = 0 degrees • Longitude Lines: run north-south (N/S) to locate places east-west (E/W) on the globe. Prime meridian = 0 degrees • Relative Location: where something is in relation to its surrounding environment. ...
... locate places northsouth (N/S) on the globe. Equator = 0 degrees • Longitude Lines: run north-south (N/S) to locate places east-west (E/W) on the globe. Prime meridian = 0 degrees • Relative Location: where something is in relation to its surrounding environment. ...
Unit 1 Physical Geography
... world is usually described in spatial terms Spatial relations- refer to the links that places and people have to one another because of their location You could use the terms ...
... world is usually described in spatial terms Spatial relations- refer to the links that places and people have to one another because of their location You could use the terms ...
Geography Study Guide
... - census: a population count and survey conducted every 10 years by the government. Gathers information about people. - cartographers: geographers who make maps. - time zones: there are 24 time zones around the earth (one for each hour of one complete rotation) (24 time zones, each zone covering 15 ...
... - census: a population count and survey conducted every 10 years by the government. Gathers information about people. - cartographers: geographers who make maps. - time zones: there are 24 time zones around the earth (one for each hour of one complete rotation) (24 time zones, each zone covering 15 ...
UNIT 1 Studying Geography and Introduction to Early History
... • Every place on Earth can be found using the latitude and longitude grid. It’s how your GPS works. • LATITUDE LINES run East to West and are parallel to the Equator. These lines are measured in degrees North or South of the Equator. • LONGITUDE LINES are half-circles that run from the North Pole to ...
... • Every place on Earth can be found using the latitude and longitude grid. It’s how your GPS works. • LATITUDE LINES run East to West and are parallel to the Equator. These lines are measured in degrees North or South of the Equator. • LONGITUDE LINES are half-circles that run from the North Pole to ...
Small Scale Maps
... East or West is the International Date Line By international agreement - 0 degrees longitude runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England Numbers get higher the farther you move either East of West Longitude lines measure East or West of the Prime Meridian ...
... East or West is the International Date Line By international agreement - 0 degrees longitude runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England Numbers get higher the farther you move either East of West Longitude lines measure East or West of the Prime Meridian ...
Name___________________ Period__________________ World
... These regions are made up of different places that are linked together and function as a unit. Examples include the transit system such as transporting people via train, bus, subway, etc. Malls or other central points are also examples of these regions known as __________ _____________________ ...
... These regions are made up of different places that are linked together and function as a unit. Examples include the transit system such as transporting people via train, bus, subway, etc. Malls or other central points are also examples of these regions known as __________ _____________________ ...
Geography Exercise ppt
... Mesoamerica Central Mexico and South Mexico through Central America, including Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. Sometimes Nicaragua, and Northern Costa Rica are included. ...
... Mesoamerica Central Mexico and South Mexico through Central America, including Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. Sometimes Nicaragua, and Northern Costa Rica are included. ...
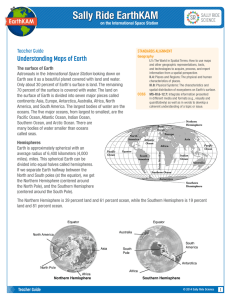
Teacher Guide - Sally Ride EarthKAM
... equator, and from 0° to 90° South for locations south of the equator. Notice on the figure that the lines of latitude run in the east-west direction and are parallel to the equator. Any other location directly east or west of you lies at the same latitude that you do. EarthKAM coordinates ISS EarthK ...
... equator, and from 0° to 90° South for locations south of the equator. Notice on the figure that the lines of latitude run in the east-west direction and are parallel to the equator. Any other location directly east or west of you lies at the same latitude that you do. EarthKAM coordinates ISS EarthK ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.