Maps - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... • Equator divides the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres ...
... • Equator divides the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres ...
Terms and Concepts - Geography (Pechacek)2
... surroundings and how the physical environment often affects humans ...
... surroundings and how the physical environment often affects humans ...
geo2200_1midterm_stu..
... Latitude increases from the equator to the north pole or south pole o These are the two fixed reference points for the Earth Is strongly related to yearly patterns, like sunlight and seasons Lines are called parallels Longitude – measure of (angular) distance east or west of a point on the Earth ...
... Latitude increases from the equator to the north pole or south pole o These are the two fixed reference points for the Earth Is strongly related to yearly patterns, like sunlight and seasons Lines are called parallels Longitude – measure of (angular) distance east or west of a point on the Earth ...
Basics of Geography
... Tell where the location of the scale is. Name and give symbols of 5 things located in the legend. What two states are included on this map? What river separates the two states listed in #3? What is this a map of? ...
... Tell where the location of the scale is. Name and give symbols of 5 things located in the legend. What two states are included on this map? What river separates the two states listed in #3? What is this a map of? ...
What city is near 6 degrees north latitude and 10 degrees west
... 11. If you needed to tell your Japanese pen pal where your city is located on the globe you would use your map to help you figure out what to tell him. What else would be helpful in describing your city’s location? Latitude and longitude 12. What is a line of longitude? (Start out by saying: a refer ...
... 11. If you needed to tell your Japanese pen pal where your city is located on the globe you would use your map to help you figure out what to tell him. What else would be helpful in describing your city’s location? Latitude and longitude 12. What is a line of longitude? (Start out by saying: a refer ...
The Five Themes of Geography (Or, how to make studying the earth
... Pennsylvania Pennsylvania is bordered by New York on the north, Ohio on the west, West Virginia, Maryland and Delaware on the south and New Jersey on the east. Harrisburg is about 12 miles west of Hershey. ...
... Pennsylvania Pennsylvania is bordered by New York on the north, Ohio on the west, West Virginia, Maryland and Delaware on the south and New Jersey on the east. Harrisburg is about 12 miles west of Hershey. ...
Australia * a unique continent
... Why is it important? The topography of Australia is the result of processes that have taken place over millions of years. Plate movements have given the continent its basic form, but the processes of weathering and erosion have shaped the features. ...
... Why is it important? The topography of Australia is the result of processes that have taken place over millions of years. Plate movements have given the continent its basic form, but the processes of weathering and erosion have shaped the features. ...
Document
... Five Themes of Geography 1) Location 2) Regions 3) Movement 4) Place 5) Human Interaction 6) Rotate-When the Earth turns or spins on its own axis. It takes 24 hours for the Earth to rotate one time. 7) Revolve -When the Earth orbits the sun in a circular path. It takes 365 ¼ days for the Earth to re ...
... Five Themes of Geography 1) Location 2) Regions 3) Movement 4) Place 5) Human Interaction 6) Rotate-When the Earth turns or spins on its own axis. It takes 24 hours for the Earth to rotate one time. 7) Revolve -When the Earth orbits the sun in a circular path. It takes 365 ¼ days for the Earth to re ...
Quiz 1 - Word Document
... important / large area to another important / large area. hinterlands - either rural or urban or both, that is closely linked economically with a nearby town or city. International Date Line - an arc that fro the most part follows 180º longitude, although it deviates in several place to avoid dividi ...
... important / large area to another important / large area. hinterlands - either rural or urban or both, that is closely linked economically with a nearby town or city. International Date Line - an arc that fro the most part follows 180º longitude, although it deviates in several place to avoid dividi ...
5 Themes PP
... places, and things are located, and the ways in which they interact with each other. 2 Parts: • 1. Physical – How internal processes shape the world that we see everyday. • 2. Cultural – Why people are where they are, and what they do. ...
... places, and things are located, and the ways in which they interact with each other. 2 Parts: • 1. Physical – How internal processes shape the world that we see everyday. • 2. Cultural – Why people are where they are, and what they do. ...
Rubenstein Chapter 1.2 - Mounds View Public Schools
... Meridian: drawn between North and South poles (longitude) Parallel: a circle drawn on the globe parallel to the equator at right angles to the meridians (latitude) Prime Meridian: line of longitude that passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England -known as 0º longitude ...
... Meridian: drawn between North and South poles (longitude) Parallel: a circle drawn on the globe parallel to the equator at right angles to the meridians (latitude) Prime Meridian: line of longitude that passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England -known as 0º longitude ...
exercise1_figures
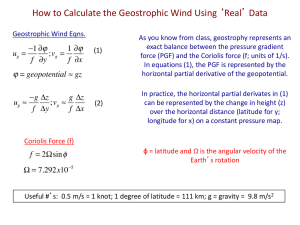
... How to Calculate the Geostrophic Wind Using ‘Real’ Data Geostrophic Wind Eqns. ...
... How to Calculate the Geostrophic Wind Using ‘Real’ Data Geostrophic Wind Eqns. ...
Chapter 1 notes - Freedom Area School District
... Low latitudes (tropics)- latitudes between tropic of cancer and the tropic of capricorn Middle latitudes (temperate regions)- between the tropic of cancer and the arctic circle and between the tropic of capricorn and the antarctic circle High latitudes (polar regions)- north of the arctic circle and ...
... Low latitudes (tropics)- latitudes between tropic of cancer and the tropic of capricorn Middle latitudes (temperate regions)- between the tropic of cancer and the arctic circle and between the tropic of capricorn and the antarctic circle High latitudes (polar regions)- north of the arctic circle and ...
File
... 3. A word that means “study of Earth” is geology. 4. A distance measured in degrees north or south of the equator is called latitude. 5. A distance measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian is called longitude. 6. The contour interval tells you the difference in elevation between two ad ...
... 3. A word that means “study of Earth” is geology. 4. A distance measured in degrees north or south of the equator is called latitude. 5. A distance measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian is called longitude. 6. The contour interval tells you the difference in elevation between two ad ...
Date: The Five Themes of Geography Aim: Do now: Studying the
... 2. Place identifies the natural and human features that make one place different from every other place. You can identify a specific place by its landforms, climate, plants, animals, people or cultures. You might even think of a place as a geographic signature. Use the signature to help you understa ...
... 2. Place identifies the natural and human features that make one place different from every other place. You can identify a specific place by its landforms, climate, plants, animals, people or cultures. You might even think of a place as a geographic signature. Use the signature to help you understa ...
KS3 Year 7 Geography Key Terms # Glossary Definition 1 HIC High
... Gradual increase in the Earth’s temperature, which may be caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Measure of the steepness of a slope ...
... Gradual increase in the Earth’s temperature, which may be caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Measure of the steepness of a slope ...
What is Geography?
... • Geographers study how the natural environment influences people, how people’s activities affect Earth, and how the world is changing. ...
... • Geographers study how the natural environment influences people, how people’s activities affect Earth, and how the world is changing. ...
Introduction To World Geography
... • Location is related to the global grid system of latitude and longitude. • Absolute location – is the actual space a place occupies on the earth’s surface. It is usually referred to in mathematical form using degrees (latitude and longitude coordinates). • Relative location – refers to the locatio ...
... • Location is related to the global grid system of latitude and longitude. • Absolute location – is the actual space a place occupies on the earth’s surface. It is usually referred to in mathematical form using degrees (latitude and longitude coordinates). • Relative location – refers to the locatio ...
Science Flipbook 9
... latitude ---------------longitude ---------------continents ---------------elevation ---------------Water cycle ---------------latitude ---------------longitude ---------------continents ---------------elevation ---------------Water cycle ...
... latitude ---------------longitude ---------------continents ---------------elevation ---------------Water cycle ---------------latitude ---------------longitude ---------------continents ---------------elevation ---------------Water cycle ...
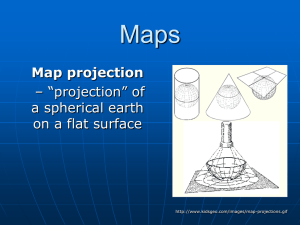
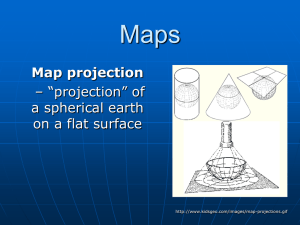
Maps
... Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. ...
... Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. ...
9SST Unit 1 Test chapters 1 and 2 Ms Lambert
... Literally, half a sphere, a ______________________ is one way to divide the earth into regions. ...
... Literally, half a sphere, a ______________________ is one way to divide the earth into regions. ...
5 Themes of Geography Vocabulary:
... coordinates - the points of longitude and latitude that identify a location (41N, 73W) latitude lines - east-west lines that surround the globe and measure distances north and south of the equator. They are also called parallels. parallels - another term for latitude lines. Parallel lines never inte ...
... coordinates - the points of longitude and latitude that identify a location (41N, 73W) latitude lines - east-west lines that surround the globe and measure distances north and south of the equator. They are also called parallels. parallels - another term for latitude lines. Parallel lines never inte ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.