* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Maps
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
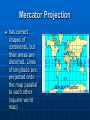
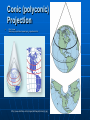
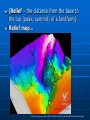
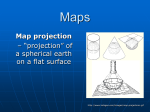
Maps Map projection – “projection” of a spherical earth on a flat surface http://www.kidsgeo.com/images/map-projections.gif Latitude and Longitude Latitude and Longitude are spherical coordinates on the surface of the earth PreTest… http://www.quia.com/quiz/294825.html Latitude Angular distance measured in degrees North or South of the equator • Lines of latitude that run parallel to the equator. • Equator divides the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres Longitude Angular distance measured in degrees East or West of the prime meridian. • lines of longitude, called meridians, run perpendicular to lines of latitude • all pass through both poles. • each longitude line is part of a great circle. Equator—The line which encircles the Earth at an equal distance from the North and South Poles. Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. Prime Meridian—The meridian of longitude 0 degrees, used as the origin for the measurement of longitude. The meridian of Greenwich, England, is the internationally accepted prime meridian in most cases. Mercator Projection has correct shapes of continents, but their areas are distorted. Lines of longitude are projected onto the map parallel to each other (square world map) Mercator Projection Robinson Projection has accurate continent shapes and shows accurate land area http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/mapproj/mapproj.html Gnomonic Projection used to plot the shortest distance between two points, projected as if a sheet of paper were laid on a point of the Earth’s surface http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/mapproj/mapproj.html Conic (or polyconic) Projection used to produce a map of small areas. They’re made by projecting points and lines from a globe onto a cone. http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/mapproj/mapproj.html Conic (polyconic) Projection http://wwwatlas.usgs.gov/articles/mapping/a_projections.html http://www.bartleby.com/images/A4images/A4conprj.jpg Cool website Follow the link below… http://www.nationalgeographic.com/x peditions/hall/index.html?node=20 Map Scale – the relationship between the distances on the map and actual distances on Earth’s surface 3 types of map scales • Verbal: statement “1 inch equals 100 miles” • Graphic: line divided into equal parts and marked in units (bar scale) • Numerical: written as a fraction scale (1/100,000 and 1/24,000) or a ratio scale (1:100,000 or 1:24,000) Which map scale do you see? http://www.calvin.edu/academic/geology/courses/topomap/scale/scaler.jpg Topographic Maps shows the changes in elevation of Earth’s surface Topographic Maps Contour Line – a line on a map that connects points of equal elevation Contour Interval – difference in elevation between two adjacent (side-byside) contour lines http://raider.muc.edu/~mcnaugma/Topographic%20Maps/contour.htm Rules to Remember Contour lines: • close around hills and basins or depressions • never cross • only touch if there is a vertical slope/gradient (like a cliff) • that form V’s that point upstream (to the source) whenever they cross streams Landforms the smaller features of the earth’s landscape defined by their shape, size and elevation… Mountain – an elevated area of land, higher than a hill, with sloping sides Valley an area of land lower in elevation than its surroundings Valley (topographic map) The blue line is the river valley • Note the steep sides of the river walls Plain an extensive , flat area of land, usually without trees http://chapters.marssociety.org/canada/expedition-mars.org/ExpeditionTwo/files/photos/Stony-desert-plain.jpg Plateau A fairly flat area of land above surrounding land (area of flat land with high ‘relief’) http://parkerlab.bio.uci.edu/pictures/photography%20pictures/Sunset%20from%20Tonto%20Plateau.jpg (Relief – the distance from the base to the top (peak, summit) of a landform) Relief map… http://faculty.gg.uwyo.edu/heller/Sed%20Strat%20Class/SedStrat%208/canyon800x600.jpg Canyon a valley with very steep sides http://photos.mongabay.com/it/749Petra.htm Canyon DiPetra, Grand Canyon, AZ Strait a narrow passage of ocean water joining two larger bodies of water ie. Strait of Gibraltar between Africa and Europe http://pds.jpl.nasa.gov/planets/images/full/earth/strait.jpg Bay a body of ocean water mostly surrounded by land and smaller than a sea or ocean http://content.answers.com/main/content/wp/en/d/d2/Wpdms_usgs_photo_san_francisco_bay.jpg a land projection of land surrounded on 3 sides by water http://www.mlahanas.de/Greece/Regions/ManiPeninsula.html Peninsula Mani Peninsula Satellite image Island land completely surrounded by water New Zealand's most active volcano, White Island, was in a state of frequent eruption from 1976 to 2000. http://www.geonet.org.nz/images/volcano/our-volcanoes/White-Island-28766-20-lge.jpg Lagoon a shallow body of salt water mostly or completely surrounded by land http://www.recreationvictoria.com/esquimaltlagoon/images/photos/esquimalt_lagoon-2.jpg Archipelago a group or chain of islands http://lincoln.midcoast.com/~prospec/wizolution/cad/archipelago.jpg Archipelago a group or chain of islands One more slide Congratulations – you found the hidden extra credit!!! Find: The magnetic declination for our school A bench mark (picture) Locate the nearest bench mark to school The latitude and longitude of our school down to the nearest tenth of a second. The latitude and longitude of your house down to the nearest tenth of a second. Present this information to me after school any day before we finish the map unit…. Then sing the hokey-pokey-with me (only one verse) and get a bonus homework assignment. Azimuthal for example… polar projection… the north pole is ‘touching’ the map and the longitudinal lines radiate outward.