* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography - Maria Regina School
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
Ordnance Survey wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
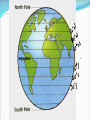
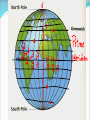
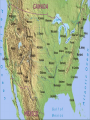
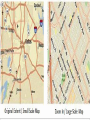
What is geography? • Study of Earth’s surface and people in their environment • The study of many exciting things about our Earth and all of us who live here • Includes studying – cities – states – countries – bodies of water (oceans, lakes, and rivers) – land (plains, mountains, and volcanoes) – people Globes A globe is a model that shows Earth as it is seen from outer space. It shows large bodies of land or continents. The seven continents are: Europe, Asia, North America, South America, Africa, Antarctica, and Australia. The Earth has five oceans: Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, Arctic Ocean and Southern Ocean. How can you find directions on maps? Many maps include a compass rose or a drawing that shows directions. A compass rose usually shows cardinal and intermediate directions. What are cardinal directions? The four cardinal directions are north, south, east, and west or N, S, E, and W. How can you determine intermediate directions? Intermediate directions are northeast, northwest, southwest, and southeast or NE, NW, SW, and SE. Intermediate directions are halfway between cardinal directions. What is a map scale? The map scale tells you how much smaller the distance on a map is compared with the actual size. Scales usually show two lines: miles and kilometers. How do you use a scale? You can use a ruler to measure directions on a map. What information does a map key give? A symbol is anything that stands for something else. Black dots stand for a city. Other symbols include triangles, squares, and lines. Symbols can be different on different maps. A map key tells you what the symbol stands for. Locator Map Locator Map – shows where this map is located in the larger context Sometimes called an inset map What is a hemisphere? Hemisphere means “half of a sphere.” There are four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western. The Northern and Southern hemispheres are divided by the equator. The Prime Meridian divides the Western and Eastern hemispheres. Grid Lines Lines of latitude and longitude found on some maps Five Themes of Geography Location Place Human Interaction Movement Region Remember – MR. LIP or MR. HELP Location Absolute Location – the exact position on the Earth, uses longitude and latitude Ex. 76 N, 38 E Relative Location – location of something in relation to another place Ex. (My house is beside the big black fence with the cows). What are latitude lines? The zero degree latitude line is the equator. Latitude lines measure the distance north or south of the equator. The Equator divides the Earth in half – The Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere. What are longitude lines? Lines that run north to south are longitude lines. The zero degree longitude line is the Prime Meridian. Longitude lines measure the distance east and west of the prime meridian. The Prime Meridian divides the Earth just like the Equator and creates the Northern and Southern Hemisphere. Place • All places have human and physical characteristics • Physical characteristics- animal life, mountains, lakes, etc. • Human characteristics- architecture, communication, transportation networks, etc. • Languages, as well as religious and political ideas shape a place. When speaking about or describing place you might mention: how many people, what the people do, the climate or other physical features. Ex. The Mississippi Delta is very flat and contains lots of fertile farmland. There are a lot of farmers Region Bigger than a place or location An area with at least one unifying physical feature; such as climate, landforms, population or history. Ex. The regions of the United States (New England, East coast, the South, etc.) Movement How people, goods, and/or ideas get from one place to another. Ex. Marco Polo and the spice trade Ex. Buddhism being brought from India to China via the Silk Road. Human Interaction How people affect their environment and how their environment affects them. Can be positive and negative ways Ex. Houses on stilts in coastal areas and the main trade being fishing. Political Maps A political map shows information such as countries, states, cities, and other important political features. Although they use state and national boundaries, they can also use colors to highlight countries or states. Physical Maps Physical maps display the physical or natural features. Elevation maps use color to show the height of land above sea level. Elevation Maps Special Purpose Maps Show information about a specific place or period in history Historical maps - show information about the past or where past events took place Distribution maps - show how language, religion, population, and rainfall are distributed throughout the area Maps at Different Scales Small-scale maps Show a large area (continent or region) Don’t show many details Large-scale maps Show a small area Has more details (can see buildings, roads, etc.)