Chapter 1 Guided Notes Ans
... Where is it? - Absolute location—exact place where a geographic feature is found - Relative location—location of a place compared to places around it Absolute Location - Earth is divided into two equal halves, vertically and horizontally - Each vertical and horizontal half is called a hemisphere - A ...
... Where is it? - Absolute location—exact place where a geographic feature is found - Relative location—location of a place compared to places around it Absolute Location - Earth is divided into two equal halves, vertically and horizontally - Each vertical and horizontal half is called a hemisphere - A ...
Solar Energy and a Spherical Earth
... A beam of sunlight that strikes the equator is perpendicular to Earth’s surface Earth’s surface absorbs the maximum amount of energy from the Sun at the equator Energy reaching a region at a higher or lower latitude is spread over a larger area Therefore the Earth’s surface in this region absorbs le ...
... A beam of sunlight that strikes the equator is perpendicular to Earth’s surface Earth’s surface absorbs the maximum amount of energy from the Sun at the equator Energy reaching a region at a higher or lower latitude is spread over a larger area Therefore the Earth’s surface in this region absorbs le ...
The Basics of Geography
... Location: Where is it? Place: What is it like? Region: How are places similar or different? Movement: How do people, goods, and ideas from one location to another? – Human-Environment Interaction: How do people relate to the physical world ...
... Location: Where is it? Place: What is it like? Region: How are places similar or different? Movement: How do people, goods, and ideas from one location to another? – Human-Environment Interaction: How do people relate to the physical world ...
Name
... 9. 1:1,000 indicates what kind of map scale? ______________________________________________________ 10. How many contour lines would be needed to show an island 250 feet high on a map with a contour interval of 50 feet? ____________________________________ 11. What is the name of the contour lines w ...
... 9. 1:1,000 indicates what kind of map scale? ______________________________________________________ 10. How many contour lines would be needed to show an island 250 feet high on a map with a contour interval of 50 feet? ____________________________________ 11. What is the name of the contour lines w ...
The Five Themes of Geography - Great Valley School District
... A specific place on the Earth’s surface Uses a grid system Latitude and longitude A global address ...
... A specific place on the Earth’s surface Uses a grid system Latitude and longitude A global address ...
Introduction to Geography
... • The precise location (mathematical location) of a place can be designated more precisely by dividing each degree into 60 minutes (“) Minneapolis is 45o53” North latitude and 93o13” West longitude Paris, France is 48o51” North latitude and 2O20” East longitude Marshall Islands are 10o00” North lati ...
... • The precise location (mathematical location) of a place can be designated more precisely by dividing each degree into 60 minutes (“) Minneapolis is 45o53” North latitude and 93o13” West longitude Paris, France is 48o51” North latitude and 2O20” East longitude Marshall Islands are 10o00” North lati ...
Phys Geo Review Key
... El Nino can make the hurricanes stronger because it heats up the water to a higher temperature 18. What causes earthquakes? Plate tectonics, pressure or friction from two plates coming together 19. Which natural disaster is monitored with a seismograph? earthquake 20. What is the Ring of Fire? Ring ...
... El Nino can make the hurricanes stronger because it heats up the water to a higher temperature 18. What causes earthquakes? Plate tectonics, pressure or friction from two plates coming together 19. Which natural disaster is monitored with a seismograph? earthquake 20. What is the Ring of Fire? Ring ...
Missouri Geography - North Platte R-1
... • Absolute - Exact Location using latitude and longitude • Latitude lines measuring North and South from the Equator. • Longitude lines measuring East and West from the Prime Meridian. ...
... • Absolute - Exact Location using latitude and longitude • Latitude lines measuring North and South from the Equator. • Longitude lines measuring East and West from the Prime Meridian. ...
Chapter 1 Coordinate Systems
... General Cartesian Coordinates Let’s review some systems in which we may already be familiar. These basic systems will springboard us into understanding the concepts of the more complicated systems. Let’s first review the Cartesian coordinate system—perhaps the first system we learned in school. To ...
... General Cartesian Coordinates Let’s review some systems in which we may already be familiar. These basic systems will springboard us into understanding the concepts of the more complicated systems. Let’s first review the Cartesian coordinate system—perhaps the first system we learned in school. To ...
Unit 1 - Earth`s Dimensions Review Powerpoint
... on a globe of the Earth? A. Latitude lines are parallel and longitude lines meet at the poles B. Latitude lines are parallel and longitude lines meet at the equator C. Longitude lines are parallel and latitude lines meet at the equator D. Longitude lines are parallel and latitude lines meet at the p ...
... on a globe of the Earth? A. Latitude lines are parallel and longitude lines meet at the poles B. Latitude lines are parallel and longitude lines meet at the equator C. Longitude lines are parallel and latitude lines meet at the equator D. Longitude lines are parallel and latitude lines meet at the p ...
Measuring the Earth
... surface you need two numbers or coordinates. Coordinate system- system for determining coordinates. What is the name of the coordinate system used to find a location on the Earth’s surface? Latitude-longitude Measured in degrees and minutes: 60minutes In 1 degree. ...
... surface you need two numbers or coordinates. Coordinate system- system for determining coordinates. What is the name of the coordinate system used to find a location on the Earth’s surface? Latitude-longitude Measured in degrees and minutes: 60minutes In 1 degree. ...
Unit 1: Chapter 1 Section 1
... Location is the position on the Earth’s surface. Relative location is used when comparing a different location. i.e. New Jersey is east of Pennsylvania near the Atlantic Ocean. or Harrisburg is located between Pittsburgh and Philadelphia. Absolute location is located by using a grid system such as l ...
... Location is the position on the Earth’s surface. Relative location is used when comparing a different location. i.e. New Jersey is east of Pennsylvania near the Atlantic Ocean. or Harrisburg is located between Pittsburgh and Philadelphia. Absolute location is located by using a grid system such as l ...
5 Themes of Geography - South McKeel Academy
... pole to pole, pole to pole, pole to pole It's a LONG, LONG way from pole to pole, so we call those LONGITUDES.” Longitude is measured from the Prime Meridian (which is the longitude, with positive values going east and negative values going west. ...
... pole to pole, pole to pole, pole to pole It's a LONG, LONG way from pole to pole, so we call those LONGITUDES.” Longitude is measured from the Prime Meridian (which is the longitude, with positive values going east and negative values going west. ...
5themesofgeography 1
... pole to pole, pole to pole, pole to pole It's a LONG, LONG way from pole to pole, so we call those LONGITUDES.” Longitude is measured from the Prime Meridian (which is the longitude, with positive values going east and negative values going west. ...
... pole to pole, pole to pole, pole to pole It's a LONG, LONG way from pole to pole, so we call those LONGITUDES.” Longitude is measured from the Prime Meridian (which is the longitude, with positive values going east and negative values going west. ...
ESSR_PNE_CoordntesSeasns_V01
... – An imaginary giant sphere, centered on the earth – All objects seem to be on the surface of this imaginary sphere – Earth’s poles extends and intersect with the celestial sphere as the North Celestial Pole and the South Celestial Pole – Earth’s equator extends and intersects with the celestial sph ...
... – An imaginary giant sphere, centered on the earth – All objects seem to be on the surface of this imaginary sphere – Earth’s poles extends and intersect with the celestial sphere as the North Celestial Pole and the South Celestial Pole – Earth’s equator extends and intersects with the celestial sph ...
5 Themes of Geography Worksheet
... ______________________________, but the lines of ____________________ are ______________________. ...
... ______________________________, but the lines of ____________________ are ______________________. ...
5 Themes of Geography NOTES Learning Targets: PG4
... of the Andes mountain to create flat land for farming. The terraces also helped to keep rainwater from running off. They reduced erosion. The government built raised aqueducts to carry water to farmlands for irrigation. •3. Greenwich, England is located on the Prime Meridian which is zero degrees lo ...
... of the Andes mountain to create flat land for farming. The terraces also helped to keep rainwater from running off. They reduced erosion. The government built raised aqueducts to carry water to farmlands for irrigation. •3. Greenwich, England is located on the Prime Meridian which is zero degrees lo ...
Science / Chapter 2 - Serra Catholic Elementary School
... LATITUDE – Degrees north and south of the equator (Equator = 0 degrees) LONGITUDE – Degrees east and west of the prime meridian. ...
... LATITUDE – Degrees north and south of the equator (Equator = 0 degrees) LONGITUDE – Degrees east and west of the prime meridian. ...
Map Master Skills Handbook
... Five Themes of Geography: Just by paging through this first chapter you can probably figure out that “Geography” is a huge topic to study. When some people hear the word “Geography” they think about studying states and capitals. Although that’s part of Geography, there is so much more! To make the s ...
... Five Themes of Geography: Just by paging through this first chapter you can probably figure out that “Geography” is a huge topic to study. When some people hear the word “Geography” they think about studying states and capitals. Although that’s part of Geography, there is so much more! To make the s ...
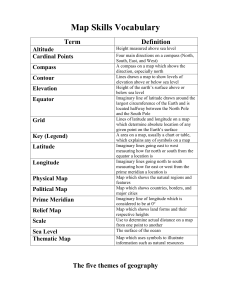
Map Skills Vocabulary - White Plains Public Schools
... Imaginary lines going east to west measuring how far north or south from the equator a location is Imaginary lines going north to south measuring how far east or west from the prime meridian a location is Map which shows the natural regions and features Map which shows countries, borders, and major ...
... Imaginary lines going east to west measuring how far north or south from the equator a location is Imaginary lines going north to south measuring how far east or west from the prime meridian a location is Map which shows the natural regions and features Map which shows countries, borders, and major ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide: Mapping Earth`s Surface Section 2
... 29. The units scientists use to measure distances around a circle are called ______________________. 30. The imaginary line that circles the Earth halfway between the North and South Poles is the _____________. 31. Half of the earth’s surface is called a _______________________________ (northern or ...
... 29. The units scientists use to measure distances around a circle are called ______________________. 30. The imaginary line that circles the Earth halfway between the North and South Poles is the _____________. 31. Half of the earth’s surface is called a _______________________________ (northern or ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.