How do Scientists determine the boundaries of the plates?
... boundaries, describe how two plates move relative to each other. CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES are colliding together, DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES are pulling apart, and TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES slide past each other. By plotting the locations of earthquakes, scientists have not only been able to locate plate boundari ...
... boundaries, describe how two plates move relative to each other. CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES are colliding together, DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES are pulling apart, and TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES slide past each other. By plotting the locations of earthquakes, scientists have not only been able to locate plate boundari ...
IntroBasics
... The Global Grid of Latitude and Longitude lines essentially forms a giant coordinate plane on Earth. We use this plane to determine specific locations on our planet. Each location has a set of Coordinates. These coordinates are found by finding a locations numerical latitude and cardinal direction f ...
... The Global Grid of Latitude and Longitude lines essentially forms a giant coordinate plane on Earth. We use this plane to determine specific locations on our planet. Each location has a set of Coordinates. These coordinates are found by finding a locations numerical latitude and cardinal direction f ...
Five Themes of Geography Cornell Notes
... • Relative Location – Uses landmarks, distances, etc. – Used more often by general population ...
... • Relative Location – Uses landmarks, distances, etc. – Used more often by general population ...
Human geography
... farmland stretching from Ohio to Nebraska in the United States. It is a formal region because corn is its primary crop. • Functional region-- incorporates a central node and a surrounding area that is connected to the node by some defined function. For example, a cell tower provides the central node ...
... farmland stretching from Ohio to Nebraska in the United States. It is a formal region because corn is its primary crop. • Functional region-- incorporates a central node and a surrounding area that is connected to the node by some defined function. For example, a cell tower provides the central node ...
Geography - Barren County Schools
... communication (ideas) have all played major roles in shaping our world. People everywhere interact. They travel from place to place and they communicate. We live in a global village and global economy. ...
... communication (ideas) have all played major roles in shaping our world. People everywhere interact. They travel from place to place and they communicate. We live in a global village and global economy. ...
WORLD GEOGRAPHY
... Relationships between people in different places How and Why are place related to one another? THREE TYPES OF MOVEMENT Movement of PEOPLE MIGRATION: Move to a new location for settlement - forced or voluntary Movement of GOODS Goods being moved from one place to another ...
... Relationships between people in different places How and Why are place related to one another? THREE TYPES OF MOVEMENT Movement of PEOPLE MIGRATION: Move to a new location for settlement - forced or voluntary Movement of GOODS Goods being moved from one place to another ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... Two Types of Location: Absolute Location A specific place on the Earth’s surface Uses a grid system Latitude and longitude A global address ...
... Two Types of Location: Absolute Location A specific place on the Earth’s surface Uses a grid system Latitude and longitude A global address ...
Five Themes Power Point 2012 Five Themes PowerPoint
... of sunlight. Part of the year there is no sunlight and the other part of the year there is no darkness. ...
... of sunlight. Part of the year there is no sunlight and the other part of the year there is no darkness. ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... ________________ and southern ________________. The equator is located at _____ latitude. The farthest latitude north of the equator is 90 N, this location is called the ______________ ____________. The farthest latitude south of the equator is 90 S, this location is called the ______________ __ ...
... ________________ and southern ________________. The equator is located at _____ latitude. The farthest latitude north of the equator is 90 N, this location is called the ______________ ____________. The farthest latitude south of the equator is 90 S, this location is called the ______________ __ ...
Unit 1
... scores will be entered as total points into the gradebook in the District Assessments category. 3. Tests must be done in class. The test is not to be sent home for any reason. Exceptions must be authorized by the social studies coordinator. 4. Students should not be given more than one block period ...
... scores will be entered as total points into the gradebook in the District Assessments category. 3. Tests must be done in class. The test is not to be sent home for any reason. Exceptions must be authorized by the social studies coordinator. 4. Students should not be given more than one block period ...
Geography Unit One
... Latitude and Longitude Lines of latitude are measured north and south of the equator. The Equator is zero (0) degrees of latitude. Other lines of latitude are called parallels because they are parallel to the equator. Lines of latitude are measured from zero to 90 degrees north latitude . . . ...
... Latitude and Longitude Lines of latitude are measured north and south of the equator. The Equator is zero (0) degrees of latitude. Other lines of latitude are called parallels because they are parallel to the equator. Lines of latitude are measured from zero to 90 degrees north latitude . . . ...
Geographic Fundamentals
... with lines of latitude. The Greenwich meridian or prime meridian is the line of longitude from which all other lines are measured – east and west – around the globe. Lines of longitude are measured from 0 degrees at the prime meridian to 180 degrees at another line called the International Date ...
... with lines of latitude. The Greenwich meridian or prime meridian is the line of longitude from which all other lines are measured – east and west – around the globe. Lines of longitude are measured from 0 degrees at the prime meridian to 180 degrees at another line called the International Date ...
Unit 2: Geography
... divided into North and South and East and West Latitude: Imaginary lines that circle the Earth parallel to the Equator Longitude: Imaginary lines that circle the earth from Pole to Pole, measuring distance east or west of the Prime Meridian Projection: a way of showing the round earth on a flat map ...
... divided into North and South and East and West Latitude: Imaginary lines that circle the Earth parallel to the Equator Longitude: Imaginary lines that circle the earth from Pole to Pole, measuring distance east or west of the Prime Meridian Projection: a way of showing the round earth on a flat map ...
“Take Five”
... Qualitative—uses colors, symbols, dots or lines to help illustrate patterns related to a specific idea Cartograms—info about a country based on a set of data other than land area Flow-line maps—illustrate movement of people, ...
... Qualitative—uses colors, symbols, dots or lines to help illustrate patterns related to a specific idea Cartograms—info about a country based on a set of data other than land area Flow-line maps—illustrate movement of people, ...
100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300
... the way people have divided the earth into different governmental boundaries like countries, states, cities, etc. C 200 ...
... the way people have divided the earth into different governmental boundaries like countries, states, cities, etc. C 200 ...
The 5 Themes of Geography
... Location – Absolute: Latitude and Longitude GPS system Exact location on the globe: Hemispheres, Prime Meridian, Equator, North and South Poles ...
... Location – Absolute: Latitude and Longitude GPS system Exact location on the globe: Hemispheres, Prime Meridian, Equator, North and South Poles ...
A Closer Look at Earth - James M. Hill High School
... Longitude is the angle measured east or west from the 0° line, which passes through Greenwich, England. For example, the eastern tip of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, is at 60° west longitude. Latitude is the angle measured north or south of the equator. For example, the border between the western ...
... Longitude is the angle measured east or west from the 0° line, which passes through Greenwich, England. For example, the eastern tip of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, is at 60° west longitude. Latitude is the angle measured north or south of the equator. For example, the border between the western ...
Chapter 1
... 13. A pattern of lines on a chart or map that help to determine location is called a ___________. 14. ____________ _____________ are used to find a place on a map using two sets of numbers, representing the x and y axis. ...
... 13. A pattern of lines on a chart or map that help to determine location is called a ___________. 14. ____________ _____________ are used to find a place on a map using two sets of numbers, representing the x and y axis. ...
horizonschpt3(1)key
... Intro to the Geography of Western Canada Directions: Read pages 93-98 in your text Horizons: Canada Moves West 1. On a separate piece of paper, provide definitions for the following terms; ...
... Intro to the Geography of Western Canada Directions: Read pages 93-98 in your text Horizons: Canada Moves West 1. On a separate piece of paper, provide definitions for the following terms; ...
File
... Climate Zones (Tropical, Temperate, Polar) – Divisions of the Earth's climates into general climate zones according to average temperatures and average rainfall. The three major climate zones on the Earth are the polar, temperate, and tropical zones. ...
... Climate Zones (Tropical, Temperate, Polar) – Divisions of the Earth's climates into general climate zones according to average temperatures and average rainfall. The three major climate zones on the Earth are the polar, temperate, and tropical zones. ...
AP Human Geography – Vocabulary List Section 1: Thinking
... -Relative location: Position on Earth’s surface relative to other features. (Ex: My house is east of I-75). Longitude: angular distance east or west on the earth's surface, measured by the angle contained between the meridian of a particular place and some prime meridian, as that of Greenwich, Engla ...
... -Relative location: Position on Earth’s surface relative to other features. (Ex: My house is east of I-75). Longitude: angular distance east or west on the earth's surface, measured by the angle contained between the meridian of a particular place and some prime meridian, as that of Greenwich, Engla ...
What Is Human Geography?
... ▫ Longitude: The vertical lines on a map. Also called meridians. 0◦ Longitude = The Prime Meridian. Degrees Long. are measured East or West of the Prime Meridian. ...
... ▫ Longitude: The vertical lines on a map. Also called meridians. 0◦ Longitude = The Prime Meridian. Degrees Long. are measured East or West of the Prime Meridian. ...
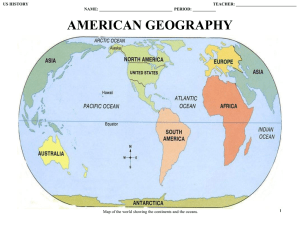
unit 1: american geography
... Imagine that you are the captain of a U.S. aircraft carrier in the Persian Gulf. You get a message that an unidentified fighter plane is headed your way. The plane’s current location is 28°N latitude, 50°E longitude. Where is the plane? You would know if you understood latitude and longitude. Mapmak ...
... Imagine that you are the captain of a U.S. aircraft carrier in the Persian Gulf. You get a message that an unidentified fighter plane is headed your way. The plane’s current location is 28°N latitude, 50°E longitude. Where is the plane? You would know if you understood latitude and longitude. Mapmak ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.