Fundamental vs. Total RMS
... A significant advantage delivered by the MCEMAX is the ability to segregate the Fundamental and Total RMS values of voltage and current. Most multi-meters will normally deliver Total RMS, which provides a value similar to our Total Voltage or current value. However, our Fundamental value will always ...
... A significant advantage delivered by the MCEMAX is the ability to segregate the Fundamental and Total RMS values of voltage and current. Most multi-meters will normally deliver Total RMS, which provides a value similar to our Total Voltage or current value. However, our Fundamental value will always ...
How Things Work - How Everything Works
... pn-Junction (after) • After p-type meets n-type: – Insulating depletion region appears at junction – Depletion region is electrically polarized ...
... pn-Junction (after) • After p-type meets n-type: – Insulating depletion region appears at junction – Depletion region is electrically polarized ...
Linear Biphasic Stimulus Isolator
... The Model BSI- 1A Biphasic Stimulus Isolator is totally battery powered utilizing optimum packaging design to provide maximum isolation of stimulus signals. This instrument is a truly linear device which will convert any waveform from 0 to plus and minus 10 volts into a constant current or constant ...
... The Model BSI- 1A Biphasic Stimulus Isolator is totally battery powered utilizing optimum packaging design to provide maximum isolation of stimulus signals. This instrument is a truly linear device which will convert any waveform from 0 to plus and minus 10 volts into a constant current or constant ...
3 – The Power BJT 2
... as the control variable. The active region is defined where flat, horizontal portions of voltagecurrent curves show “constant” iC current, because the collector current does not change significantly with VCE for a given iB. Those portions are used only for small signal transistors operating as linea ...
... as the control variable. The active region is defined where flat, horizontal portions of voltagecurrent curves show “constant” iC current, because the collector current does not change significantly with VCE for a given iB. Those portions are used only for small signal transistors operating as linea ...
LA78045 - IHS.com
... ON Semiconductor and the ON logo are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www ...
... ON Semiconductor and the ON logo are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www ...
Operating point of a transistor
... -In DC analysis of common emitter circuits , the operating point Q is fixed somewhere on the load line and its best to be in the middle. -In AC analysis , Q will oscillate along the load line so the circuit components must be good chosen to capture Q in good oscillation region away from cutoff or sa ...
... -In DC analysis of common emitter circuits , the operating point Q is fixed somewhere on the load line and its best to be in the middle. -In AC analysis , Q will oscillate along the load line so the circuit components must be good chosen to capture Q in good oscillation region away from cutoff or sa ...
Factsheet: Conductors, Connections and Polarity
... It takes a minimum of two wires to have an electrical circuit. Electric current involves the flow of electrons. Current is measured in amperes (amps for short). It travels from a source, through the device it operates, called the load, and then back to the source. In AC wiring, present in buildings, ...
... It takes a minimum of two wires to have an electrical circuit. Electric current involves the flow of electrons. Current is measured in amperes (amps for short). It travels from a source, through the device it operates, called the load, and then back to the source. In AC wiring, present in buildings, ...
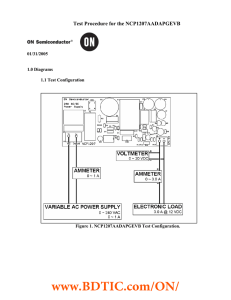
www.BDTIC.com/ON/ Test Procedure for the NCP1207AADAPGEVB 01/31/2005
... Figure 3. Gate Driver and Drain Voltage at Very Light Load ...
... Figure 3. Gate Driver and Drain Voltage at Very Light Load ...
Multifunctional Block of High Voltage Power Supply
... Comparator of "dead zone"; Error amplifier of power; Error amplifier of a signal of current limitation; Two output transistors with open emitters and collecting channels. The LM3524 provides a stable on-board oscillator. Its frequency is set by an external resistor, Rt and capacitor, Ct. The ...
... Comparator of "dead zone"; Error amplifier of power; Error amplifier of a signal of current limitation; Two output transistors with open emitters and collecting channels. The LM3524 provides a stable on-board oscillator. Its frequency is set by an external resistor, Rt and capacitor, Ct. The ...
DS9503 ESD Protection Diode with Resistors
... This DS9503 is designed as an ESD protection device for 1–Wire MicroLAN interfaces. In contrast to the DS9502, the DS9503 includes two 5Ω isolation resistors on chip. Although 5Ω are negligible during communication, they represent a high impedance relative to the conducting diode during an ESD event ...
... This DS9503 is designed as an ESD protection device for 1–Wire MicroLAN interfaces. In contrast to the DS9502, the DS9503 includes two 5Ω isolation resistors on chip. Although 5Ω are negligible during communication, they represent a high impedance relative to the conducting diode during an ESD event ...
1.5A Negative LDO Offers Fast Transient Response, Low Output
... 1.5A negative low dropout linear regulator featuring fast transient response, low noise, and precision current limit. With its wide input voltage range of -1.8V to -30V and adjustable output voltage from -1.220V to -29.5V, the device’s common emitter NPN power transistor design requires only a singl ...
... 1.5A negative low dropout linear regulator featuring fast transient response, low noise, and precision current limit. With its wide input voltage range of -1.8V to -30V and adjustable output voltage from -1.220V to -29.5V, the device’s common emitter NPN power transistor design requires only a singl ...
Real Op-Amp Input and Output Resistances
... input terminals of a real op-amp. Q: Well of course! We just studied this topic. We already know that there is a bias current IB flowing into (or out of) real op-amp terminals! ...
... input terminals of a real op-amp. Q: Well of course! We just studied this topic. We already know that there is a bias current IB flowing into (or out of) real op-amp terminals! ...
High Voltage CMOS Amplifier Enables High Impedance Sensing
... Sensing with a Single IC – Design Note 513 Jon Munson Introduction Accurately measuring voltages requires minimizing the impact of the instrument connection to the tested circuit. Typical digital voltmeters (DVMs) use 10M resistor networks to keep loading effects to an inconspicuous level, but even ...
... Sensing with a Single IC – Design Note 513 Jon Munson Introduction Accurately measuring voltages requires minimizing the impact of the instrument connection to the tested circuit. Typical digital voltmeters (DVMs) use 10M resistor networks to keep loading effects to an inconspicuous level, but even ...
10 Transistor Inverter Applications II
... configuration. In this configuration, the βeta factors of two transistors are combined by using the emitter current of one transistor as the input base current of a second transistor as shown in Fig. 10.1. The effective βeta factor is then the product of the βeta factor of the two individual transis ...
... configuration. In this configuration, the βeta factors of two transistors are combined by using the emitter current of one transistor as the input base current of a second transistor as shown in Fig. 10.1. The effective βeta factor is then the product of the βeta factor of the two individual transis ...
The FEE board requires 4 channels of DAC for the voltage regulator
... expected that a simple 2 or 3 transistor amplifier will give adequate performance at a lower power level than would be achieved with a design based on an op-amp. A common-base input stage will be used to handle the SiPM capacitance; an input transistor per SiPM might be considered. The response of a ...
... expected that a simple 2 or 3 transistor amplifier will give adequate performance at a lower power level than would be achieved with a design based on an op-amp. A common-base input stage will be used to handle the SiPM capacitance; an input transistor per SiPM might be considered. The response of a ...
Summary of Series and Parallel Circuits
... to a series circuit is equal to the total number of individual voltage drops in the series circuit. VT = sum of all voltage drops. ...
... to a series circuit is equal to the total number of individual voltage drops in the series circuit. VT = sum of all voltage drops. ...
Explore: How does electricity work? Supplies: Batteries of different
... I = Current (Current is measured in Amps. Current is charged particles which flow from the voltage source through conductive material whenever there is a complete loop of power source/conductors/loads.) R = Resistance (Resistance is the opposition {to flow} that a material body offers to the passage ...
... I = Current (Current is measured in Amps. Current is charged particles which flow from the voltage source through conductive material whenever there is a complete loop of power source/conductors/loads.) R = Resistance (Resistance is the opposition {to flow} that a material body offers to the passage ...