Electronic glossary
... Electric motors work through the interaction between electricity and magnetism. The motor’s rotor is an electromagnet – a tightly rolled coil of copper through which a current is passed. Surrounding the rotor are two magnets, one with the north pole facing the rotor and the other with the south pole ...
... Electric motors work through the interaction between electricity and magnetism. The motor’s rotor is an electromagnet – a tightly rolled coil of copper through which a current is passed. Surrounding the rotor are two magnets, one with the north pole facing the rotor and the other with the south pole ...
“Fuzzy Logic Speed Controllers Using FPGA Technique
... Unijunction transistor can trigger larger thyristors with a pulse at base B1.With the emitter disconnected, the total resistance RBB, a datasheet item, is the sum of RB1 and RB2 . RBBO ranges from 412kΩ for different device types. The intrinsic standoff ratio η is the ratio of RB1 to RBBO. It varies ...
... Unijunction transistor can trigger larger thyristors with a pulse at base B1.With the emitter disconnected, the total resistance RBB, a datasheet item, is the sum of RB1 and RB2 . RBBO ranges from 412kΩ for different device types. The intrinsic standoff ratio η is the ratio of RB1 to RBBO. It varies ...
BE LAB
... There are 2 types of transistor NPN and PNP. Emitter is the terminal which emitts charge carriers,heavily doped region collector is the terminal which collects the charge carries and moderately doped region or terminal. Base is the region through which charge carriers passes and thinly doped region. ...
... There are 2 types of transistor NPN and PNP. Emitter is the terminal which emitts charge carriers,heavily doped region collector is the terminal which collects the charge carries and moderately doped region or terminal. Base is the region through which charge carriers passes and thinly doped region. ...
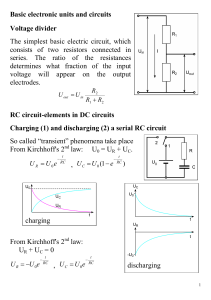
Basic electronic units and circuits Voltage divider The simplest basic
... FET (Field Effect Transistor) The controlling voltage sets the thickness of the empty layer, which can be seen in a diode. Changing the cross section area of a conductor can be used to regulate the current. The great advantage of the FET is that, practically, there is no current on the controlling e ...
... FET (Field Effect Transistor) The controlling voltage sets the thickness of the empty layer, which can be seen in a diode. Changing the cross section area of a conductor can be used to regulate the current. The great advantage of the FET is that, practically, there is no current on the controlling e ...
Modelling Electricity
... What is current, voltage and resistance? Current – the flow of electrons around the circuit Voltage – driving force which pushes the current around Resistance – anything in the circuit which slows the flow down ...
... What is current, voltage and resistance? Current – the flow of electrons around the circuit Voltage – driving force which pushes the current around Resistance – anything in the circuit which slows the flow down ...
Electrical resistance - Tasker Milward Physics Website
... resistance. 1. A 6V cell is connected into a circuit with a 3 resistor and an ammeter. Use the circuit symbol sheet to help you – draw this circuit. Calculate the current. 2. A 10 resistor is connected into a circuit with a cell and an ammeter. 2A of current flows. Calculate the voltage of the cel ...
... resistance. 1. A 6V cell is connected into a circuit with a 3 resistor and an ammeter. Use the circuit symbol sheet to help you – draw this circuit. Calculate the current. 2. A 10 resistor is connected into a circuit with a cell and an ammeter. 2A of current flows. Calculate the voltage of the cel ...
S R 1 2
... In this experiment we will examine the step response of several RC and RLC circuits. We begin by finding the output waveform v(t) from RC circuits designed to operate as “analog computers”, where the derivative with respect to time (or the integral) of an input waveform vi(t) is taken continuously. ...
... In this experiment we will examine the step response of several RC and RLC circuits. We begin by finding the output waveform v(t) from RC circuits designed to operate as “analog computers”, where the derivative with respect to time (or the integral) of an input waveform vi(t) is taken continuously. ...
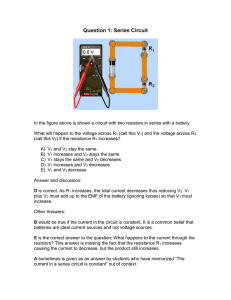
Question 1 - cloudfront.net
... D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current s ...
... D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current s ...
Chapter-10 Electricity
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. ...
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... • The total load (resistance) in a series circuit with “n” loads is the sum of the resistance of the “n” objects. Rtot = R1 + R2 + … + Rn. ...
... • The total load (resistance) in a series circuit with “n” loads is the sum of the resistance of the “n” objects. Rtot = R1 + R2 + … + Rn. ...
Document
... (or devices) and conducting wires to connect different components. It typically has other components like current or voltage measuring devices and switches. There are two types of circuits, series and parallel. Compound circuits are a combination of one or more series and parallel circuits. ...
... (or devices) and conducting wires to connect different components. It typically has other components like current or voltage measuring devices and switches. There are two types of circuits, series and parallel. Compound circuits are a combination of one or more series and parallel circuits. ...
Section G2: Current Sources and Active Loads
... suitable for the design of IC amplifiers since, even for a relatively simple multistage amplification system, many resistors and large capacitors are required. This is problematic for a couple of reasons, most importantly the cost of chip “real-estate” and fabrication concerns. However, fabrication ...
... suitable for the design of IC amplifiers since, even for a relatively simple multistage amplification system, many resistors and large capacitors are required. This is problematic for a couple of reasons, most importantly the cost of chip “real-estate” and fabrication concerns. However, fabrication ...
MASTER INSTRUMENT CORPORATION SINGLE-PHASE BRIDGE RECTIFIER RB151 THRU RB157
... l High isolation voltage from case to leads l High temperature soldering guaranteed: 260 oC/10 second, at 5 lbs. (2.3kg) tension. ...
... l High isolation voltage from case to leads l High temperature soldering guaranteed: 260 oC/10 second, at 5 lbs. (2.3kg) tension. ...
CENTRIPENTAL ACCELERATION AND FORCE PROBLEMS
... occurs in the current? 12. If the resistance of a circuit remains constant while the voltage across the circuit decreases to half its former value, what change occurs in the current? 13. Why is it that a bird can perch without harm on a high voltage wire? ...
... occurs in the current? 12. If the resistance of a circuit remains constant while the voltage across the circuit decreases to half its former value, what change occurs in the current? 13. Why is it that a bird can perch without harm on a high voltage wire? ...
Exam - ISY@LiU
... Draw the input voltage vs, resistor voltage vr, and input current is shapes, indicate where each diode is on (conducting) or off (not conducting), and at what angles current and voltage changes happen. ...
... Draw the input voltage vs, resistor voltage vr, and input current is shapes, indicate where each diode is on (conducting) or off (not conducting), and at what angles current and voltage changes happen. ...
Circuits - cottonphysics
... •The charges do more work as they pass through the larger resistor. ...
... •The charges do more work as they pass through the larger resistor. ...