Voltage regulators 723
... Output voltage ranging from 2 to 7 Volts and the load current of more than 150mA can be obtained by connecting a transistor Q1 as shown in Figure. The functional equations are Vo Vref Rsc ...
... Output voltage ranging from 2 to 7 Volts and the load current of more than 150mA can be obtained by connecting a transistor Q1 as shown in Figure. The functional equations are Vo Vref Rsc ...
TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIER
... • This is analogous to a transistor operating in the linear region. Small changes in the base current cause much larger but directly proportional changes in the current flowing from collector to emitter. • The transistor can be biased using a DC power supply and resistors to act as an amplifier. • ...
... • This is analogous to a transistor operating in the linear region. Small changes in the base current cause much larger but directly proportional changes in the current flowing from collector to emitter. • The transistor can be biased using a DC power supply and resistors to act as an amplifier. • ...
(A) (B) - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... Everything turned in single spaced and typed Due at next lab unless announced otherwise 10% reduction each day lab is late EVERYTHING must be turned in by Friday of week 14 ...
... Everything turned in single spaced and typed Due at next lab unless announced otherwise 10% reduction each day lab is late EVERYTHING must be turned in by Friday of week 14 ...
Test Equipment
... Five virtual instruments allow for instant, accurate circuit analysis Pre-designed circuit library included & Low cost - only $50.00 ...
... Five virtual instruments allow for instant, accurate circuit analysis Pre-designed circuit library included & Low cost - only $50.00 ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... So we use an uppercase V to indicate the voltage variables in s domain. To find the transfer function, we need to relate the output voltage with the input voltage. Let’s try to label all the node voltage variables in the circuit. This node is a reference node, so it is zero volts. For the non-invert ...
... So we use an uppercase V to indicate the voltage variables in s domain. To find the transfer function, we need to relate the output voltage with the input voltage. Let’s try to label all the node voltage variables in the circuit. This node is a reference node, so it is zero volts. For the non-invert ...
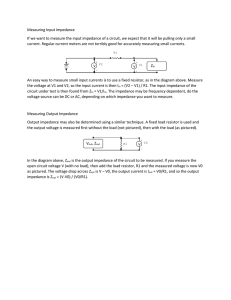
Measuring Input Impedance If we want to measure the input
... In the diagram above, Zout is the output impedance of the circuit to be measured. If you measure the open circuit voltage V (with no load), then add the load resistor, R1 and the measured voltage is now V0 as pictured. The voltage drop across Zout is V – V0, the output current is Iout = V0/R1, and s ...
... In the diagram above, Zout is the output impedance of the circuit to be measured. If you measure the open circuit voltage V (with no load), then add the load resistor, R1 and the measured voltage is now V0 as pictured. The voltage drop across Zout is V – V0, the output current is Iout = V0/R1, and s ...
Lecture_1
... of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sources supply a fixed current I independent of the resistance of the load. ( ...
... of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sources supply a fixed current I independent of the resistance of the load. ( ...
Student 2
... increases across the parallel branches. The energy carried by the electrons is the same. Current, unlike voltage raised between circuits. The current drawn by a resistor depends on its resistance (Ohms Law states that resistance is inversely proportional to current) Low resistance has high current a ...
... increases across the parallel branches. The energy carried by the electrons is the same. Current, unlike voltage raised between circuits. The current drawn by a resistor depends on its resistance (Ohms Law states that resistance is inversely proportional to current) Low resistance has high current a ...
Troubleshooting Techniques
... Summary of Transistor Bias Circuits Troubleshooting Transistor You can view the transistor as two diodes connected as shown in the figures below ...
... Summary of Transistor Bias Circuits Troubleshooting Transistor You can view the transistor as two diodes connected as shown in the figures below ...
two load line of vdb amplifier
... Advantages and Disadvantages:Advantages are as below Each transistor is at cutoff when there is no input signal Improved efficiency where there is an input signal. The maximum efficiency of a class B push-pull amplifier is 78.5 %. Disadvantage are as below use of transformers. Audio transformers ar ...
... Advantages and Disadvantages:Advantages are as below Each transistor is at cutoff when there is no input signal Improved efficiency where there is an input signal. The maximum efficiency of a class B push-pull amplifier is 78.5 %. Disadvantage are as below use of transformers. Audio transformers ar ...
EUP2412 500kHz Synchronous Step-Up Converter with 600mA LDO
... inrush current. The EUP2412 synchronous step-up convert regulates the output voltage up to 6V. When the synchronous step-up convert is disabled, the internal conduction path from SW to OUT is fully blocked. This output disconnect feature isolates the output from the input and reduces the shutdown cu ...
... inrush current. The EUP2412 synchronous step-up convert regulates the output voltage up to 6V. When the synchronous step-up convert is disabled, the internal conduction path from SW to OUT is fully blocked. This output disconnect feature isolates the output from the input and reduces the shutdown cu ...
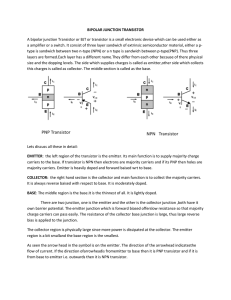
20 Bipolar Transistors and Amplifiers
... The resistance of the forward-biased B-E junction is very low. Hence the base current IB ≅ Vin/R1 = (VinDC+VinAC)/R1 The collector current IC does not depend on the collector voltage if the latter is high enough. Hence, IC ≅ β IB; The voltage drop across the load resistance R2: V2= IC R2; The output ...
... The resistance of the forward-biased B-E junction is very low. Hence the base current IB ≅ Vin/R1 = (VinDC+VinAC)/R1 The collector current IC does not depend on the collector voltage if the latter is high enough. Hence, IC ≅ β IB; The voltage drop across the load resistance R2: V2= IC R2; The output ...
OSI
... Specific outputs can be selected to interface with any data acquisition system from a simple recorder to computer-, SCADA-, or PLC-based system. The DW5 is widely used in a variety of applications, including hydroelectric generator output measurement, end-of-line appliance testing for energy consump ...
... Specific outputs can be selected to interface with any data acquisition system from a simple recorder to computer-, SCADA-, or PLC-based system. The DW5 is widely used in a variety of applications, including hydroelectric generator output measurement, end-of-line appliance testing for energy consump ...
6.2 Electric Current Name: Current and Voltage Difference Electric
... Electric Current-The ___________________________ of electric charge in a __________ direction. o Measured in ___________________ ...
... Electric Current-The ___________________________ of electric charge in a __________ direction. o Measured in ___________________ ...