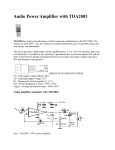
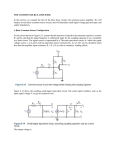
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SECTION – A (Marks : 2 Each) Q.1 (a) What is an a.c. load line? Ans
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
SECTION – A (Marks : 2 Each) Q.1 (a) What is an a.c. load line? Ans.: The dc load resistance is Rc but the A load resistance is (Rc || RL). If a load line is drawn the slope of which is -1 / (Rc || R1). Then it is called as an AC load line and it is to be used when the transistor is operating as an amplifier. The AC load line thus represents the AC operating conditions of a circuit. Q.1 (b) What is the function of bypass capacitors? Ans.: Bypass capacitor CE: The capacitor connected in parallel with the emitter resistor RE is called as the emitter bypass capacitor. This capacitor offers a low reactance to the amplified as signal. Therefore the emitter resistor RE gets bypass through CE for only the ac signals. This will increase the voltage gain of the amplifier. Moreover as CE acts as open circuit for de voltages. It does not bypass RE for dc conditions. This presence of CE does not alter the dc biasing conditions. Q.1 (c) List the types of coupling. Ans.: The coupling techniques are: 1. R-C coupling. 2. Transformer coupling 3. Direct coupling. Q.1 (d) What do h-parameters signify? Ans.: The four parameters associated with this model are input impedance, voltage ratio, current gain and output conductance. Since their units are completely different from each other, this set of parameters is called as hybrid parameters. Q.1 (e) Define harmonic distortion. Ans.: Harmonic distortion: The harmonic distortion suggests the presence of those frequency components in the amplifier output which are absent on the input side of the amplifier. The frequency component which has the same frequency of the input is known as the fundamental frequency component. The other frequency components in the output, which are integer multiples of fundamental frequency component are known as “Harmonics”. If the frequency, of the fundamental component is say F0 Hz the 2 f0, 3 f0, 4f0 … etc. are the harmonic components. R f0 is called as second harmonic, e f0 is called as third harmonic and so on. Q.1 (f) What is thermal run away? Ans.: The internal heating process is cumulative as explained below: 1. An increase in collector current Ic increases the power dissipated in the collector-base junction of the transistor. 2. This will increase the temperature of C-B junction. 3. As the transistor has a negative temperature coefficient of resistivity. Increased junction temperature reduces the resistance. 4. The reduced resistance will increase the collector current further. This becomes a cumulative processes which will finally damage the transistor due to excessive heating. This process is known as “Thermal Runaway”. Q.1 (g) What is cross-over distortion? Ans.: In class B amplifiers the transistors are biased at cut-off. These transistors can enter the active region if and only if their base emitter junction is forward biased. To forward bias these junctions the input voltage must be greater than the cut-in voltage of the junction. The cut-in voltage is 0.2 V for Ge and 0.7 V for Si transistor. Thus as long as the input voltage is less than the cut-in voltage, the transistors will remain in the off state and the output will be zero. The output signal gets distorted near the zero crossing. Therefore this distortion is called as the “cross-over distortion.” Q.1 (h) Define stagger tuning. Ans.: Stagger tuning is a technique used in order to increase the bandwidth of an RF tuned amplifier without sacrificing on the amplifier gain. A number of tuned circuits are used to operate in union. For example if a two stage amplifier is used with a tuned circuit at the input of each stage and a double tuned circuit is connected in the collector of each stage. Q.1 (i) What is the criterion for oscillations? Ans.: The Barkhausen criterion states that: 1. An oscillator will operate at that frequency for which the total phase shift introduced, as the signal proceeds from the input terminals, through the amplifier and feedback network and bank again to the input; is precisely 0º or 360º or integral multiple of 360º. 2. At the oscillator frequency, the magnitude of the product of open loop gain of the amplifier A and the feedback factor β is equal to or greater than unity. The product A β is called as the “loop gain”. Q. (j) Define the term stability Ans.: Stability is a process of stabilizing the Q – point (bias point) of the circuit or Q – point of a transistor amplifier which depends on leakage current Ico, current gain βdc and Base to emitter voltage VBE. SECTION – B (Marks : 5 Each) Q.2 Discuss the hybrid pi CE transistor model. Q.3 Prove that the minimum transistor power dissipation of a class B push-pull amplifier is given by: P D(max) = 0.2P I(max) Q.4 Discuss the features of power amplifier design. Q.5 Explain the voltage series feedback. Q.6 Discuss the working of crystal oscillators. SECTION – C (Marks: 10 Each) Q. 7 Describe the construction, working and applications of Weinbridge oscillator. Q.8 Discuss the design, construction applications of regulated power supplies. Q.9 Write short notes on the following: (a) Tuned amplifier (b) Zener diode as voltage regulator.