* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operating point of a transistor
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
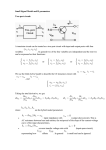
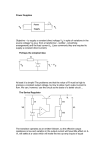
Monday 11/1/2010 Electronics circuit I lab Section : A Fourth report. Written By: Raed Suleiman Group: Abbass Taher Raed Suleiman Tarek Fawaz. Instructor Dr: Nahida Abdallah Fall 2009-2010 Equipments: -Com3lab. -Pc. -Connecting wires. Objectives: -To know the characteristics of circuits containing transistors. - To know the control characteristics and power dissipation with various types of configuration in AC or DC. -To know the load line characteristics. -To know the voltage and current gains along with power dissipation and phase difference in AC analysis using the common emitter I)Operating point of a transistor : To determine the operating point of a transistor consider the following circuit configuration: When we draw the load line where Q is moving here (having R2 as a variable resistor) , the load line in this voltage divider circuit will look like this : Here the drawing shows Ic vs Uce where Q is located , the best place for Q is the middle of the line , as i moves towards Ic it is reaching saturation and towards Uce it is reaching cutoff. Transistor in common emitter circuit \ emitter amplifier : The general configuration of the common emitter circuit is simple as follows : The emitter is at the ground and there is no resistor at the emitter here in this case. The emitter is grounded with respect to the alternating voltage. -Now we study the AC analysis of common emitter circuit , the capacitors will act as short. Consider the following voltage divider circuit with common emitter : The main aspects of transistor circuits is : 1) Input and output impedance 2) Current and voltage gain 3) Power dissipation This circuit (with AC generator and voltmeters set as shown) will allow us to measure the voltage gain : Here we have the values of U2 and U2 as shown and we can calculate the voltage gain of this transistor by dividing them. The input impedance is R2 and the output is R4. -Now for the current gain ,we do the following circuit: This configuration allows us to measure the current gain . NB : when one of the bypass capacitor is connected , R4 will have no effect and so affecting the whole current and voltage gains of the circuit. -For power dissipation calculation we connect the same circuit to an oscilloscope as : Here we can calculate the power dissipation and observe the phase shift under AC current. As a result, the AC power dissipation is negative and reduces the DC power dissipation. Conclusion: -In DC analysis of common emitter circuits , the operating point Q is fixed somewhere on the load line and its best to be in the middle. -In AC analysis , Q will oscillate along the load line so the circuit components must be good chosen to capture Q in good oscillation region away from cutoff or saturation. -At the operating point, the alternating current is prevented from lowering the base emitter voltage beyond the forward threshold. -The operating point is located on the slop of the collector and/or emitter resistance in the output characteristic quadrant. -to prevent a rise in temperature from shifting the operating point, this point is stabilized by the emitter resistance. -What important in transistor circuits is the voltage and current gains in it and its power dissipation inside the transistor , they determine the function of the circuit . -Similar techniques are used to analyze the common base circuit and other types of transistor circuits. - The AC power dissipation is negative and reduces the DC power dissipation.