* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Small Signal Model and H parameters
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
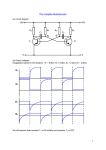
Small Signal Model and H parameters Two-port circuit: A transistor circuit can be treated as a two-port circuit with input and output ports with four variables . In general two of the four variables are independent and the rest two can be expressed as their functions: We use the third hybrid model to describe the CE transistor circuit with , , and , : Taking the total derivative, we get: where are the hybrid model parameters: : input impedance with (output short-circuit). This is AC resistance between base and emitter, the reciprocal of the slope of the current-voltage curve of the input characteristics. : reverse transfer voltage ratio with representing how affects . In general (input open-circuit), is small and can be ignored. : forward transfer current ratio or current amplification factor with (output short-circuit). Typically, : output admittance with is in the range of 20 to 200. (input open-circuit). It is slope of the current-voltage curve in the output characteristics. In general and can be ignored. is small If all variables , , and are small signals (around the DC operating point and far away from either the cut-off or the saturation region), these differential quantities can be rewritten as In general, and are small and could be assumed zero to further simplify the model (right of the figure above) containing only two components, a resistor source and a current . The base and emitter forms a PN junction with a resistance as discussed in the section of diodes. Typically, if , then is about (room temperature) and . Based on this small signal model, a transistor can be analyzed as a two-port circuit containing a resistor source . and a current