The_Structure_of_Protein_Activity
... aspartic acid unit, calculate the approximate number of amino acid molecules that are needed to produce on molecule of haemoglobin. 3. How does the hydrogen bonding explain: a) The solubility of many proteins in water. b) The precise 3D structure of those enzymes which are proteins. c) The eleastici ...
... aspartic acid unit, calculate the approximate number of amino acid molecules that are needed to produce on molecule of haemoglobin. 3. How does the hydrogen bonding explain: a) The solubility of many proteins in water. b) The precise 3D structure of those enzymes which are proteins. c) The eleastici ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Physics
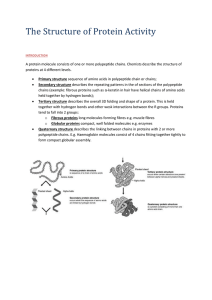
... Primary Structure – amino acid sequence Secondary Structure – α and β helices Tertiary Structure – folding Quaternary Structure – compacted subunits To do this, a PowerPoint presentation will be provided with integrated computer simulations and embedded short videos ♦ Have students evaluate regions ...
... Primary Structure – amino acid sequence Secondary Structure – α and β helices Tertiary Structure – folding Quaternary Structure – compacted subunits To do this, a PowerPoint presentation will be provided with integrated computer simulations and embedded short videos ♦ Have students evaluate regions ...
Center for Biological Physics* Math and Science Teachers Fellows
... Primary Structure – amino acid sequence Secondary Structure – α and β helices Tertiary Structure – folding Quaternary Structure – compacted subunits To do this, a PowerPoint presentation will be provided with integrated computer simulations and embedded short videos Have students evaluate regions of ...
... Primary Structure – amino acid sequence Secondary Structure – α and β helices Tertiary Structure – folding Quaternary Structure – compacted subunits To do this, a PowerPoint presentation will be provided with integrated computer simulations and embedded short videos Have students evaluate regions of ...
View video content as a PDF
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
ProteinChipâ technology is one of the most exciting advancements
... ProteinChip technology is one of the most exciting advancements in protein analysis in the last 5 years. The Protein Biology SystemTM (PBS) combines the power of mass analysis with chromatography surfaces on an integrated platform. The PBS can easily be used by biologists, biochemists, and clinicia ...
... ProteinChip technology is one of the most exciting advancements in protein analysis in the last 5 years. The Protein Biology SystemTM (PBS) combines the power of mass analysis with chromatography surfaces on an integrated platform. The PBS can easily be used by biologists, biochemists, and clinicia ...
Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can
... 9. Believe it or not, you have hydrochloric acid in your stomach. It’s nasty stuff that can burn skin and eat away at almost anything. What is it doing in your stomach and why doesn’t it eat up your insides? ...
... 9. Believe it or not, you have hydrochloric acid in your stomach. It’s nasty stuff that can burn skin and eat away at almost anything. What is it doing in your stomach and why doesn’t it eat up your insides? ...
Interaction Site Evolution
... DNA is the blueprint for generating strings of amino acids which fold into proteins. The interactions these proteins form with each other are primary components of organismal physiology. Proteins assume very specific shapes, and the amino acids on their surface involved in protein interactions are s ...
... DNA is the blueprint for generating strings of amino acids which fold into proteins. The interactions these proteins form with each other are primary components of organismal physiology. Proteins assume very specific shapes, and the amino acids on their surface involved in protein interactions are s ...
custom protein production service
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
About Proteins
... Proteins can also change shape by other ways. If chemicals or heat are added to the protein, it can cause the amino acids to fold in different ways, changing the shape of the protein. This can be seen using an egg. Think about what the protein of an egg looks like. It is the clear part. When you coo ...
... Proteins can also change shape by other ways. If chemicals or heat are added to the protein, it can cause the amino acids to fold in different ways, changing the shape of the protein. This can be seen using an egg. Think about what the protein of an egg looks like. It is the clear part. When you coo ...
Lh6Ch04bProt
... Amyloid Fibers Stabilized by F Different Amyloid diseases depend on organ the fibers occur ...
... Amyloid Fibers Stabilized by F Different Amyloid diseases depend on organ the fibers occur ...
Lecture 1
... Protein 3 contains a prosthetic group. The secondary structure of protein 3 is all a-helix. These proteins have both secondary and tertiary structure. ...
... Protein 3 contains a prosthetic group. The secondary structure of protein 3 is all a-helix. These proteins have both secondary and tertiary structure. ...
Protein Reading Questions Due Monday File
... 8. Explain the properties of the amino acid groups below, based on their R-group: a. Nonpolar side chains/Hydrophobic: b. Polar side chains/ Hydrophilic: c. Electrically charged side chains/Hydrophilic: 9. What are the bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide called AND what type of bond is it? ...
... 8. Explain the properties of the amino acid groups below, based on their R-group: a. Nonpolar side chains/Hydrophobic: b. Polar side chains/ Hydrophilic: c. Electrically charged side chains/Hydrophilic: 9. What are the bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide called AND what type of bond is it? ...
Quiz-2
... 7. Ramchandran’s plot for poly-glycine shows four big squares of allowed conformations which is very different from any polypeptide. Explain why? 8. Find out the primary structure of the peptide based on the information provided below. a) Amino acid composition: Arg-1, Lys-2, Gly-3, Tyr-2, Thr-3, Me ...
... 7. Ramchandran’s plot for poly-glycine shows four big squares of allowed conformations which is very different from any polypeptide. Explain why? 8. Find out the primary structure of the peptide based on the information provided below. a) Amino acid composition: Arg-1, Lys-2, Gly-3, Tyr-2, Thr-3, Me ...
$doc.title
... enzyme is a chaperone protein related to the class of Sso7d proteins from the hyperthermophilic bacteria Sulfolobus solfataricus2. These proteins have demonstrated the unique ability to renature proteins from pre-formed protein aggregates. In addition, DBF has been shown to specifically refold prote ...
... enzyme is a chaperone protein related to the class of Sso7d proteins from the hyperthermophilic bacteria Sulfolobus solfataricus2. These proteins have demonstrated the unique ability to renature proteins from pre-formed protein aggregates. In addition, DBF has been shown to specifically refold prote ...
1. Protein Interactions
... amino acids have a oneletter symbol. A sequence of three symbols, as shown for RNA (right) is called a Amino acids have a central codon carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2) MSE-536 ...
... amino acids have a oneletter symbol. A sequence of three symbols, as shown for RNA (right) is called a Amino acids have a central codon carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2) MSE-536 ...
IB2.14.3 Building a protein
... All the basic structural material of the human body is made of proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitro ...
... All the basic structural material of the human body is made of proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitro ...
Abstract
... distribution of amino acid sequences that are members of a protein family, signals from amino acid coevolution at different sequence positions in multiple sequence alignments can be exploited to infer spatial contacts within the three dimensional folded structure of proteins. We developed a computat ...
... distribution of amino acid sequences that are members of a protein family, signals from amino acid coevolution at different sequence positions in multiple sequence alignments can be exploited to infer spatial contacts within the three dimensional folded structure of proteins. We developed a computat ...
Reading Guide: Pratt and Cornely, Chapter 4, pp 87
... List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in h-bonding? 15. What is an irregular sec ...
... List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in h-bonding? 15. What is an irregular sec ...
Relationship between amino acids sequences and protein structures
... from different families and with very low sequence similarities but with an identical SSS have a common sequence pattern. To find common sequence regularities a new algorithm of the multiple sequences alignment was developed. The proposed method involves ‘projecting’ common supersecondary structural ...
... from different families and with very low sequence similarities but with an identical SSS have a common sequence pattern. To find common sequence regularities a new algorithm of the multiple sequences alignment was developed. The proposed method involves ‘projecting’ common supersecondary structural ...
Protein folding
... Denaturation may not require complete unfolding of proteins. It might be still a folded structure but in random conformation. Denaturation is cooperative, I.e. changes in one part of protein acelerate the unfolding of the other part. ...
... Denaturation may not require complete unfolding of proteins. It might be still a folded structure but in random conformation. Denaturation is cooperative, I.e. changes in one part of protein acelerate the unfolding of the other part. ...
Protein folding

Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil.Each protein exists as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil when translated from a sequence of mRNA to a linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any stable (long-lasting) three-dimensional structure (the left hand side of the first figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as the native state. The resulting three-dimensional structure is determined by the amino acid sequence (Anfinsen's dogma). Experiments beginning in the 1980s indicate the codon for an amino acid can also influence protein structure.The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins may remain unfolded, so that protein dynamics is important. Failure to fold into native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances misfolded proteins have modified or toxic functionality. Several neurodegenerative and other diseases are believed to result from the accumulation of amyloid fibrils formed by misfolded proteins. Many allergies are caused by incorrect folding of some proteins, because the immune system does not produce antibodies for certain protein structures.