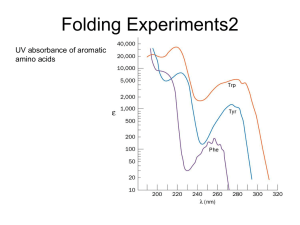
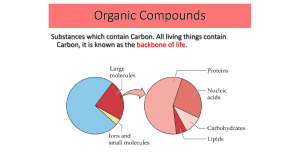
DN: Protein
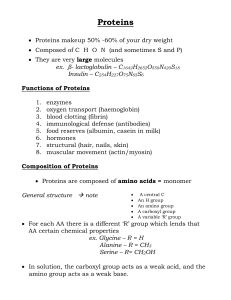
... sequence of the 20 different amino acids as illustrated on the left. In the feed lab, protein is distinguishable from carbohydrate and lipid due to its content of nitrogen (N) feed proteins typically contain about 16% N. This property makes it possible to estimate the protein content of a feedstuff ...
... sequence of the 20 different amino acids as illustrated on the left. In the feed lab, protein is distinguishable from carbohydrate and lipid due to its content of nitrogen (N) feed proteins typically contain about 16% N. This property makes it possible to estimate the protein content of a feedstuff ...
Center for Structural Biology
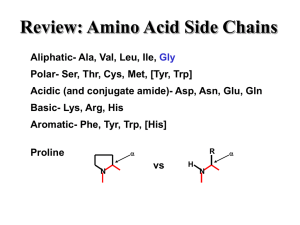
... Side chain properties specify core/exterior Some interactions inside, others outside Specific structures result from side chain interactions Hydrophobic interactions (interior) Hydrogen bonds (interior and exterior) Ionic Interactions (exterior) ...
... Side chain properties specify core/exterior Some interactions inside, others outside Specific structures result from side chain interactions Hydrophobic interactions (interior) Hydrogen bonds (interior and exterior) Ionic Interactions (exterior) ...
Amino acids
... solubility (scleroproteins, albumins, histones, globulins) function (proteins of basic metabolism, specialized cells) ...
... solubility (scleroproteins, albumins, histones, globulins) function (proteins of basic metabolism, specialized cells) ...
Improving Function Prediction Using Patterns of Native Disorder in
... Instrinsically unstructured (disordered) proteins adopt little or no stable secondary structure in their native state. Proteins containing long disordered regions are abundant within eukaryotic genomes and can be predicted successfully from amino sequence. Disordered regions have been shown to be im ...
... Instrinsically unstructured (disordered) proteins adopt little or no stable secondary structure in their native state. Proteins containing long disordered regions are abundant within eukaryotic genomes and can be predicted successfully from amino sequence. Disordered regions have been shown to be im ...
Chemistry 160 Protein Structure Homework
... 5. Describe 3 types of interactions that stabilize protein structure. 6. What drives protein folding? 7. Give two ways amino acid sequences are determined. 8. A small protein was cleaved in two separate experiments by chymotrypsin and by trypsin. The chymotrypsin fragments were: MAVKTMPW, ATF, AMERT ...
... 5. Describe 3 types of interactions that stabilize protein structure. 6. What drives protein folding? 7. Give two ways amino acid sequences are determined. 8. A small protein was cleaved in two separate experiments by chymotrypsin and by trypsin. The chymotrypsin fragments were: MAVKTMPW, ATF, AMERT ...
Proteins
... – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together ...
... – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together ...
Proteins - CasimiroSBI4U
... peptide bonds, arranged in a specific linear sequence. Peptide bond = covalent bond formed by condensation reaction that links carboxyl group of one amino acid to amino group of another. ...
... peptide bonds, arranged in a specific linear sequence. Peptide bond = covalent bond formed by condensation reaction that links carboxyl group of one amino acid to amino group of another. ...
A sample for a final examination
... 1. An experimentalist would like to design a simple sequence of alanine and arginine only that will fold into the known structure of lysozyme. He asks his friend (a computational biologist) to estimate the significance of his design (before he is going to do all the hard synthesis work). The compute ...
... 1. An experimentalist would like to design a simple sequence of alanine and arginine only that will fold into the known structure of lysozyme. He asks his friend (a computational biologist) to estimate the significance of his design (before he is going to do all the hard synthesis work). The compute ...
Capturing denaturing proteins * Small Heat Shock Protein substrate
... Elizabeth Vierling and Indu Santhanagopalan Protein aggregation resulting from stress, disease or mutation poses a major threat to all cells. The ubiquitous small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) act as molecular chaperones to prevent irreversible protein aggregation and are significant components of the ...
... Elizabeth Vierling and Indu Santhanagopalan Protein aggregation resulting from stress, disease or mutation poses a major threat to all cells. The ubiquitous small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) act as molecular chaperones to prevent irreversible protein aggregation and are significant components of the ...
slides
... structure of the folding transition state in small protein domains that fold in a two-state manner. Since the folding transition state is by definition a transient and partially unstructured state, its structure is difficult to determine by traditional methods such as protein NMR or X-ray crystallog ...
... structure of the folding transition state in small protein domains that fold in a two-state manner. Since the folding transition state is by definition a transient and partially unstructured state, its structure is difficult to determine by traditional methods such as protein NMR or X-ray crystallog ...
BB 450/500 Lecture 5 Highlights
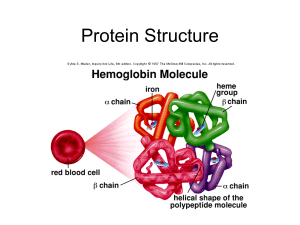
... protein. The word polypeptide refers to a polymer of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides and is folded and may be covalently modified. 11. Hemoglobin (and many other proteins) have multiple polypeptide subunits. Interactions between the subunits include disulfide bonds, ionic ...
... protein. The word polypeptide refers to a polymer of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides and is folded and may be covalently modified. 11. Hemoglobin (and many other proteins) have multiple polypeptide subunits. Interactions between the subunits include disulfide bonds, ionic ...
Visually Demonstrating the Principles of Protein Folding
... tools. (PDB tools) Targeted for high school students and lower ...
... tools. (PDB tools) Targeted for high school students and lower ...
Slide 1
... The kinetic Theory of Protein Folding Folding proceeds through a definite series of steps or a Pathway. A protein does not try out all possible rotations of conformational angles, but only enough to find the pathway. ...
... The kinetic Theory of Protein Folding Folding proceeds through a definite series of steps or a Pathway. A protein does not try out all possible rotations of conformational angles, but only enough to find the pathway. ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
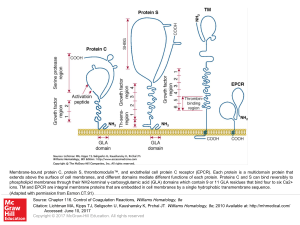
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Daniel Kaganovich Molecular Mechanism of
... throughout the cell. Our lab uses high-resolution 3D time-lapse imaging to study the way in which cells orchestrate the function of a vast and dynamic protein folding quality control system, which includes chaperones that enhance protein folding and regulate protein aggregation. From basic findings ...
... throughout the cell. Our lab uses high-resolution 3D time-lapse imaging to study the way in which cells orchestrate the function of a vast and dynamic protein folding quality control system, which includes chaperones that enhance protein folding and regulate protein aggregation. From basic findings ...
protein folding
... makes these tools different from each other is their form (i.e. their shape and structure). ...
... makes these tools different from each other is their form (i.e. their shape and structure). ...
Proceedings of a meeting held at Allerton House, Monticello, Illinois
... these angles to better than a tenth of a radian, there would be 10300 possible configurations in our theoretical protein. In nature, proteins apparently do not sample all of these possible configurations since they fold in a few seconds, and even postulating a minimum time for going from one conform ...
... these angles to better than a tenth of a radian, there would be 10300 possible configurations in our theoretical protein. In nature, proteins apparently do not sample all of these possible configurations since they fold in a few seconds, and even postulating a minimum time for going from one conform ...
Knuffke Prezi- Macromolecules
... • Secondary structure + random coiled subunits + S-S bonds • Caused by interactions of R groups ...
... • Secondary structure + random coiled subunits + S-S bonds • Caused by interactions of R groups ...
The World of Chemistry
... 5. What may be the result of a change of one amino acid in a protein structure? Give an example. ...
... 5. What may be the result of a change of one amino acid in a protein structure? Give an example. ...
Protein folding

Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil.Each protein exists as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil when translated from a sequence of mRNA to a linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any stable (long-lasting) three-dimensional structure (the left hand side of the first figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as the native state. The resulting three-dimensional structure is determined by the amino acid sequence (Anfinsen's dogma). Experiments beginning in the 1980s indicate the codon for an amino acid can also influence protein structure.The correct three-dimensional structure is essential to function, although some parts of functional proteins may remain unfolded, so that protein dynamics is important. Failure to fold into native structure generally produces inactive proteins, but in some instances misfolded proteins have modified or toxic functionality. Several neurodegenerative and other diseases are believed to result from the accumulation of amyloid fibrils formed by misfolded proteins. Many allergies are caused by incorrect folding of some proteins, because the immune system does not produce antibodies for certain protein structures.