TASK A - Via Lingua Budapest
... What were the factors which influenced the successful acquisition of this skill? (e.g. necessity, motivation, obligation, peer pressure, curiosity, trial and error, early success, observation of others, participation, repetition, reading, following instructions, self teaching, being ...
... What were the factors which influenced the successful acquisition of this skill? (e.g. necessity, motivation, obligation, peer pressure, curiosity, trial and error, early success, observation of others, participation, repetition, reading, following instructions, self teaching, being ...
APA Style - ETSU.edu
... None can be singular or plural. When the noun following is single, use singular; when the noun following is plural, use plural. If you mean “not one”, use not one. ...
... None can be singular or plural. When the noun following is single, use singular; when the noun following is plural, use plural. If you mean “not one”, use not one. ...
E. Questions with
... Ex: Are there any eggs in the refrigerator? No, there aren't any eggs in the refrigerator. ...
... Ex: Are there any eggs in the refrigerator? No, there aren't any eggs in the refrigerator. ...
POSTER PROJECT
... words for the definition. Plan ahead and think of some things you can draw that show the part of speech. This website has more information about the parts of speech: https://arts.uottawa.ca/writingcentre/en/hypergrammar/the-parts-of-speech ...
... words for the definition. Plan ahead and think of some things you can draw that show the part of speech. This website has more information about the parts of speech: https://arts.uottawa.ca/writingcentre/en/hypergrammar/the-parts-of-speech ...
Eight Parts of Speech
... Proper noun is the name of a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Proper nouns are always capitalized. Concrete nouns name an object that can be seen, heard, smelled, touched, or tasted. Abstract nouns name ideas, qualities, or states (feelings). Singular nouns name one person, place, thing, or ...
... Proper noun is the name of a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Proper nouns are always capitalized. Concrete nouns name an object that can be seen, heard, smelled, touched, or tasted. Abstract nouns name ideas, qualities, or states (feelings). Singular nouns name one person, place, thing, or ...
Parts of Speech Review Warm- Ups Monday, September 21, 2015 A
... 2. What do you know about pronouns? 3. Everybody can learn English Grammar. 4. This is a quiz for ESL students. This quiz is for us. 5. Whom did they ask for help with English pronouns? Wednesday, September 23, 2015 ...
... 2. What do you know about pronouns? 3. Everybody can learn English Grammar. 4. This is a quiz for ESL students. This quiz is for us. 5. Whom did they ask for help with English pronouns? Wednesday, September 23, 2015 ...
Latin (grammar - lite)
... Prepositions are followed by either the accusative or ablative case. Your red vocab booklet tells you which case goes with each preposition. They must be translated before the noun after them in Latin. Note especially in + accusative = into, onto; in + ablative = in, on. ...
... Prepositions are followed by either the accusative or ablative case. Your red vocab booklet tells you which case goes with each preposition. They must be translated before the noun after them in Latin. Note especially in + accusative = into, onto; in + ablative = in, on. ...
parts of speech - 220112012salinaunisel
... On the ground Brother saw a __________. It was the color of __________ and had a texture like __________. It reminded him of ...
... On the ground Brother saw a __________. It was the color of __________ and had a texture like __________. It reminded him of ...
Parts of Speech lesson 1
... and pronouns. Adjectives are modifiers and give information about the nouns and pronouns that they modify. Proper adjectives modify proper form and begin with a capital letter. Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs and describe. Examples of Adjectives: Proper adjectives: Persian rug, Mexican ric ...
... and pronouns. Adjectives are modifiers and give information about the nouns and pronouns that they modify. Proper adjectives modify proper form and begin with a capital letter. Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs and describe. Examples of Adjectives: Proper adjectives: Persian rug, Mexican ric ...
Adding Pronoun Constraints to a Grammar
... • other pronouns in subject position occur with plural verb forms – I eat. *I eats. They eat. *They eats. – ignore special case of ‘be’ – J&M treats ‘do’ as aux, so must include number agreement for aux ...
... • other pronouns in subject position occur with plural verb forms – I eat. *I eats. They eat. *They eats. – ignore special case of ‘be’ – J&M treats ‘do’ as aux, so must include number agreement for aux ...
Parts of Speech
... PRONOUNS • Pronouns can replace the nouns in a sentence to make the sentence easier to understand. • Common pronouns include: I, me, my, her, she, him, his, they, theirs, ours, them, us, you, it • Any word that ends in –self or –selves • Words like that, few, many, some, anyone, several, all, etc. ...
... PRONOUNS • Pronouns can replace the nouns in a sentence to make the sentence easier to understand. • Common pronouns include: I, me, my, her, she, him, his, they, theirs, ours, them, us, you, it • Any word that ends in –self or –selves • Words like that, few, many, some, anyone, several, all, etc. ...
Grammar Review - cloudfront.net
... Demonstrative pronouns – points specific things out (this, that, these, those) Indefinite pronouns – not referring to a specific person or thing (anyone, each) Reflexive pronouns – self, selves forms (myself, himself, ourselves, etc.) Possessive Pronouns – Caution – These words can act as ad ...
... Demonstrative pronouns – points specific things out (this, that, these, those) Indefinite pronouns – not referring to a specific person or thing (anyone, each) Reflexive pronouns – self, selves forms (myself, himself, ourselves, etc.) Possessive Pronouns – Caution – These words can act as ad ...
Business English At Work, 3/e - Walla Walla Community College
... Adverbs answer the questions: In what manner? We work efficiently in the morning. Where? She moved the deadlines forward. When? We prepare the summary yearly. To what extent? He carefully designed the Web site. ...
... Adverbs answer the questions: In what manner? We work efficiently in the morning. Where? She moved the deadlines forward. When? We prepare the summary yearly. To what extent? He carefully designed the Web site. ...
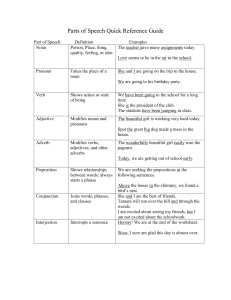
Parts of Speech Quick Reference Guide
... Hooray! We are at the end of the worksheet. Wow, I sure am glad this day is almost over. ...
... Hooray! We are at the end of the worksheet. Wow, I sure am glad this day is almost over. ...
Greek I
... serves as the object of a preposition. Possessive – as the name implies, shows possession. The main words in English that change their forms according to the function they perform are pronouns, e.g. he, him, his. ...
... serves as the object of a preposition. Possessive – as the name implies, shows possession. The main words in English that change their forms according to the function they perform are pronouns, e.g. he, him, his. ...
Parts of Speech - Northampton Community College
... How many? (How many dogs? Four dogs.) Adverbs: Adverbs usually describe (or “modify”) a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Often, but not always, adverbs end in –ly. They may answer one of these questions: When? Go immediately to jail. (Describing when you should go.) How? The class is ver ...
... How many? (How many dogs? Four dogs.) Adverbs: Adverbs usually describe (or “modify”) a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Often, but not always, adverbs end in –ly. They may answer one of these questions: When? Go immediately to jail. (Describing when you should go.) How? The class is ver ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Adverbs – modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They tell how, when, where and how much. Prepositions – show a relationship between its object and another word in the sentence. Conjunctions – join words, phrases and clauses. Interjections – exclamatory word that shows feeling/emotion ...
... Adverbs – modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They tell how, when, where and how much. Prepositions – show a relationship between its object and another word in the sentence. Conjunctions – join words, phrases and clauses. Interjections – exclamatory word that shows feeling/emotion ...
English Grammar - HCC Learning Web
... You can press those leaves under glass. can have more than ...
... You can press those leaves under glass. can have more than ...
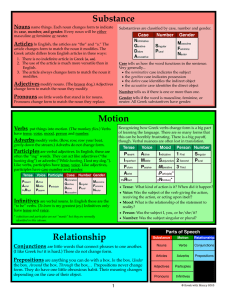
Substance Nouns
... article changes form to match the noun it modifies. The Greek article differs from English articles in three ways: 1. There is no indefinite article in Greek (a, an). 2. The use of the article is much more versatile than in English. 3. The article always changes form to match the noun it ...
... article changes form to match the noun it modifies. The Greek article differs from English articles in three ways: 1. There is no indefinite article in Greek (a, an). 2. The use of the article is much more versatile than in English. 3. The article always changes form to match the noun it ...
NOUNS-VERBS-ADJECTIVES
... 1. Tim went to the store to eat some candy. 2. Since I like eggs, I eat them every day. 3. Girls are stronger than boys. 4. Michigan is far away from Pennsylvania, as it shows on the map. 5. Whenever I get tired, I stop near a street light and go to sleep. 6. If at first you don’t succeed, try, try ...
... 1. Tim went to the store to eat some candy. 2. Since I like eggs, I eat them every day. 3. Girls are stronger than boys. 4. Michigan is far away from Pennsylvania, as it shows on the map. 5. Whenever I get tired, I stop near a street light and go to sleep. 6. If at first you don’t succeed, try, try ...
Chapter Two
... Adverbs answer the questions: In what manner? We work efficiently in the morning. Where? She moved the deadlines forward. When? We prepare the summary yearly. To what extent? He carefully designed the Web site. ...
... Adverbs answer the questions: In what manner? We work efficiently in the morning. Where? She moved the deadlines forward. When? We prepare the summary yearly. To what extent? He carefully designed the Web site. ...
Modern Greek grammar

The grammar of Standard Modern Greek, as spoken in present-day Greece and Cyprus, is basically that of Demotic Greek, but it has also assimilated certain elements of Katharevousa, the archaic, learned variety of Greek imitating Classical Greek forms, which used to be the official language of Greece through much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Modern Greek grammar has preserved many features of Ancient Greek, but has also undergone changes in a similar direction as many other modern Indo-European languages, from more synthetic to more analytic structures.