Latin 101: How to Identify Grammatical Forms in Context
... Quīntus nōlēbat diūtius in lūdō Orbiliī studēre. studēre: infinitive of studeō c. imperative: identify as imperative sing. or pl.; supply the 1st sing. of the verb example: nolīte ludere, puerī, sed audīte. audīte: imperative plural of audiō d. participles: PAP, 1st singular of the verb; case, numbe ...
... Quīntus nōlēbat diūtius in lūdō Orbiliī studēre. studēre: infinitive of studeō c. imperative: identify as imperative sing. or pl.; supply the 1st sing. of the verb example: nolīte ludere, puerī, sed audīte. audīte: imperative plural of audiō d. participles: PAP, 1st singular of the verb; case, numbe ...
Adjectives/Adverbs - Mrs. Moore`s 7th Grade English Class
... Adjectives – words we use to describe people, places, and things words that modify nouns and pronouns tell what kind, which one, how many, or how much includes possessive nouns and pronouns (my, our, your, his, her, its, their) includes demonstrative pronouns (this, that these those) inclu ...
... Adjectives – words we use to describe people, places, and things words that modify nouns and pronouns tell what kind, which one, how many, or how much includes possessive nouns and pronouns (my, our, your, his, her, its, their) includes demonstrative pronouns (this, that these those) inclu ...
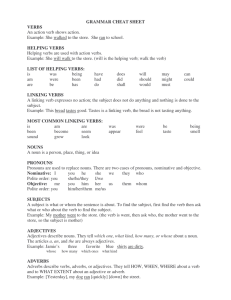
GRAMMAR CHEAT SHEET VERBS An action verb shows action
... A subject is what or whom the sentence is about. To find the subject, first find the verb then ask what or who about the verb to find the subject. Example: My mother went to the store. (the verb is went, then ask who, the mother went to the store, so the subject is mother) ...
... A subject is what or whom the sentence is about. To find the subject, first find the verb then ask what or who about the verb to find the subject. Example: My mother went to the store. (the verb is went, then ask who, the mother went to the store, so the subject is mother) ...
Latin 101: How to Identify Grammatical Forms in Context
... filiae: dative singular feminine Or, What is the case of horā? ablative Why is it in that case? abl. of time* relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: ...
... filiae: dative singular feminine Or, What is the case of horā? ablative Why is it in that case? abl. of time* relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: ...
Parts of Speech - Capital Community College
... You can press those leaves under glass. can have more than one object ...
... You can press those leaves under glass. can have more than one object ...
Parts of Speech - Capital Community College
... You can press those leaves under glass. can have more than one object ...
... You can press those leaves under glass. can have more than one object ...
File
... PRONOUNS Pronouns take the place of nouns to name persons, places, things, or ideas. PERSONAL PRONOUNS: I, me, you, he, him, she, her, it, we, us, they, them POSSESSIVE PERSONAL PRONOUNS: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs INDEFINITE PRONOUNS: Anybody, anyo ...
... PRONOUNS Pronouns take the place of nouns to name persons, places, things, or ideas. PERSONAL PRONOUNS: I, me, you, he, him, she, her, it, we, us, they, them POSSESSIVE PERSONAL PRONOUNS: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs INDEFINITE PRONOUNS: Anybody, anyo ...
1. Lexical Categories Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Prepositions, Adverbs
... Morphological distribution - determined by the kind of affixes that a given word takes and other morphology. Looking at characteristic inflectional and derivational endings of words e.g.: if elements can take endings such as –s, -‘s, s’ or -ment -dom, -er, we can say they are nouns Syntactic distr ...
... Morphological distribution - determined by the kind of affixes that a given word takes and other morphology. Looking at characteristic inflectional and derivational endings of words e.g.: if elements can take endings such as –s, -‘s, s’ or -ment -dom, -er, we can say they are nouns Syntactic distr ...
1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order
... 1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order pattern: subject + ( frequency adverb ) + verb + indirect object + direct object + manner + place + time adverbials 2- SUBJECT – VERB AGREEMENT: “People are friendly” 3- ADJECTIVES: Adjectives come before nouns and don’t change form: “She ha ...
... 1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order pattern: subject + ( frequency adverb ) + verb + indirect object + direct object + manner + place + time adverbials 2- SUBJECT – VERB AGREEMENT: “People are friendly” 3- ADJECTIVES: Adjectives come before nouns and don’t change form: “She ha ...
Plural Nouns - Net Start Class
... them to mean more than one. class – classes radish – radishes beach – beaches box - boxes For most nouns that end in y, you would drop the y and add ies to the noun to change them to mean more than one. lady – ladies ...
... them to mean more than one. class – classes radish – radishes beach – beaches box - boxes For most nouns that end in y, you would drop the y and add ies to the noun to change them to mean more than one. lady – ladies ...
The Eight Basic Parts of Speech
... Reflexive Pronouns: Words ending in -self or -selves, show the subject acting upon itself. For example: “The carpenter hit himself on the thumb.” Demonstrative Pronouns: This, that, these, those, point to a particular person or thing: For example: “These are my favorite flowers.” ...
... Reflexive Pronouns: Words ending in -self or -selves, show the subject acting upon itself. For example: “The carpenter hit himself on the thumb.” Demonstrative Pronouns: This, that, these, those, point to a particular person or thing: For example: “These are my favorite flowers.” ...
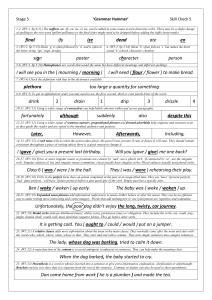
Stage 5 Check 10 – Answers
... 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go before other verbs. ...
... 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go before other verbs. ...
APP-Writing-Glossary-L1-and-2
... The word technique consists of only one morpheme having two syllables. Even though the word has two syllables, it is a single morpheme because it cannot be broken down into smaller meaningful parts. ...
... The word technique consists of only one morpheme having two syllables. Even though the word has two syllables, it is a single morpheme because it cannot be broken down into smaller meaningful parts. ...
Parts of Speech
... A pronoun is a word that is used in place of one or more nouns or pronouns. I, me, my, mine, we , us, our, ours, you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, its, it, they, them, their, theirs, myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, itself, themselves, this, that, these, those ...
... A pronoun is a word that is used in place of one or more nouns or pronouns. I, me, my, mine, we , us, our, ours, you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, its, it, they, them, their, theirs, myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, itself, themselves, this, that, these, those ...
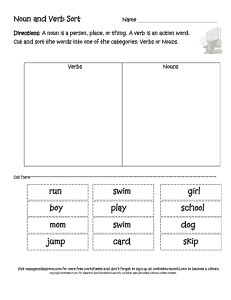
Noun and Verb Sort - Ms. Sugar`s Classroom
... Directions: A noun is a person, place, or thing. A verb is an action word. Sort the nouns and verbs by using the key below to shade in the correct color. ...
... Directions: A noun is a person, place, or thing. A verb is an action word. Sort the nouns and verbs by using the key below to shade in the correct color. ...
final ify ize dead ate en sign poster character person I will see you in
... 1-2. (W5:1. Sp 6:11) The suffixes ate, ify, en, ize ,or ise, can be added to some nouns to turn them into verbs. There may be a slight change of spelling to the root word (pollen-pollinate) or the final letter might need to be dropped before adding the suffix (note-notify). ...
... 1-2. (W5:1. Sp 6:11) The suffixes ate, ify, en, ize ,or ise, can be added to some nouns to turn them into verbs. There may be a slight change of spelling to the root word (pollen-pollinate) or the final letter might need to be dropped before adding the suffix (note-notify). ...
REV Grammar Handout
... Misplaced Modifier: a modifier that is placed far from the word it modifies, a modifier whose placement changes the meaning of a sentence, or a split infinitive (437-38) Dangling Modifier: a phrase or clause (often using “-ed” or “-ing”) that is not correctly attached to the object it describes (438 ...
... Misplaced Modifier: a modifier that is placed far from the word it modifies, a modifier whose placement changes the meaning of a sentence, or a split infinitive (437-38) Dangling Modifier: a phrase or clause (often using “-ed” or “-ing”) that is not correctly attached to the object it describes (438 ...
Modern Greek grammar

The grammar of Standard Modern Greek, as spoken in present-day Greece and Cyprus, is basically that of Demotic Greek, but it has also assimilated certain elements of Katharevousa, the archaic, learned variety of Greek imitating Classical Greek forms, which used to be the official language of Greece through much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Modern Greek grammar has preserved many features of Ancient Greek, but has also undergone changes in a similar direction as many other modern Indo-European languages, from more synthetic to more analytic structures.