* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GRAMMAR CHEAT SHEET VERBS An action verb shows action
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kagoshima verb conjugations wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
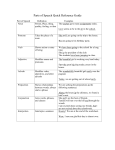
GRAMMAR CHEAT SHEET VERBS An action verb shows action. Example: She walked to the store. She ran to school. HELPING VERBS Helping verbs are used with action verbs. Example: She will walk to the store. (will is the helping verb; walk the verb) LIST OF HELPING VERBS: is was being am were been are be has have had do does did shall will should would may might must can could LINKING VERBS A linking verb expresses no action; the subject does not do anything and nothing is done to the subject. Example: This bread tastes good. Tastes is a linking verb, the bread is not tasting anything. MOST COMMON LINKING VERBS: is am are been become seem sound grow look was appear were feel be taste being smell NOUNS A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea PRONOUNS Pronouns are used to replace nouns. There are two cases of pronouns, nominative and objective. Nominative: I you he she we they who Polite order: you she/he/they I/we Objective: me you him her us them whom Polite order: you him/her/them me/us SUBJECTS A subject is what or whom the sentence is about. To find the subject, first find the verb then ask what or who about the verb to find the subject. Example: My mother went to the store. (the verb is went, then ask who, the mother went to the store, so the subject is mother) ADJECTIVES Adjectives describe nouns. They tell which one, what kind, how many, or whose about a noun. The articles a, an, and the are always adjectives. Example: Jamie’s three favorite blue shirts are dirty. whose how many which ones what kind ADVERBS Adverbs describe verbs, adverbs, or adjectives. They tell HOW, WHEN, WHERE about a verb and to WHAT EXTENT about an adjective or adverb. Example: [Yesterday], my dog ran [quickly] [down] the street. MOST COMMON ADVERBS: not so n’t very COMMON PREPOSITIONS: about among beneath above around beside across at besides after before between against behind beyond along below but too quite by concerning down during except for from in inside into like near rather somewhat of off on onto out outside over past since through to toward under until up upon with within without PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun. The last noun in a prepositional phrase is considered the object of the preposition (O.P.) CONJUNCTIONS A conjunction is a word that links words, phrases, or clauses. One way to remember conjunctions is to think of the acronym F A N B O Y S for and nor but or yet so UNDERLINGIN/ITALICS The following need to be underlined or in italics (italics is the same as underlining titles of books pamphlets TV shows software magazines long poems radio shows web sites musical compositions plays visual art newspapers films comic strips QUOTATIONS The following need to be placed in quotation marks: Titles of short works Short poems Chapters in books Songs One-act plays Articles Short stories Essays Titles or parts of larger works TV Episodes