Julius vs. Augustus
... • He ordered marble temples, theaters, public baths, and stadiums to be built in the Forum • New waterways were built called aqueducts • Police and fire protection • Taxes were used to improve the city and a census was ordered every five years to keep track of who paid and who didn’t ...
... • He ordered marble temples, theaters, public baths, and stadiums to be built in the Forum • New waterways were built called aqueducts • Police and fire protection • Taxes were used to improve the city and a census was ordered every five years to keep track of who paid and who didn’t ...
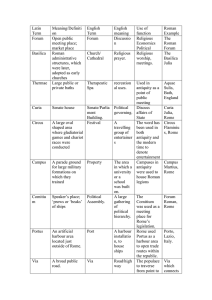
WH 1 Lesson 28 Instructional Resource 1
... He later took them both to Rome, where they were staying when he died ...
... He later took them both to Rome, where they were staying when he died ...
A.P. World History Rome Review Sheet Location/Geography
... - Rome successfully expanded into Greece, Anatolia (Turkey), Syria, Israel, and Egypt either through direct conquests or by making client-states. - As Rome’s power grew civil wars occurred, such as when the roman general and politician, Sulla, took Rome by military force and ruled as dictator. The F ...
... - Rome successfully expanded into Greece, Anatolia (Turkey), Syria, Israel, and Egypt either through direct conquests or by making client-states. - As Rome’s power grew civil wars occurred, such as when the roman general and politician, Sulla, took Rome by military force and ruled as dictator. The F ...
Name Jo Schmo Julius Caesar was born in 100 BC. He came from a
... In 65 BC Caesar got into politics. His job was organising public entertainment in Rome. Using his money he made sure that Rome had the best. There were great festivals and sports events. Because of this the public loved him. In 60 BC, Caesar entered into a political alliance with Crassus and Pompey ...
... In 65 BC Caesar got into politics. His job was organising public entertainment in Rome. Using his money he made sure that Rome had the best. There were great festivals and sports events. Because of this the public loved him. In 60 BC, Caesar entered into a political alliance with Crassus and Pompey ...
Julius Caesar - Oak Ridge High School
... class, descended from the original 100 founders of Rome ...
... class, descended from the original 100 founders of Rome ...
The Fall of the republic Glossary of key words
... Chief magistrates under the republic. Two elected each year, so that no one man would become two powerful. Performed the jobs the king had done, eg chief judge, chief general, head of state etc. ...
... Chief magistrates under the republic. Two elected each year, so that no one man would become two powerful. Performed the jobs the king had done, eg chief judge, chief general, head of state etc. ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Antony, and Marcus Lepidus defeated those who killed _______. Then they formed the Second Triumvirate and ________ up the Roman empire amongst themselves. It didn’t last long because Lepidus _______, and Antony and Octavian became _______. Antony married ___________________ but then they both killed ...
... Antony, and Marcus Lepidus defeated those who killed _______. Then they formed the Second Triumvirate and ________ up the Roman empire amongst themselves. It didn’t last long because Lepidus _______, and Antony and Octavian became _______. Antony married ___________________ but then they both killed ...
Ancient Rome Quiz 2 STUDY GUIDE
... 10.Who was given the name Augustus after he took power? Octavian 11.The Roman Empire spread over nearly all the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. 12.March 15, 44 B.C., the day Caesar was assassinated in the Senate, is also known as the Ides of March. Circle the best answer of the two choices ...
... 10.Who was given the name Augustus after he took power? Octavian 11.The Roman Empire spread over nearly all the lands surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. 12.March 15, 44 B.C., the day Caesar was assassinated in the Senate, is also known as the Ides of March. Circle the best answer of the two choices ...
Presentazione standard di PowerPoint
... The amphitheater was built on a site just east of the Roman Forum. Its construction was begun by Vespasian in 72 AD and it was inaugurated by Titus in 80, with further modifications being made during Domitian's reign. No longer in use after the sixth century, the huge structure was reused in variou ...
... The amphitheater was built on a site just east of the Roman Forum. Its construction was begun by Vespasian in 72 AD and it was inaugurated by Titus in 80, with further modifications being made during Domitian's reign. No longer in use after the sixth century, the huge structure was reused in variou ...
Quick Trip Through Roman History!
... • Cincinnatus was a farmer who was called to serve as dictator during an early Roman war. • He remained dictator only for 16 days, until the war was over---then resigned the dictatorship to go back to farming. • He was a role model of civic duty! ...
... • Cincinnatus was a farmer who was called to serve as dictator during an early Roman war. • He remained dictator only for 16 days, until the war was over---then resigned the dictatorship to go back to farming. • He was a role model of civic duty! ...
William Shakespeare`s The Tragedy of Julius Caesar Act II
... Using the pathfinders and helpful websites, please research the following information about ancient Rome. In your lesson, you will address this historical content and explain/analyze the historical accuracy of Shakespeare’s tragedy. Research the following: 1. What are the origins of the Roman Senate ...
... Using the pathfinders and helpful websites, please research the following information about ancient Rome. In your lesson, you will address this historical content and explain/analyze the historical accuracy of Shakespeare’s tragedy. Research the following: 1. What are the origins of the Roman Senate ...
HIST-UA 105 (= CLASS-UA 267) The History of the Roman Republic
... In the sixth century B.C., Rome was an obscure village. By the end of the fourth century B.C., Rome was master of Italy; by the end of the third century, it was the dominant power in the Western Mediterranean. Within another 150 years, Rome had taken control of the entire Mediterranean world, as wel ...
... In the sixth century B.C., Rome was an obscure village. By the end of the fourth century B.C., Rome was master of Italy; by the end of the third century, it was the dominant power in the Western Mediterranean. Within another 150 years, Rome had taken control of the entire Mediterranean world, as wel ...
Stage 28: Imperium - Mrs. Allgood's Latin Class
... The forum was between two of Rome’s hills, the Capitoline and the Palatine Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus was on the Capitoline, as the center of the Roman state religion. The Emperor came to pray for the safety of the Roman people, and consuls took their vows on January 1st at the beginning of t ...
... The forum was between two of Rome’s hills, the Capitoline and the Palatine Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus was on the Capitoline, as the center of the Roman state religion. The Emperor came to pray for the safety of the Roman people, and consuls took their vows on January 1st at the beginning of t ...
Fall of the Roman Republic
... to be not from old senatorial families. The Senate was jealous of the power of these generals, and didn’t want to share land Soldiers who didn’t own any land with their landless soldiers. It were taken into the army, and after refused to give Pompey’s fighting for several years, they came veterans a ...
... to be not from old senatorial families. The Senate was jealous of the power of these generals, and didn’t want to share land Soldiers who didn’t own any land with their landless soldiers. It were taken into the army, and after refused to give Pompey’s fighting for several years, they came veterans a ...