File - Science
... This level of classification is more specific than domain, but less specific than phylum. ...
... This level of classification is more specific than domain, but less specific than phylum. ...
KINGDOMS AND CLASSIFICATION pp. 337
... naming and grouping organisms according to characteristics and evolutionary history ...
... naming and grouping organisms according to characteristics and evolutionary history ...
Q4 Describe the factors that affect the flux of
... Acid base status à in acidaemia, upregulation of the K/H+ antiporter occurs (pumping H+ into cell and K+ out of cell). Reduced activity of the Na/K ATPase may also occur Osmolality à cellular dehyd ...
... Acid base status à in acidaemia, upregulation of the K/H+ antiporter occurs (pumping H+ into cell and K+ out of cell). Reduced activity of the Na/K ATPase may also occur Osmolality à cellular dehyd ...
A1987G155900001
... stimulate the AlP-driven H + pump of the plasma membrane, whereas its effects on solute transport, cell enlargement, transpiration, and seed germination would all be consequences of this primary activation of the proton pump. This scheme fit in beautifully with the view, rapidly developing in animal ...
... stimulate the AlP-driven H + pump of the plasma membrane, whereas its effects on solute transport, cell enlargement, transpiration, and seed germination would all be consequences of this primary activation of the proton pump. This scheme fit in beautifully with the view, rapidly developing in animal ...
research abstract form
... Transforming Growth Factor (TGFβ) superfamily, bind the BMP receptor (BMPR) complex on the surface of the cell. Intracellular signaling is then transmitted primarily through the Smad-dependant and other pathways. Mutations in BMPRII (one of two subunits of the BMP receptor) have been found in a perc ...
... Transforming Growth Factor (TGFβ) superfamily, bind the BMP receptor (BMPR) complex on the surface of the cell. Intracellular signaling is then transmitted primarily through the Smad-dependant and other pathways. Mutations in BMPRII (one of two subunits of the BMP receptor) have been found in a perc ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Comparison of the GLA containing zymogens. The figure shows basic structural elements of the GLA-containing zymogens. Each circle is an amino acid. The prepro leader sequence contains the signal peptide, as well as elements that direct carboxylation of glutamyl residues. Cleavage of the leader seque ...
... Comparison of the GLA containing zymogens. The figure shows basic structural elements of the GLA-containing zymogens. Each circle is an amino acid. The prepro leader sequence contains the signal peptide, as well as elements that direct carboxylation of glutamyl residues. Cleavage of the leader seque ...
Abstract - WSU Horticulture
... mutants were drastically compromised in their affinity to calmodulin (CaM), but our unpublished data indicated that the synthetic-peptides corresponding to the mutated CaM-binding domains were able to interact with CaM. These results led us to hypothesize that there is an intramolecular interaction ...
... mutants were drastically compromised in their affinity to calmodulin (CaM), but our unpublished data indicated that the synthetic-peptides corresponding to the mutated CaM-binding domains were able to interact with CaM. These results led us to hypothesize that there is an intramolecular interaction ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... acids of groups 1a and 2a such as Na⫹ and Ca2⫹, which form ionic bonds with hard Lewis bases, for example the oxygen of protein carboxylates. The metalloids As(III) and Sb(III) of group 5a have properties similar to those of soft Lewis acids. For the purposes of this review, alkali and alkaline eart ...
... acids of groups 1a and 2a such as Na⫹ and Ca2⫹, which form ionic bonds with hard Lewis bases, for example the oxygen of protein carboxylates. The metalloids As(III) and Sb(III) of group 5a have properties similar to those of soft Lewis acids. For the purposes of this review, alkali and alkaline eart ...
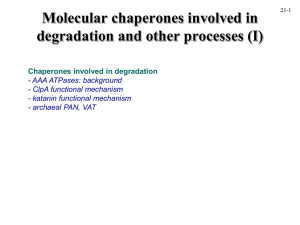
lecture 21
... them into the ‘folding chamber’ AAA ATPases undergo conformational changes upon nucleotide binding/hydrolysis (whether it’s simply binding or hydrolysis may differ between different proteins and is a topic of debate) ...
... them into the ‘folding chamber’ AAA ATPases undergo conformational changes upon nucleotide binding/hydrolysis (whether it’s simply binding or hydrolysis may differ between different proteins and is a topic of debate) ...
Chapter 11: Membrane transport
... Many proteins use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to fuel transport. (2) V-type ATPase Multimeric transporters often work in the reverse direction (ATP synthesis) F1Fo ATPase is the mitochondrial ATP synthase H+-ATPase of lysosomes acidify the organelle ...
... Many proteins use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to fuel transport. (2) V-type ATPase Multimeric transporters often work in the reverse direction (ATP synthesis) F1Fo ATPase is the mitochondrial ATP synthase H+-ATPase of lysosomes acidify the organelle ...
Study Guide for cell structure, membrane transport
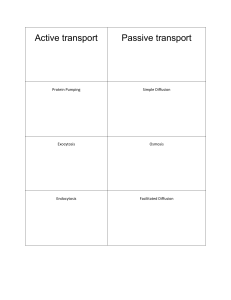
... Review the structure of a plasma membrane with attention paid to the role of proteins in the membrane Identify what type of substances can pass through membranes under certain circumstances Differentiate between passive and active transport Define concentration gradient, solute, solvent Describe dif ...
... Review the structure of a plasma membrane with attention paid to the role of proteins in the membrane Identify what type of substances can pass through membranes under certain circumstances Differentiate between passive and active transport Define concentration gradient, solute, solvent Describe dif ...
Document
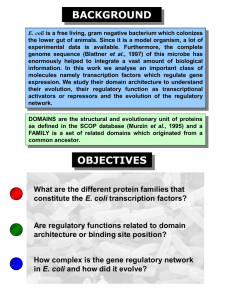
... enormously helped to integrate a vast amount of biological information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional ...
... enormously helped to integrate a vast amount of biological information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional ...
Cell and Molecular Biology 5/e
... plant and animal steroids Ouabain! Digitalis!: increased Na+ conc inside heart leads to stimulation of Na+Ca2+ exchanger, which extrudes sodium in exchange for inward movement of calcium. Increased intracellular Calcium stimulates muscle contraction. ...
... plant and animal steroids Ouabain! Digitalis!: increased Na+ conc inside heart leads to stimulation of Na+Ca2+ exchanger, which extrudes sodium in exchange for inward movement of calcium. Increased intracellular Calcium stimulates muscle contraction. ...
Structural domains of P450-containing monooxygenase
... [email protected] All known P450-containing monooxygenase systems share common structural and functional domain architecture. Apart from P450 itself, these systems can comprise several fundamentally different protein components or domains, all of which are shared by other multicomponent/multido ...
... [email protected] All known P450-containing monooxygenase systems share common structural and functional domain architecture. Apart from P450 itself, these systems can comprise several fundamentally different protein components or domains, all of which are shared by other multicomponent/multido ...
Identification and Characterization of a Novel, Isoform-Specific Phosphorylation
... In vertebrates collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs) form a class of cytosolic phosphoproteins composed of five isoforms, CRMP1-5. This class of proteins has been most readily described with their involvement in Semaphorin 3A signaling, resulting in growth cone collapse of migratory neurons. ...
... In vertebrates collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs) form a class of cytosolic phosphoproteins composed of five isoforms, CRMP1-5. This class of proteins has been most readily described with their involvement in Semaphorin 3A signaling, resulting in growth cone collapse of migratory neurons. ...
can bioimaging show the connection
... nutrient and gravity sensing, and protein sorting [1-4]. Many elements of the secretory machinery in animals and plants are still lacking or are poorly characterized [5-6]. In the past years, more and more evidence is accumulating suggesting the involvement of a subfamily of P-type ATPases in vesicl ...
... nutrient and gravity sensing, and protein sorting [1-4]. Many elements of the secretory machinery in animals and plants are still lacking or are poorly characterized [5-6]. In the past years, more and more evidence is accumulating suggesting the involvement of a subfamily of P-type ATPases in vesicl ...
active transport by pumps- abc transporter, symports
... The pump, with bound ATP, binds 3 intracellular Na+ ions. ATP is hydrolyzed, leading to phosphorylation of the pump at a highly conserved aspartate residue and subsequent release of ADP. A conformational change in the pump exposes the Na+ ions to the outside. The phosphorylated form of the pump has ...
... The pump, with bound ATP, binds 3 intracellular Na+ ions. ATP is hydrolyzed, leading to phosphorylation of the pump at a highly conserved aspartate residue and subsequent release of ADP. A conformational change in the pump exposes the Na+ ions to the outside. The phosphorylated form of the pump has ...
Apyrase from potato (A6237) - Datasheet - Sigma
... ATP diphosphohydrolase, ADP diphosphohydrolase, Adenosine 5′-diphosphatase, Adenosine 5′-triphosphatase Product Description A large number of plant and animal tissues contain pyrophosphohydrolases commonly called apyrases. These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of a broad range of nucleoside tri- and ...
... ATP diphosphohydrolase, ADP diphosphohydrolase, Adenosine 5′-diphosphatase, Adenosine 5′-triphosphatase Product Description A large number of plant and animal tissues contain pyrophosphohydrolases commonly called apyrases. These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of a broad range of nucleoside tri- and ...
Transport
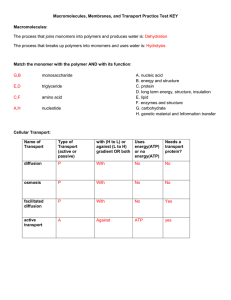
... o Facilitated diffusion requires a protein carrier or channel Active transport o Energy in the form of ATP is required o Movement from low to high areas of concentration o Examples are: 1. Primary active transport Phosphorylation occurs (from ATP hydrolysis)- to transport protein allowing it to ...
... o Facilitated diffusion requires a protein carrier or channel Active transport o Energy in the form of ATP is required o Movement from low to high areas of concentration o Examples are: 1. Primary active transport Phosphorylation occurs (from ATP hydrolysis)- to transport protein allowing it to ...
Wilson`s disease and the copper ATPase transporters
... of information on protein families and domains. Examining the database, information on the Wilson’s disease protein and its homologues can be found in InterPro entries IPR001757 and its child entry IPR027256 (Table 1). From the description of IPR001757 , we know that ATP7B belongs to a broad family ...
... of information on protein families and domains. Examining the database, information on the Wilson’s disease protein and its homologues can be found in InterPro entries IPR001757 and its child entry IPR027256 (Table 1). From the description of IPR001757 , we know that ATP7B belongs to a broad family ...
P-type ATPase

The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are α-helical bundle primary transporters referred to as P-type ATPases because they catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump. In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2.Most members of this transporter family are specific for the pumping of a large array of cations, however one subfamily is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane.Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase), the plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase), the proton-potassium pump (H+,K+-ATPase), and the calcium pump (Ca2+-ATPase).