Cyanovirin-N
... • Macaques that did develop the infection likely subjected to vaginal trauma during procedure. • Results suggest that CV-N is a promising agent as a topical vaginal microbicide for the prevention of sexual transmission of HIV infection. ...
... • Macaques that did develop the infection likely subjected to vaginal trauma during procedure. • Results suggest that CV-N is a promising agent as a topical vaginal microbicide for the prevention of sexual transmission of HIV infection. ...
Membrane channels and pumps
... µ’ = µ0 + RT ln c’ + zF!’ µ’’ = µ0 + RT ln c’’ + zF!’’ "G = µ’’ - µ’ = RT ln c’’/c’ + zF (!’’ - !’) "G > 0 active transport "G < 0 passive transport ...
... µ’ = µ0 + RT ln c’ + zF!’ µ’’ = µ0 + RT ln c’’ + zF!’’ "G = µ’’ - µ’ = RT ln c’’/c’ + zF (!’’ - !’) "G > 0 active transport "G < 0 passive transport ...
Name: Date: Kingdoms and Domains – Section 15.4 Worksheet The
... 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The scientific view of life was more complex in Linnaeus’s time. _____________________ 2. What fundamental traits did Linnaeus use to separate plants from animals? _____________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The scientific view of life was more complex in Linnaeus’s time. _____________________ 2. What fundamental traits did Linnaeus use to separate plants from animals? _____________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
Another way ……
... In the transmembrane helices, the majority of the missing side chains face the lipid environment. The loss of electron density occurs just above the ligand-binding site, near the predicted lipid-water interface, suggesting that ligand binding and/or the lipid environment contributes to the order of ...
... In the transmembrane helices, the majority of the missing side chains face the lipid environment. The loss of electron density occurs just above the ligand-binding site, near the predicted lipid-water interface, suggesting that ligand binding and/or the lipid environment contributes to the order of ...
Classification of Organisms - Illini West High School Dist
... species – Phylogenetic Diagram (phylogenetic tree) • Looks like a family tree and has branching pattern that indicates how closely related subset taxa are thought to be ...
... species – Phylogenetic Diagram (phylogenetic tree) • Looks like a family tree and has branching pattern that indicates how closely related subset taxa are thought to be ...
HSC70 (Hsp73) Protein (active) Catalog# SPR
... peptides (3). When hsc70 (constitutively expressed) present in mammalian cells was truncated, ATP binding activity was found to reside in an N-terminal fragment of 44 kDa which lacked peptide binding capacity. Polypeptide binding ability therefore resided within the C-terminal half (4). The structur ...
... peptides (3). When hsc70 (constitutively expressed) present in mammalian cells was truncated, ATP binding activity was found to reside in an N-terminal fragment of 44 kDa which lacked peptide binding capacity. Polypeptide binding ability therefore resided within the C-terminal half (4). The structur ...
Membrane Transport
... • Inhibit growth of other bacteria (even other strains of E. coli) • Single colicin molecule can kill a host! ...
... • Inhibit growth of other bacteria (even other strains of E. coli) • Single colicin molecule can kill a host! ...
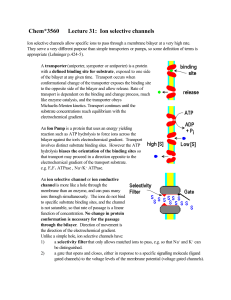
Chem*3560 Lecture 31: Ion selective channels
... where the hydration layer must be stripped off. The channel provides ligands to substitute for the H2 O coordination shell, and these ligands are spaced to match a specific ionic radius. If the ion is too large, it clearly won't fit, e.g. K+ (radius 1.33 Å) in a Na+ (radius 0.95 Å) specific channel. ...
... where the hydration layer must be stripped off. The channel provides ligands to substitute for the H2 O coordination shell, and these ligands are spaced to match a specific ionic radius. If the ion is too large, it clearly won't fit, e.g. K+ (radius 1.33 Å) in a Na+ (radius 0.95 Å) specific channel. ...
Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... transporter (Yernool, et al., 2004). The X-ray data indicate a trimeric structure. (A) A view of the trimer extracellularly and perpendicular to the bilayer. (B) A view from the bilayer plane. The trimer forms a deep bowl that allows extracellular solutes to access the extracellular glutamate-bindin ...
... transporter (Yernool, et al., 2004). The X-ray data indicate a trimeric structure. (A) A view of the trimer extracellularly and perpendicular to the bilayer. (B) A view from the bilayer plane. The trimer forms a deep bowl that allows extracellular solutes to access the extracellular glutamate-bindin ...
Cellopolis WS
... 5. The following organelles were not shown in the diagram of Cellopolis. Give the name of a city structure that could have been included in the picture that would represent the functions of each of these parts. a. Pili - __________________________________________________________________ b. Cell memb ...
... 5. The following organelles were not shown in the diagram of Cellopolis. Give the name of a city structure that could have been included in the picture that would represent the functions of each of these parts. a. Pili - __________________________________________________________________ b. Cell memb ...
Learning Objectives Chapter 3 Human Biology
... Active vs passive transport Diffusion and Osmosis, Bulk transport (endocytosis and Exocytosis) Tonicity Learn all the eukaryotic animal cell organelles (including the membrane and the cytoplasm, structure and function Aerobic Respiration: You should be able to give a thorough accurate and detailed ...
... Active vs passive transport Diffusion and Osmosis, Bulk transport (endocytosis and Exocytosis) Tonicity Learn all the eukaryotic animal cell organelles (including the membrane and the cytoplasm, structure and function Aerobic Respiration: You should be able to give a thorough accurate and detailed ...
Integral membrane proteins and free electron lasers
... The first integral membrane protein X-ray crystal structure was solved in 1985 (Deisenhofer et al., 1985). Thirty years later, they remain a frontier of structural biology, and an area of intense fundamental and practical interest. The structural and functional bases of many critical biological proc ...
... The first integral membrane protein X-ray crystal structure was solved in 1985 (Deisenhofer et al., 1985). Thirty years later, they remain a frontier of structural biology, and an area of intense fundamental and practical interest. The structural and functional bases of many critical biological proc ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... indicated: serines with a pink spot, threonines with a blue spot, and lysines with a green spot and cysteines with an orange spot. For Homo sapiens, it is also indicated the position in the sequence and the type of post-translational modification P=phosphorylation, A=acetylation, R=changing of the r ...
... indicated: serines with a pink spot, threonines with a blue spot, and lysines with a green spot and cysteines with an orange spot. For Homo sapiens, it is also indicated the position in the sequence and the type of post-translational modification P=phosphorylation, A=acetylation, R=changing of the r ...
Oct_7
... Different types of membrane lipids (we talked about this last time) [ chart of Phospholipid composition of organelles ] o Note that sphingomyelin high in plasma membrane [ Inner / Outer membranes - curvature stress - phosphatidyl choline, big methyl group on outer membranes. Which ones on the insi ...
... Different types of membrane lipids (we talked about this last time) [ chart of Phospholipid composition of organelles ] o Note that sphingomyelin high in plasma membrane [ Inner / Outer membranes - curvature stress - phosphatidyl choline, big methyl group on outer membranes. Which ones on the insi ...
Functional domains of the BRCA2 protein
... Published in Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine by Cambridge University Press (2001) ...
... Published in Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine by Cambridge University Press (2001) ...
Leukaemia Section t(4;12)(p16;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... lympthoma with a t(4;12)(p16;p13) chromosomal translocation. ...
... lympthoma with a t(4;12)(p16;p13) chromosomal translocation. ...
August 24, 2010 Dr. Cynthia Smas Distinguish the major kinetic
... 4. Describe how the Na/K ATPase primary active transporter functions to drive secondary active transport of glucose. Understand the concept of symporters and antiporters a. Cells must maintain electrochemical gradients to function b. Na/K ATPase pumps use ATP to pump Na and K each against their esta ...
... 4. Describe how the Na/K ATPase primary active transporter functions to drive secondary active transport of glucose. Understand the concept of symporters and antiporters a. Cells must maintain electrochemical gradients to function b. Na/K ATPase pumps use ATP to pump Na and K each against their esta ...
Analyses of the Regulatory Mechanisms of Tankyrase and Its Role
... proteins by adding one or a polymer chain of the ADP-ribose group. This modification regulates various aspects of many proteins, including their biological activity and destruction. Through this modification, tankyrase controls several important cellular processes such as cell proliferation and telo ...
... proteins by adding one or a polymer chain of the ADP-ribose group. This modification regulates various aspects of many proteins, including their biological activity and destruction. Through this modification, tankyrase controls several important cellular processes such as cell proliferation and telo ...
CLASS COPY Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice
... Type of Transport (active or passive) ...
... Type of Transport (active or passive) ...
P-type ATPase

The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are α-helical bundle primary transporters referred to as P-type ATPases because they catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump. In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2.Most members of this transporter family are specific for the pumping of a large array of cations, however one subfamily is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane.Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase), the plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase), the proton-potassium pump (H+,K+-ATPase), and the calcium pump (Ca2+-ATPase).