* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C9. Metal ions in biological systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
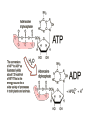
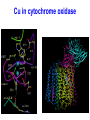
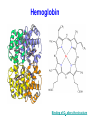
C9. Metal ions in biological systems April 4th General • Many metal ions have role in biological processes of the body • The ions have different physical and chemical properties – Charge density – Complex formation – Oxidation states • Minerals in food The most important ions • • • • • • • • • Ion Ca2+ Mg2+ Fe2+ Cu2+ Zn2+ Co3+ Na+ K+ • • • • • • • • Role: 1.5-2% of body mass, bones, teeth Bones and teeth, intracellular activity Hemoglobin, O2 transfer Cofactor in enzymes Cofactor in enzymes,growth, healing In vitamin B12 Water balance, nerve impulses, fluids inside and outside cells ATP = adenosine triphosphate • A nucleotide (ribose sugar, adenine base and three phosphate groups) • Energy currency of the cell, providing the energy for most of the energy-consuming activities • It regulates many biochemical pathways ATP as energy source • • • • • The exothermic reaction is (hydrolysis): ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + E ADP is adenosine diphosphate Pi is phosphate group, HOPO32Reversible process Na+/K+ pump • Found in membranes of cells. • Produces electrical and chemical gradient across a cell membrane. • It plays a very important role in nerve cell membranes. • Transmission of nerve impulses. • Channel = tunnel-like trans membrane protein: Na+-K+ ATPase • K+ inside a cell • Na+ outside a cell • Cell surface membranes pump Na+ ions out of cell and K+ in. Na+/K+ pump • The pump requires energy: • ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + E • With 1 mol ATP: • 3 mol of Na+ and 2 mol of K+ pumped out/in • Animation Electron transport • Energy from food is released through many redox reactions (mitochondria) • Transition metals have many oxidation states. • => They can carry charges. • Cytochromes are oxidizing enzymes. • Contain copper or iron as cofactors. • Cu2+ + e– ↔ Cu+; Fe3+ + e– ↔ Fe2+ • Animation Cu in cytochrome oxidase Hemoglobin as oxygen carrier • In each hemoglobin molecule there are four heme groups • Heme = Fe2+ surrounded by phorphyrin group, four N act as ligands. • As O2 carrier: O2 binds to Fe2+ as a ligand • Reversible process • CO and CN– bind irreversible to Fe2+ Hemoglobin Binding of O2 alters the structure