Aldehydes and ketones
... Explain why Tollens reagent can be used to distinguish an aldehyde from either an alcohol or a ketone? ...
... Explain why Tollens reagent can be used to distinguish an aldehyde from either an alcohol or a ketone? ...
effective: september 2003 curriculum guidelines
... Upon completion of this course, the students will be able to: 1. given the formula, I.R., U.V., mass spect., 1H and 13C N.M.R.’s of an unknown organic compound, be able to determine the structure of that unknown. 2. given the structural formula of an organic compound, be able to predict the number o ...
... Upon completion of this course, the students will be able to: 1. given the formula, I.R., U.V., mass spect., 1H and 13C N.M.R.’s of an unknown organic compound, be able to determine the structure of that unknown. 2. given the structural formula of an organic compound, be able to predict the number o ...
Chem 322 Exam 2 April 16, 2012 /100 Name Please do the easiest
... c. (3) Explain why different paths are followed. In (a) there are no good leaving groups on the carbonyl C, so we have a simple addition to it. In (b) there is a good LG, so we see a nucleophilic addition followed by an elimination. Thus the first step of this reaction looks like a substitution. ...
... c. (3) Explain why different paths are followed. In (a) there are no good leaving groups on the carbonyl C, so we have a simple addition to it. In (b) there is a good LG, so we see a nucleophilic addition followed by an elimination. Thus the first step of this reaction looks like a substitution. ...
Dehydration notes
... • Major product based on Zaitsevs rule? • Role of all chemicals added during extraction work up? ...
... • Major product based on Zaitsevs rule? • Role of all chemicals added during extraction work up? ...
Polyesters are condensation polymers.
... Note that sometimes other molecules (HCl for eg) are lost in other condensation reactions. It is the elimination of a molecule which makes it a condensation reaction, not the loss of water. ...
... Note that sometimes other molecules (HCl for eg) are lost in other condensation reactions. It is the elimination of a molecule which makes it a condensation reaction, not the loss of water. ...
Chapter 6: Alkynes, reactions of alkynes, and multistep synthesis
... 3. if 2 triple bonds, diyne a. if 3 trple bonds, triyne b. if 4, tetrayne, then pentayne, hexayne, heptayne, etc 4. with number (#) as prefix a. funct grp has priority with numbering 5. if more than 1 subst., place all in alphabetical order in front 6. if counting from either end is tie in yne #, us ...
... 3. if 2 triple bonds, diyne a. if 3 trple bonds, triyne b. if 4, tetrayne, then pentayne, hexayne, heptayne, etc 4. with number (#) as prefix a. funct grp has priority with numbering 5. if more than 1 subst., place all in alphabetical order in front 6. if counting from either end is tie in yne #, us ...
Alcohols
... aldehyde. State what you would observe in the test. Reagent ............................................................................................................. ...
... aldehyde. State what you would observe in the test. Reagent ............................................................................................................. ...
2.10 Assessed Homework Task - A
... aldehyde. State what you would observe in the test. Reagent ............................................................................................................. ...
... aldehyde. State what you would observe in the test. Reagent ............................................................................................................. ...
4.6, 4.7 test - A
... Suggest one reason why phenylamine cannot be prepared from bromobenzene in a similar way. Outline a synthesis of phenylamine from benzene. In your answer you should give reagents and conditions for each step, but equations and mechanisms are not required. ...
... Suggest one reason why phenylamine cannot be prepared from bromobenzene in a similar way. Outline a synthesis of phenylamine from benzene. In your answer you should give reagents and conditions for each step, but equations and mechanisms are not required. ...
MULTISTEP SYNTHESIS PROTECTING GROUPS
... Notice that the amide group is carried all the way through the synthesis. It is not modified into amine until the very end, when the final step is reached. The question then is, why not start the synthesis with an amine group in the first place? The amide group can be thought of as a protected amine ...
... Notice that the amide group is carried all the way through the synthesis. It is not modified into amine until the very end, when the final step is reached. The question then is, why not start the synthesis with an amine group in the first place? The amide group can be thought of as a protected amine ...
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Epoxides
... aromatic ring has been converted into an epoxide. What happens to aromatic compounds when they enter the body as a foreign substance (such as cigarette smoke, drugs, charcoalbroiled meats or automobile exhaust)? ...
... aromatic ring has been converted into an epoxide. What happens to aromatic compounds when they enter the body as a foreign substance (such as cigarette smoke, drugs, charcoalbroiled meats or automobile exhaust)? ...
Alkene Addition Reactions
... The shifting group migrates with its pair of electrons therefore the name hydride (H-‐) or methide (CH3-‐). The order of migrating groups is H > CH3. Alcohols can be produced by addition of ...
... The shifting group migrates with its pair of electrons therefore the name hydride (H-‐) or methide (CH3-‐). The order of migrating groups is H > CH3. Alcohols can be produced by addition of ...
Microsoft Word
... Despite the significance of the nitrileoxide cycloaddition reaciton a tool for the versatile synthesis of substituted isoxazolines, its actual application for the preparation of spiroxazolines has been limited. High synthetic utility of the isoxazoline moiety and the biological significance due to t ...
... Despite the significance of the nitrileoxide cycloaddition reaciton a tool for the versatile synthesis of substituted isoxazolines, its actual application for the preparation of spiroxazolines has been limited. High synthetic utility of the isoxazoline moiety and the biological significance due to t ...
delhi private school
... Q11. How will you distinguish between the following: 3 marks (i) Propanoic acid and propanal (ii) Ethanal and Benzaldehyde (iii) Pentan-3-one and Pentan-2-one Q12. How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps. (a) Propanone to Propene (b) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophen ...
... Q11. How will you distinguish between the following: 3 marks (i) Propanoic acid and propanal (ii) Ethanal and Benzaldehyde (iii) Pentan-3-one and Pentan-2-one Q12. How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps. (a) Propanone to Propene (b) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophen ...
4.5 Topic Checklist Carbonyl Compounds
... appreciate the hazards of synthesis using HCN/KCN know that aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols using reducing agents such as NaBH4. Mechanisms showing H– are required (equations showing [H] as reductant are acceptable) understand the mechanism of the react ...
... appreciate the hazards of synthesis using HCN/KCN know that aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols using reducing agents such as NaBH4. Mechanisms showing H– are required (equations showing [H] as reductant are acceptable) understand the mechanism of the react ...
orgchem rev integ odd numbers
... t-BuOK, t-BuOH – Bulky bases Bulky bases as catalysts follows Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule – is an empirical rule for predicting the favored alkene products in elimination reactions. Attachment to the least substituted Carbon ...
... t-BuOK, t-BuOH – Bulky bases Bulky bases as catalysts follows Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule Anti-Zaitsev’s Rule – is an empirical rule for predicting the favored alkene products in elimination reactions. Attachment to the least substituted Carbon ...
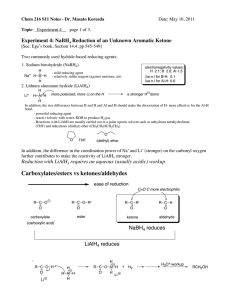
Carboxylates/esters vs ketones/aldehydes
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
2009_outline_4
... I. Structure and Nomenclature - The Acyl Group A. Acids - RCOOH B. Acid Halides - RCOX C. Anhydrides - (RCO)2O ...
... I. Structure and Nomenclature - The Acyl Group A. Acids - RCOOH B. Acid Halides - RCOX C. Anhydrides - (RCO)2O ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... HCl, which is often troublesome. A more practical variation is to add a weak base such as pyridine to react with the HCl and neutralize it. This gives us a procedure for making esters from acyl chlorides which uses the following reaction statement: ...
... HCl, which is often troublesome. A more practical variation is to add a weak base such as pyridine to react with the HCl and neutralize it. This gives us a procedure for making esters from acyl chlorides which uses the following reaction statement: ...
Wolff rearrangement

The Wolff rearrangement is a reaction in organic chemistry in which an α-diazocarbonyl compound is converted into a ketene by loss of dinitrogen with accompanying 1,2-rearrangement. The Wolff rearrangement yields a ketene as an intermediate product, which can undergo nucleophilic attack with weakly acidic nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, and amines, to generate carboxylic acid derivatives or undergo [2+2] cycloaddition reactions to form four-membered rings. The mechanism of the Wolff rearrangement has been the subject of debate since its first use. No single mechanism sufficiently describes the reaction, and there are often competing concerted and carbene-mediated pathways; for simplicity, only the textbook, concerted mechanism is shown below. The reaction was discovered by Ludwig Wolff in 1902. The Wolff rearrangement has great synthetic utility due to the accessibility of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, variety of reactions from the ketene intermediate, and stereochemical retention of the migrating group. However, the Wolff rearrangement has limitations due to the highly reactive nature of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, which can undergo a variety of competing reactions.The Wolff rearrangement can be induced via thermolysis, photolysis, or transition metal catalysis. In this last case, the reaction is sensitive to the transition metal; silver (I) oxide or other Ag(I) catalysts work well and are generally used. The Wolff rearrangement has been used in many total syntheses; the most common use is trapping the ketene intermediate with nucleophiles to form carboxylic acid derivatives. The Arndt-Eistert homologation is a specific example of this use, wherein a carboxylic acid may be elongated by a methylene unit. Another common use is in ring-contraction methods; if the α-diazo ketone is cyclic, the Wolff rearrangement results in a ring-contracted product. The Wolff rearrangement works well in generating ring-strained systems, where other reactions may fail.