Chemistry Test: Transmutation Multiple Choice 1. Identify the new
... b. undergo nuclear fission. d. react chemically. Which statement is true about half-lives? a. Different atoms of the same nuclide have different half-lives. b. Each radioactive isotope has its own half-life. c. All radioactive nuclides of an element have the same half-life. d. All radioactive nuclid ...
... b. undergo nuclear fission. d. react chemically. Which statement is true about half-lives? a. Different atoms of the same nuclide have different half-lives. b. Each radioactive isotope has its own half-life. c. All radioactive nuclides of an element have the same half-life. d. All radioactive nuclid ...
entc 4390 medical imaging
... •But protons repel one another (Coulomb Force) and when Z is large it becomes harder to put more protons into a nucleus without adding even more neutrons to provide more of the Strong Force. •For this reason, in heavier nuclei N>Z. ...
... •But protons repel one another (Coulomb Force) and when Z is large it becomes harder to put more protons into a nucleus without adding even more neutrons to provide more of the Strong Force. •For this reason, in heavier nuclei N>Z. ...
Unit 2 Overview
... experiments that lead to our current understanding of atomic structure. This unit is divided into three parts, the proton, the neutron, and the electron. In part one, we will take a closer look at how the number of protons is related to the identity of an element and how it played a critical role in ...
... experiments that lead to our current understanding of atomic structure. This unit is divided into three parts, the proton, the neutron, and the electron. In part one, we will take a closer look at how the number of protons is related to the identity of an element and how it played a critical role in ...
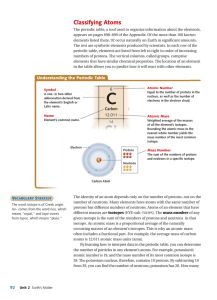
Classifying Atoms
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
Physical Science EOCT Review Notes
... If the atomic number for arsenic is 33 and the atomic mass is 75 then: How many protons does arsenic have? ...
... If the atomic number for arsenic is 33 and the atomic mass is 75 then: How many protons does arsenic have? ...
Atomic Structure
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
Chapter 29
... • These forces should cause the nucleus to fly apart • The nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range force, called the nuclear force • This is an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles • The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive for ...
... • These forces should cause the nucleus to fly apart • The nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range force, called the nuclear force • This is an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles • The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive for ...
Chapter 25 – Types of Radiation 1. Alpha Radiation Alpha decay
... Positron decay is the mirror image of beta decay and can be described as: a. Something inside the nucleus breaks down causing a proton to become a neutron. b. It emits a positron which goes zooming off. c. The atomic number goes down by one and the mass number remains unchanged. Here is a typical po ...
... Positron decay is the mirror image of beta decay and can be described as: a. Something inside the nucleus breaks down causing a proton to become a neutron. b. It emits a positron which goes zooming off. c. The atomic number goes down by one and the mass number remains unchanged. Here is a typical po ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... formed, plus neutrons are emitted these neutrons collide with other U-235 atoms, causing them to undergo fission; they release neutrons, and so on… ...
... formed, plus neutrons are emitted these neutrons collide with other U-235 atoms, causing them to undergo fission; they release neutrons, and so on… ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: __________________________________Due date: _____________________ SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of ...
... Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: __________________________________Due date: _____________________ SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
Scientists` Consensus Ideas Atomic Structure and Nuclear Interactions
... 13. Interactions involving the particles of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) are called nuclear reactions or nuclear interactions. Nuclear reactions release enormous quantities of energy compared to chemical reactions. 14. Some elements change into other elements as a result of nuclear reactions. Ph ...
... 13. Interactions involving the particles of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) are called nuclear reactions or nuclear interactions. Nuclear reactions release enormous quantities of energy compared to chemical reactions. 14. Some elements change into other elements as a result of nuclear reactions. Ph ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
... Atomic Mass Problems Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (19.8%, 10.013 amu) and boron 11 (80.2%, 11.009 amu). What is the atomic mass of boron? ...
NASC 1110
... Nuclear reactions are changes of elemental composition in atomic interactions. In chemical reactions atomic composition does not change. Elements lighter than Fe can be produced by fusion of 2 smaller nuclei. This is possible, because binding energy increases with atomic number. ...
... Nuclear reactions are changes of elemental composition in atomic interactions. In chemical reactions atomic composition does not change. Elements lighter than Fe can be produced by fusion of 2 smaller nuclei. This is possible, because binding energy increases with atomic number. ...
Atom Structure and Isotopes
... Videoclip #2 Questions 1) What is the atomic number? number of protons in the nucleus 2) What are isotopes? Atoms with the same number of protons, but a DIFFERENT number of neutrons. 3) How many protons and neutrons are in the following carbon isotopes? Carbon-12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 ...
... Videoclip #2 Questions 1) What is the atomic number? number of protons in the nucleus 2) What are isotopes? Atoms with the same number of protons, but a DIFFERENT number of neutrons. 3) How many protons and neutrons are in the following carbon isotopes? Carbon-12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 ...
Intro to Atoms Clicker Questions 1. "atomos" means? 2. Atoms of one
... 5. In Rutherford's Atomic model, the protons - positively charged particles are located where? 6. Rutherford's proof of the proton's location in the atom came from an experiment with _______ 7. In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons are arranged how? 8. A neutron has (a) _____ charge 9. (T/F) The ...
... 5. In Rutherford's Atomic model, the protons - positively charged particles are located where? 6. Rutherford's proof of the proton's location in the atom came from an experiment with _______ 7. In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons are arranged how? 8. A neutron has (a) _____ charge 9. (T/F) The ...
Radioactive Reactions
... Radioactive Reactions • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
... Radioactive Reactions • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
Atomic Models:
... – Rutherford said electrons travel in orbits like planetsproblem- electrons also emit energy and should spiral closer to the nucleus – Bohr- only certain orbits are possible – they gain and lose energy as they move from one orbital to another • Distiguished between protons and neutron while Rutherfo ...
... – Rutherford said electrons travel in orbits like planetsproblem- electrons also emit energy and should spiral closer to the nucleus – Bohr- only certain orbits are possible – they gain and lose energy as they move from one orbital to another • Distiguished between protons and neutron while Rutherfo ...
Energy per nucleon
... a black hole (> 3 solar masses) or a neutron star (between 1.4 and 3 solar masses), where the atoms collapse into a single huge nucleus. Lighter stars become white dwarfs . ...
... a black hole (> 3 solar masses) or a neutron star (between 1.4 and 3 solar masses), where the atoms collapse into a single huge nucleus. Lighter stars become white dwarfs . ...
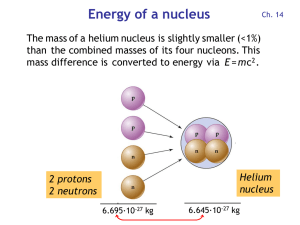
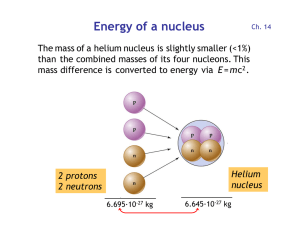
Energy of a nucleus
... a black hole (> 3 solar masses) or a neutron star (between 1.4 and 3 solar masses), where the atoms collapse into a single huge nucleus. Lighter stars become white dwarfs . • All elements heavier than iron/nickel are created during a supernova explosion, which has enough thermal energy to form nucle ...
... a black hole (> 3 solar masses) or a neutron star (between 1.4 and 3 solar masses), where the atoms collapse into a single huge nucleus. Lighter stars become white dwarfs . • All elements heavier than iron/nickel are created during a supernova explosion, which has enough thermal energy to form nucle ...
Chapter 30: Nuclear Physics What will we learn in this chapter?
... It does not depend on charge (both n and p are bound). It is strong enough to hold protons together, i.e., stronger than the electric force. It has a short range, on the order of 10-15 m. Why? Not all particles in the nucleus interact at a given point in time (saturation), unlike the electric forces ...
... It does not depend on charge (both n and p are bound). It is strong enough to hold protons together, i.e., stronger than the electric force. It has a short range, on the order of 10-15 m. Why? Not all particles in the nucleus interact at a given point in time (saturation), unlike the electric forces ...
PS 2.2
... the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table. Since it is an average, it is usually not a whole number. ...
... the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table. Since it is an average, it is usually not a whole number. ...