solutions - Physicsland
... nearly 2000 times the mass of an electron). Hence it bends very little compared to the much less massive beta particles (electrons). Gamma rays carry no electric charge and so are not affected by an electric field. 9. Gamma radiation produces not only the least change in mass and atomic numbers, but ...
... nearly 2000 times the mass of an electron). Hence it bends very little compared to the much less massive beta particles (electrons). Gamma rays carry no electric charge and so are not affected by an electric field. 9. Gamma radiation produces not only the least change in mass and atomic numbers, but ...
Atomic Structure
... following: Protons, neutrons, electrons, nucleus, electron cloud, any and all shells Write down the name, atomic number, atomic mass, and symbol ...
... following: Protons, neutrons, electrons, nucleus, electron cloud, any and all shells Write down the name, atomic number, atomic mass, and symbol ...
Atoms - Images
... 1.673 x 10-27 kg. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 x 10-27 kg. The mass of an electron is about 1836 times less than that of a proton, so they are usually neglected when calculating mass. ...
... 1.673 x 10-27 kg. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 x 10-27 kg. The mass of an electron is about 1836 times less than that of a proton, so they are usually neglected when calculating mass. ...
A. Highlights for Section 1 pages 83
... Classify three main subatomic particles o Proton In nucleus Positive charge 1 AMU o Neutron In nucleus No charge less than 1 AMU-smaller than proton o Electrons In orbit around nucleus Negative charge No mass (AMU) or very little Explain the structure o Atomic number=number of ...
... Classify three main subatomic particles o Proton In nucleus Positive charge 1 AMU o Neutron In nucleus No charge less than 1 AMU-smaller than proton o Electrons In orbit around nucleus Negative charge No mass (AMU) or very little Explain the structure o Atomic number=number of ...
20150930084161
... o What charge does a neutron have? o Where is the neutron located? o Who discovered the neutron? How do the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons compare? Know that atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. The atomic number tells you the number of what two subatomic ...
... o What charge does a neutron have? o Where is the neutron located? o Who discovered the neutron? How do the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons compare? Know that atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. The atomic number tells you the number of what two subatomic ...
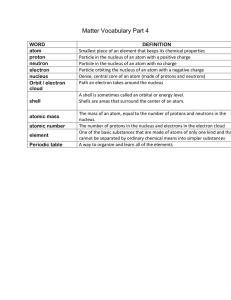
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
atoms - Trinity Regional School
... Mixture – 2 or more elements, compounds, or both physically combined. homogenous or heterogeneous ...
... Mixture – 2 or more elements, compounds, or both physically combined. homogenous or heterogeneous ...
8th Grade Science Notes Chapter 2
... atoms have 6 protons each, oxygen atoms have 8 protons each, etc. Neutral Atoms - most atoms contain the same number of electrons as protons making them electrically neutral. Isotopes - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... atoms have 6 protons each, oxygen atoms have 8 protons each, etc. Neutral Atoms - most atoms contain the same number of electrons as protons making them electrically neutral. Isotopes - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
Chapter #20 Nuclear Chemistry
... Nucleons are protons and neutrons The strong nuclear force keeps the nucleus together by overcoming the repulsive force of the protons. Neutrons are present to help dissipate the repulsive forces between the protons As the atomic number (number of protons) increases, so does the number of neutrons t ...
... Nucleons are protons and neutrons The strong nuclear force keeps the nucleus together by overcoming the repulsive force of the protons. Neutrons are present to help dissipate the repulsive forces between the protons As the atomic number (number of protons) increases, so does the number of neutrons t ...
Atomic Numbers Notes
... “Learn to enjoy the little things – there are so many of them.” 1. What does this quote mean to you? 2. How can you practice this in your everyday life? 3. How does this apply to Chemistry? ...
... “Learn to enjoy the little things – there are so many of them.” 1. What does this quote mean to you? 2. How can you practice this in your everyday life? 3. How does this apply to Chemistry? ...
File
... Fusion reactions also release very large amount of energy but require extremely high temperatures to ...
... Fusion reactions also release very large amount of energy but require extremely high temperatures to ...
Nuclear Reactions Review
... 3.Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons are A.never found. C.unnatural. B.unstable. D.stable. ...
... 3.Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons are A.never found. C.unnatural. B.unstable. D.stable. ...
Nuclear Reactions Review powerpt
... 3.Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons are A.never found. C.unnatural. B.unstable. D.stable. ...
... 3.Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons are A.never found. C.unnatural. B.unstable. D.stable. ...
A Conceptual Introduction to Chemistry, First Edition
... • Remember, isotopes are: – Atoms with the same atomic number Z, but different neutron numbers N and mass numbers A ...
... • Remember, isotopes are: – Atoms with the same atomic number Z, but different neutron numbers N and mass numbers A ...
Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
... be attracted to each other. • The strong force is about 100 x greater than the electric force (the force that would cause the protons to repel each other). • The strong force is a short range force that quickly becomes extremely weak as protons and neutrons get farther apart. ...
... be attracted to each other. • The strong force is about 100 x greater than the electric force (the force that would cause the protons to repel each other). • The strong force is a short range force that quickly becomes extremely weak as protons and neutrons get farther apart. ...
Nuclear chemistry – the study of nuclear reactions and their uses in
... 1. Proton rich nuclei can increase their ratio by either positron emission or electron capture. Both kinds of decay increase the number of neutrons and decrease the number of protons. iii. Nuclei with atomic number greater than or equal to 84. 1. Undergo alpha emission to decrease the number of neut ...
... 1. Proton rich nuclei can increase their ratio by either positron emission or electron capture. Both kinds of decay increase the number of neutrons and decrease the number of protons. iii. Nuclei with atomic number greater than or equal to 84. 1. Undergo alpha emission to decrease the number of neut ...
document
... Particles are electrons but they do not come from the electron shells which surround the nucleus – they come from the nucleus itself. Due to neutron to proton ratio being too great. The electron is emitted when a neutron sheds its negative charge and becomes a proton. (Bet you didn’t know it could ...
... Particles are electrons but they do not come from the electron shells which surround the nucleus – they come from the nucleus itself. Due to neutron to proton ratio being too great. The electron is emitted when a neutron sheds its negative charge and becomes a proton. (Bet you didn’t know it could ...
I. Ch. 21.1 Nuclear Radiation
... Chemical Change – production of ___________ _______________________ with different properties – same elements just rearranged – usually involves valence electrons. ...
... Chemical Change – production of ___________ _______________________ with different properties – same elements just rearranged – usually involves valence electrons. ...
Vocabulary and Section Summary
... The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is that atom’s atomic number. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number. Different isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. Isotopes of an element share most chemical and physical properties. The mass number ...
... The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is that atom’s atomic number. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number. Different isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. Isotopes of an element share most chemical and physical properties. The mass number ...
elements_and_the_periodic_table_2011
... Atoms are the smallest part of an element that has all the properties of an element. ...
... Atoms are the smallest part of an element that has all the properties of an element. ...
Document
... EB = strong nuclear force binding -surface tension binding + spin pairing +shell binding-Coulomb repulsion 1) strong nuclear force -- the more nucleons the better 2) surface tension -- the less surface/volume the better (U better than He) 3) spin pairing -- neutrons and protons have + and - spins, p ...
... EB = strong nuclear force binding -surface tension binding + spin pairing +shell binding-Coulomb repulsion 1) strong nuclear force -- the more nucleons the better 2) surface tension -- the less surface/volume the better (U better than He) 3) spin pairing -- neutrons and protons have + and - spins, p ...
Friday Flashback Science 8 SC-08 1.1.2 Students will understand
... SC-08 1.1.2 Students will understand that matter is made of minute particles called atoms, and atoms are composed of even smaller components. The components of an atom have measurable properties such as mass and electrical charge. Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively c ...
... SC-08 1.1.2 Students will understand that matter is made of minute particles called atoms, and atoms are composed of even smaller components. The components of an atom have measurable properties such as mass and electrical charge. Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively c ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... Atoms have very small masses - the heaviest known atom is about 4 x 10−22 g Therefore, atomic mass unit (amu) is used to describe the mass of an individual atom The proton and neutron have nearly identical mass, and are much heavier than the electron (1 proton has same mass as 1836 electrons) ...
... Atoms have very small masses - the heaviest known atom is about 4 x 10−22 g Therefore, atomic mass unit (amu) is used to describe the mass of an individual atom The proton and neutron have nearly identical mass, and are much heavier than the electron (1 proton has same mass as 1836 electrons) ...