Radioactivity - Williamstown Independent Schools
... • Electrons are categorized as “leptons” because they cannot be broken down into small particles. • Protons and Neutrons consist of smaller particles called “quarks” • There are six types of quarks: up, down, strange, charm, top and bottom. ...
... • Electrons are categorized as “leptons” because they cannot be broken down into small particles. • Protons and Neutrons consist of smaller particles called “quarks” • There are six types of quarks: up, down, strange, charm, top and bottom. ...
Nuclear Energy
... nucleus into two smaller nuclei. The fuel is a large unstable atom such as Uranium-235. When the neutron hits the U-235 nucleus, the nucleus splits apart into two smaller nuclei and 2 or more neutrons. ...
... nucleus into two smaller nuclei. The fuel is a large unstable atom such as Uranium-235. When the neutron hits the U-235 nucleus, the nucleus splits apart into two smaller nuclei and 2 or more neutrons. ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY PACKET - Student
... NUCLEAR EQUATIONS Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles (with mass and charge) and emitted particles. ...
... NUCLEAR EQUATIONS Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles (with mass and charge) and emitted particles. ...
C2.1 Key Terms Atomic number: The number of protons in the
... atom. Atoms: The smallest part of an element that can take part in chemical reactions. Electronic configuration: The arrangement of electrons in shells around the nucleus of an atom. Electrons: Negative particles of negligible mass and charge -1 (relative to a proton). Energy levels: In chemistry, s ...
... atom. Atoms: The smallest part of an element that can take part in chemical reactions. Electronic configuration: The arrangement of electrons in shells around the nucleus of an atom. Electrons: Negative particles of negligible mass and charge -1 (relative to a proton). Energy levels: In chemistry, s ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... beta particle (9.1) an electron formed in the nucleus by the conversion of a neutron into a proton. binding energy (9.3) the energy required to break down the nucleus into its component parts. breeder reactor (9.4) a nuclear reactor that produces its own fuel in the process of providing electrical e ...
... beta particle (9.1) an electron formed in the nucleus by the conversion of a neutron into a proton. binding energy (9.3) the energy required to break down the nucleus into its component parts. breeder reactor (9.4) a nuclear reactor that produces its own fuel in the process of providing electrical e ...
Unit 3 Note Outline
... Atoms that have the same number of Most elements have more than one isotope - Hydrogen has Hydrogen-1 has Hydrogen-2 has Hydrogen-3 has ...
... Atoms that have the same number of Most elements have more than one isotope - Hydrogen has Hydrogen-1 has Hydrogen-2 has Hydrogen-3 has ...
Subatomic Particles and the Nuclear Atom (4.2)
... 9.1 Identifying atomic and subatomic particles, including mesons, quarks, tachyons, and baryons Other AOD C.9.1 Describe the structure of atoms, including the location of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... 9.1 Identifying atomic and subatomic particles, including mesons, quarks, tachyons, and baryons Other AOD C.9.1 Describe the structure of atoms, including the location of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
Atomic/Nuclear
... When a gamma ray is released, the same number of neutrons and protons are present but they have settled to a lower energy level. Alpha particles are stopped by air molecules in a few centimeters. Beta particles are stopped by air molecules in a few meters. Gamma rays can travel very long distances t ...
... When a gamma ray is released, the same number of neutrons and protons are present but they have settled to a lower energy level. Alpha particles are stopped by air molecules in a few centimeters. Beta particles are stopped by air molecules in a few meters. Gamma rays can travel very long distances t ...
Nuclear Decay
... electromagnetic radiation, or both. Nuclear radiation is particles or electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus during radioactive decay. ...
... electromagnetic radiation, or both. Nuclear radiation is particles or electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus during radioactive decay. ...
The Basis of All Materials
... Many atoms for each element will have the same number of neutrons as protons Elements of the same Z that differ in the number of neutrons are isotopes. ...
... Many atoms for each element will have the same number of neutrons as protons Elements of the same Z that differ in the number of neutrons are isotopes. ...
The Atom Visible light
... Many atoms for each element will have the same number of neutrons as protons Elements of the same Z that differ in the number of neutrons are isotopes. ...
... Many atoms for each element will have the same number of neutrons as protons Elements of the same Z that differ in the number of neutrons are isotopes. ...
A – Z - washburnsciencelies
... to form a single larger nuclei. This produces far more energy than a fission reaction, and also does not have a dangerous by-product. However we currently don’t have the means to use it as a reliable energy source, as we barely get more energy out, than we put in. ...
... to form a single larger nuclei. This produces far more energy than a fission reaction, and also does not have a dangerous by-product. However we currently don’t have the means to use it as a reliable energy source, as we barely get more energy out, than we put in. ...
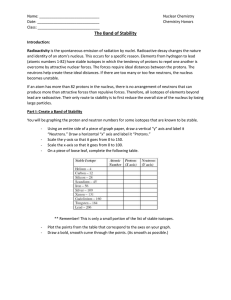
The Band of Stability
... Introduction: Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation by nuclei. Radioactive decay changes the nature and identity of an atom’s nucleus. This occurs for a specific reason. Elements from hydrogen to lead (atomic numbers 1-82) have stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to rep ...
... Introduction: Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation by nuclei. Radioactive decay changes the nature and identity of an atom’s nucleus. This occurs for a specific reason. Elements from hydrogen to lead (atomic numbers 1-82) have stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to rep ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons, and are emitted during some kinds of radioactive decay. Remember that protons determine the identity of the element : if an alpha particle is emitted, the identity of the element changes. Alpha particles are often called a helium nucleus. ...
... Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons, and are emitted during some kinds of radioactive decay. Remember that protons determine the identity of the element : if an alpha particle is emitted, the identity of the element changes. Alpha particles are often called a helium nucleus. ...
The Structure of the Atom
... Protons : + charge, relative mass = 1.007 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Neutrons: = charge, relative mass = 1.009 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Electrons: - charge, relative mass = 0.0005 atomic mass units (amu); round to 0 (not factored in when figuring total mass of an atom) ...
... Protons : + charge, relative mass = 1.007 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Neutrons: = charge, relative mass = 1.009 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Electrons: - charge, relative mass = 0.0005 atomic mass units (amu); round to 0 (not factored in when figuring total mass of an atom) ...
Keypoints of Basic Atomic Structure
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
Page 201 - ClassZone
... A key discovery leading to the current model of the atom was that atoms contain particles that have electric charges. A particle’s charge can be either positive or negative. Particles with the same charge repel each other—they are pushed apart. Particles with different charges attract each other—the ...
... A key discovery leading to the current model of the atom was that atoms contain particles that have electric charges. A particle’s charge can be either positive or negative. Particles with the same charge repel each other—they are pushed apart. Particles with different charges attract each other—the ...
nuclear chemistry - Magoffin County Schools
... Nucleus Stable? • For elements 1 – 20, need equal numbers of P+ and No. • For elements 21 – 83, increasingly more and more No than P+ are needed. • Beyond element 83, there are no stable atoms!!! ...
... Nucleus Stable? • For elements 1 – 20, need equal numbers of P+ and No. • For elements 21 – 83, increasingly more and more No than P+ are needed. • Beyond element 83, there are no stable atoms!!! ...
200
... identical. Right or wrong… explain. • A Wrong, isotopes are the same atom with different numbers of neutrons. ...
... identical. Right or wrong… explain. • A Wrong, isotopes are the same atom with different numbers of neutrons. ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioactive decay or bombardment with another particle. Many isotopes are unstable, and undergo spontaneous radioactive d ...
... changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioactive decay or bombardment with another particle. Many isotopes are unstable, and undergo spontaneous radioactive d ...
Atomic Structure Atoms
... The nature of atoms was deduced from important experiments conducted in the late 1800's up to the mid 1900's by scientists in Europe. Some of these include: Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery of x-rays in 1895. Antoine-Henri Becquerel's discovery of radioactivity one year later. J. J. Thomson's discovery o ...
... The nature of atoms was deduced from important experiments conducted in the late 1800's up to the mid 1900's by scientists in Europe. Some of these include: Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery of x-rays in 1895. Antoine-Henri Becquerel's discovery of radioactivity one year later. J. J. Thomson's discovery o ...
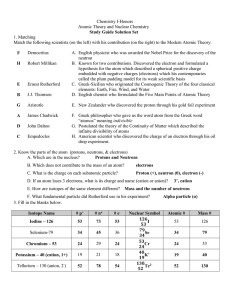
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may or may not be emitted. ...
... by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may or may not be emitted. ...
Name: Date: Period: Page # Evolution of Atomic Theory (Changed
... _______________________: atoms were like smooth, hard spheres that could not be ____________ into smaller pieces All ____________ are composed of ___________ that cannot be divided Atoms cannot be ____________ or _____________ in a chemical change __________________ are composed of more than ...
... _______________________: atoms were like smooth, hard spheres that could not be ____________ into smaller pieces All ____________ are composed of ___________ that cannot be divided Atoms cannot be ____________ or _____________ in a chemical change __________________ are composed of more than ...