The ATP-PCr energy system can operate with or without oxygen but
... The aerobic system, which is dependent on oxygen, is the most complex of the three energy systems. The metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen are responsible for most of the cellular energy produced by the body. However, aerobic metabolism is the slowest way to resynthesize AT ...
... The aerobic system, which is dependent on oxygen, is the most complex of the three energy systems. The metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen are responsible for most of the cellular energy produced by the body. However, aerobic metabolism is the slowest way to resynthesize AT ...
Biochem-5012.3B - Center for Structural Biology
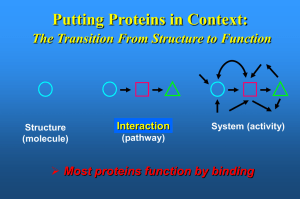
... • Storage- metals, amino acids, • Immune response- foreign matter (antigens) • Receptors- regulatory proteins, transmitters • Structure- other structural proteins ...
... • Storage- metals, amino acids, • Immune response- foreign matter (antigens) • Receptors- regulatory proteins, transmitters • Structure- other structural proteins ...
(C)
... 26. What motor protein generates the sliding of microtubules that leads to bending of cilia? (A) actin, (B) myosin, (C) dynein, (D) kinesin, (E) tubulin. 27. N-acetylglutamate functions in ammonium incorporation into metabolic intermediates as: (A) a coenzyme for glutamine synthetase (GS), (B) a com ...
... 26. What motor protein generates the sliding of microtubules that leads to bending of cilia? (A) actin, (B) myosin, (C) dynein, (D) kinesin, (E) tubulin. 27. N-acetylglutamate functions in ammonium incorporation into metabolic intermediates as: (A) a coenzyme for glutamine synthetase (GS), (B) a com ...
Chapter 8 study guide
... What pathway do electrons follow inside an active mitochondrion? Where does the oxygen for the synthesis of water come from during oxidative phosphorylation? In chemiosmotic phosphorylation, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP +P ATP? What is the result of hydrogen ...
... What pathway do electrons follow inside an active mitochondrion? Where does the oxygen for the synthesis of water come from during oxidative phosphorylation? In chemiosmotic phosphorylation, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP +P ATP? What is the result of hydrogen ...
BIOS 1700 Dr. Tanda Week 6, Session 3 1. What two subunits made
... __________________ and ______________. Ethanol fermentation occurs in ______________ and _______________. 4. T/F Glucose is more efficient than fat. 5. One fatty acid molecule can produce a large number of ATP. Why? ...
... __________________ and ______________. Ethanol fermentation occurs in ______________ and _______________. 4. T/F Glucose is more efficient than fat. 5. One fatty acid molecule can produce a large number of ATP. Why? ...
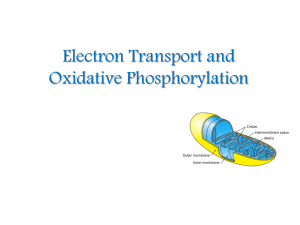
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
... The inner mitochondrial membrane contains 5 separate enzyme complexes, called compelexes I, II, III, IV and V. Each complex accepts or donates electrons to mobile carrier, such as coenzyme Q and cytochrome c. The electrons ultimately combine with oxygen and protons to form water. ...
... The inner mitochondrial membrane contains 5 separate enzyme complexes, called compelexes I, II, III, IV and V. Each complex accepts or donates electrons to mobile carrier, such as coenzyme Q and cytochrome c. The electrons ultimately combine with oxygen and protons to form water. ...
Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria)
... First, the entire process then I’ll break it Cytosol down into its parts. Pyruvate Aceyl CoA ...
... First, the entire process then I’ll break it Cytosol down into its parts. Pyruvate Aceyl CoA ...
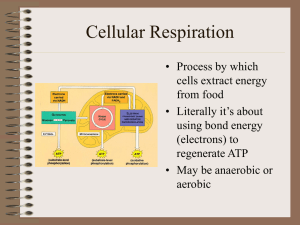
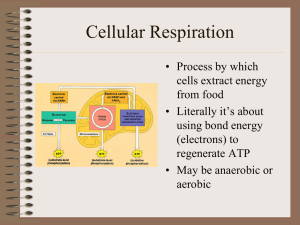
Cellular Respiration
... as a 3-Act Play • Act I: Glycolysis • Act II: The Kreb’s Cycle • Act III: Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Electron Transport Chain ...
... as a 3-Act Play • Act I: Glycolysis • Act II: The Kreb’s Cycle • Act III: Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Electron Transport Chain ...
SCI_7726_files/Cellular Respiration
... as a 3-Act Play • Act I: Glycolysis • Act II: The Kreb’s Cycle • Act III: Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Electron Transport Chain ...
... as a 3-Act Play • Act I: Glycolysis • Act II: The Kreb’s Cycle • Act III: Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Electron Transport Chain ...
TWO-DAY COURSE, Saturday and Sunday 12 Peptides and
... of proteins. This course is designed as an introduction for researchers needing to expand their knowledge of the use of mass spectrometry-based methods for the identification, characterization, and quantification of peptides and proteins. Background material in basic protein chemistry will be provid ...
... of proteins. This course is designed as an introduction for researchers needing to expand their knowledge of the use of mass spectrometry-based methods for the identification, characterization, and quantification of peptides and proteins. Background material in basic protein chemistry will be provid ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Chemiosmotic Theory
... movement of H+ makes the outer aqueous region positive and slightly acidic relative to the matrix of the mitochondrion. This difference between the two sides of the membrane (it is both an electrical and a pH difference) is called the protonmotive force, and it can drive protons back across the memb ...
... movement of H+ makes the outer aqueous region positive and slightly acidic relative to the matrix of the mitochondrion. This difference between the two sides of the membrane (it is both an electrical and a pH difference) is called the protonmotive force, and it can drive protons back across the memb ...
Name: Date: 1. The is the source of most of the cellular energy. A
... 20. The amino acids are transported to the place where they will be assembled into proteins by _____. A) ...
... 20. The amino acids are transported to the place where they will be assembled into proteins by _____. A) ...
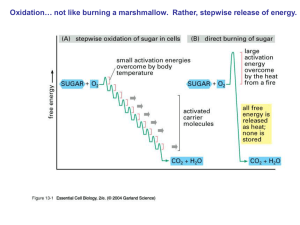
oxidation
... First 5 reactions consume energy: 2 ATP molecules are used to phosphorylate and activate glucose to 3-carbon sugar phosphate Aerobic Respiration nd 2 set of reactions: hydrogen atoms are removed (Respiration using O2) (oxidation) by NAD+ forming NADH (reduction): 2NAD+ + 4H (oxidation) 2 NADH (tha ...
... First 5 reactions consume energy: 2 ATP molecules are used to phosphorylate and activate glucose to 3-carbon sugar phosphate Aerobic Respiration nd 2 set of reactions: hydrogen atoms are removed (Respiration using O2) (oxidation) by NAD+ forming NADH (reduction): 2NAD+ + 4H (oxidation) 2 NADH (tha ...
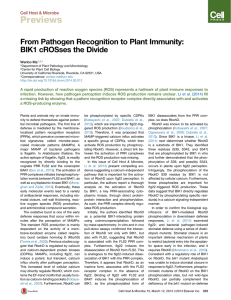
Cell Host & Microbe
... 2013). Another interesting observation made by Li et al. (2014) that supports this model was that BIK1 and its related cytoplasmic kinase PBL1 were required for the full activation of calcium influx triggered by flg22. This result indicates that RbohD activation by BIK1 may occur earlier than the ca ...
... 2013). Another interesting observation made by Li et al. (2014) that supports this model was that BIK1 and its related cytoplasmic kinase PBL1 were required for the full activation of calcium influx triggered by flg22. This result indicates that RbohD activation by BIK1 may occur earlier than the ca ...
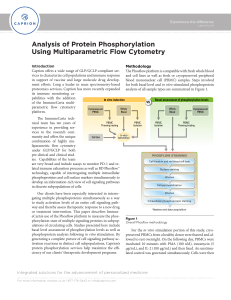
Analysis of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiparametric Flow
... a disease or a stimulus on the pathway of interest under near-native conditions. Kinases are recognized as “highly-druggable” targets for a host of therapeutic indications (including cancers, CNS disorders, pain, inflammatory diseases, immune function disorders, cardiotoxicity, and diabetes), so Imm ...
... a disease or a stimulus on the pathway of interest under near-native conditions. Kinases are recognized as “highly-druggable” targets for a host of therapeutic indications (including cancers, CNS disorders, pain, inflammatory diseases, immune function disorders, cardiotoxicity, and diabetes), so Imm ...
4 - Clark College
... • Explain the concept of a metabolic pathway, a catabolic pathway, and an anabolic pathway . • State the first and second laws of thermodynamics. • Explain the difference between kinetic energy and potential energy. • Compare and contrast endergonic and exergonic reactions. • Discuss how enzymes fun ...
... • Explain the concept of a metabolic pathway, a catabolic pathway, and an anabolic pathway . • State the first and second laws of thermodynamics. • Explain the difference between kinetic energy and potential energy. • Compare and contrast endergonic and exergonic reactions. • Discuss how enzymes fun ...
Biological Macromolecules
... **Long-term energy storage found in the liver ** Quickly broken down into glucose for immediate ...
... **Long-term energy storage found in the liver ** Quickly broken down into glucose for immediate ...
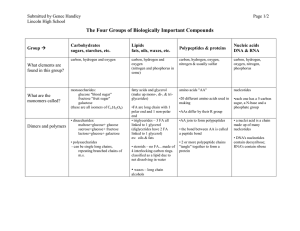
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).