G:\CLASSES\BI 205\Biol205_S10\exams\Final_S10.wpd
... (6 points) The citric acid cycle generates NADH+H+ and FADH2, which are then used in the process of oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxphos are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immed ...
... (6 points) The citric acid cycle generates NADH+H+ and FADH2, which are then used in the process of oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxphos are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immed ...
Protein and Lipid Catabolism
... Using the PMF, ATP synthesis is catalyzed by ATP synthase (ATPase), through a process called chemiosmosis ...
... Using the PMF, ATP synthesis is catalyzed by ATP synthase (ATPase), through a process called chemiosmosis ...
Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept
... c) c) ATP synthase complex – as hydrogen ions pass through the synthases, the production of ATP from ADP and Pi is catalyzed, and oxygen is reduced, forming water 4. What are the roles of NAD+ and FAD in aerobic respiration? NAD+ and FAD receive electrons at varying steps during glycolysis (NAD+ onl ...
... c) c) ATP synthase complex – as hydrogen ions pass through the synthases, the production of ATP from ADP and Pi is catalyzed, and oxygen is reduced, forming water 4. What are the roles of NAD+ and FAD in aerobic respiration? NAD+ and FAD receive electrons at varying steps during glycolysis (NAD+ onl ...
Gluconeogenesis
... converted to glucose and sucrose and exported to other tissues for starch storage. • In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
... converted to glucose and sucrose and exported to other tissues for starch storage. • In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
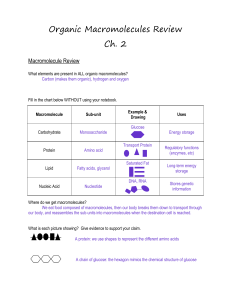
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... A protein: we use shapes to represent the different amino acids ...
... A protein: we use shapes to represent the different amino acids ...
Chapter 34-4B: Second Messengers
... are not transmembrane proteins. Steroid hormones can pass freely through cell membrane, and bind the specific receptor protein in cytosol. The receptor activated by the steroid hormone moves into the nucleus. The active receptor binds a specific region of DNA and activates or inactivates the replica ...
... are not transmembrane proteins. Steroid hormones can pass freely through cell membrane, and bind the specific receptor protein in cytosol. The receptor activated by the steroid hormone moves into the nucleus. The active receptor binds a specific region of DNA and activates or inactivates the replica ...
SBI 4U Cellular Respiration Review Game2
... 2. What is oxidative phosphorylation? 3. What is substrate-level phosphorylation? 4. What 3 modifications occur to pyruvate in pyruvate oxidation? 5. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur in the cell? 6. How molecules of ATP are produced from NADH? 7. How molecules of ATP are produced from FADH2? 8. Whe ...
... 2. What is oxidative phosphorylation? 3. What is substrate-level phosphorylation? 4. What 3 modifications occur to pyruvate in pyruvate oxidation? 5. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur in the cell? 6. How molecules of ATP are produced from NADH? 7. How molecules of ATP are produced from FADH2? 8. Whe ...
Completed Note
... Store & transmit genetic material Direct synthesis of new proteins & organic molecules RNA Translates DNA into functional proteins Several types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA…) ATP Stores potential energy in its phosphate bonds Releases energy when converted to ADP ...
... Store & transmit genetic material Direct synthesis of new proteins & organic molecules RNA Translates DNA into functional proteins Several types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA…) ATP Stores potential energy in its phosphate bonds Releases energy when converted to ADP ...
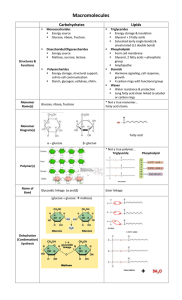
Basic Biochemistry
... Building blocks for most complex lipids Long chains with a carboxylic acid at 1 end Can be saturated or unsaturated Saturated only single C-C bonds Unsaturated has one or more C=C (double bond) ...
... Building blocks for most complex lipids Long chains with a carboxylic acid at 1 end Can be saturated or unsaturated Saturated only single C-C bonds Unsaturated has one or more C=C (double bond) ...
How many molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) can be
... Describe the clinical symptoms you would expect to find in someone with a liver glycogen phosphorylase deficiency. What symptoms would you expect such an individual to exhibit? Explain using your biochemical knowledge of glycogen phosphorylase. Anaerobic metabolism of glucose produces lactate in act ...
... Describe the clinical symptoms you would expect to find in someone with a liver glycogen phosphorylase deficiency. What symptoms would you expect such an individual to exhibit? Explain using your biochemical knowledge of glycogen phosphorylase. Anaerobic metabolism of glucose produces lactate in act ...
Biol 256 SI UNIT 1B_Biochem_Organic Molecules Macromolecules
... _____________ are biological catalyst that works by ______________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Proteins serve as effective buffers by combining with H+ or OH-. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are a type of polymer/macromolecule composed of the basic units called ____________. Each of t ...
... _____________ are biological catalyst that works by ______________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Proteins serve as effective buffers by combining with H+ or OH-. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are a type of polymer/macromolecule composed of the basic units called ____________. Each of t ...
No Slide Title
... 3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Series of proteins & electron carriers embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane (eukaryotes) or cell membrane (prokaryotes). O2 is the final electron acceptor H2O is the final product energy harvested/NADH: 2.5 ATPs (via chemiosmotic phosphorylation) ...
... 3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Series of proteins & electron carriers embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane (eukaryotes) or cell membrane (prokaryotes). O2 is the final electron acceptor H2O is the final product energy harvested/NADH: 2.5 ATPs (via chemiosmotic phosphorylation) ...
Jim Bidlack - BIO 1114 GENERAL BIOLOGY Lectures 6 and 7
... GENERAL BIOLOGY Lectures 6 and 7 - Biological molecules I. ...
... GENERAL BIOLOGY Lectures 6 and 7 - Biological molecules I. ...
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4
... tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphoryla ...
... tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphoryla ...
1 Which of the following are the smallest cells? A) human ovum B
... The amino acids are transported to the place where they will be assembled into proteins by _____. A) ...
... The amino acids are transported to the place where they will be assembled into proteins by _____. A) ...
Glycogen Slides from Class
... The cAMP binds to protein kinase A (PKA), a cAMP-dependent protein kinase, activating it. PKA in turn phosphorylates other downstream target proteins including phosphorylase kinase (PhosK) and glycogen synthase (GS). The phosphorylation of PhosK leads to its activation. Conversely, phosphorylatio ...
... The cAMP binds to protein kinase A (PKA), a cAMP-dependent protein kinase, activating it. PKA in turn phosphorylates other downstream target proteins including phosphorylase kinase (PhosK) and glycogen synthase (GS). The phosphorylation of PhosK leads to its activation. Conversely, phosphorylatio ...
The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in rat islets of
... CAMK, PKC and PKA, MAPKs phosphorylate substrate proteins on serine and/or threonine residues. However, rather than being activated directly by second messengers, MAPK activities are regulated by another family of kinases (MEKs; 4446kDa) which phosphorylate MAPKs on tyrosine and threonine residues. ...
... CAMK, PKC and PKA, MAPKs phosphorylate substrate proteins on serine and/or threonine residues. However, rather than being activated directly by second messengers, MAPK activities are regulated by another family of kinases (MEKs; 4446kDa) which phosphorylate MAPKs on tyrosine and threonine residues. ...
L01_2002
... Examples of exams from previous years are also available on the 2001 web site for ABio366. Please note, however, that the format for the exams this year ...
... Examples of exams from previous years are also available on the 2001 web site for ABio366. Please note, however, that the format for the exams this year ...
1. Categorize chemical signals in terms of the
... cyclase which is associated with the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP cAMP binds to and activates a cytoplasmic enzyme protein kinase A Protein kinase A propagates the message by phosphorylating various other proteins that lead to the cellular response ...
... cyclase which is associated with the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP cAMP binds to and activates a cytoplasmic enzyme protein kinase A Protein kinase A propagates the message by phosphorylating various other proteins that lead to the cellular response ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).