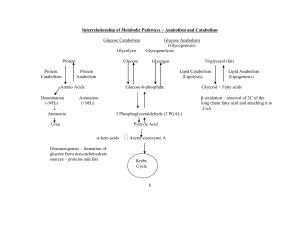
(i)
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
Homework 3-1 Reading Notes Campbell`s Chapter 9
... it needs. If there is a glut of certain amino acid, for example, the anabolic pathway that synthesizes the amino acid from an intermediate in the citric acid cycle is switched off. The most common mechanism for this control is __________________ ______________________. The _______ _______________ of ...
... it needs. If there is a glut of certain amino acid, for example, the anabolic pathway that synthesizes the amino acid from an intermediate in the citric acid cycle is switched off. The most common mechanism for this control is __________________ ______________________. The _______ _______________ of ...
The Biochemistry of Life
... in the hundreds of thousands • Both are polymers (hence "polysaccharides"); that is, each is built from repeating units, monomers, much as a chain is built from its links ...
... in the hundreds of thousands • Both are polymers (hence "polysaccharides"); that is, each is built from repeating units, monomers, much as a chain is built from its links ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... 1. Competitive inhibition – substance that resembles normal substrate competes with substrate for active site 2. Feedback inhibition – concentration of product at the end of a pathway blocks the action of a key enzyme 3. Feedback repression – inhibits at the genetic level by controlling synthesis of ...
... 1. Competitive inhibition – substance that resembles normal substrate competes with substrate for active site 2. Feedback inhibition – concentration of product at the end of a pathway blocks the action of a key enzyme 3. Feedback repression – inhibits at the genetic level by controlling synthesis of ...
Q1 Describe the physiological consequences that
... Glucose is taken up by GLUT-‐2 transporters on the surface of the pancreatic beta cells. Glucose is metabolized and phosphorylated by glucokinase, increasing the ATP in the cytoplasm and causing ATP-‐ se ...
... Glucose is taken up by GLUT-‐2 transporters on the surface of the pancreatic beta cells. Glucose is metabolized and phosphorylated by glucokinase, increasing the ATP in the cytoplasm and causing ATP-‐ se ...
Multiple Effects of Hymenocrater longiflorus on human colon cancer
... Hymenocrater longiflorus is a perennial herb. Leaves ovate- belong or lanceolate. This plant is growing above timberline or in subalpine zone between the rocks. The methanolic extract of this plant was used to study the immunoflourescence assay for γ-H2AX for RKO (colon cancer) cell line and observe ...
... Hymenocrater longiflorus is a perennial herb. Leaves ovate- belong or lanceolate. This plant is growing above timberline or in subalpine zone between the rocks. The methanolic extract of this plant was used to study the immunoflourescence assay for γ-H2AX for RKO (colon cancer) cell line and observe ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 9 Cellular
... 1. Compare the structure of a fat (see figure 5.11 in the orange book) with that of a carbohydrate (see figure 5.3 in the orange book). What features of their structures make a fat a much better fuel? ...
... 1. Compare the structure of a fat (see figure 5.11 in the orange book) with that of a carbohydrate (see figure 5.3 in the orange book). What features of their structures make a fat a much better fuel? ...
Intro to Cells and Biochemistry Molecule General Molecular Shape
... Intro to Cells and Biochemistry 1. List the things that biologically define life. 2. Choose a sports game you like to play or watch. Explain how life is like that game. 5 sentences minimum. Use actual examples from both sport and life to illustrate. 3. What is the cell considered the basic unit of l ...
... Intro to Cells and Biochemistry 1. List the things that biologically define life. 2. Choose a sports game you like to play or watch. Explain how life is like that game. 5 sentences minimum. Use actual examples from both sport and life to illustrate. 3. What is the cell considered the basic unit of l ...
Active Transport Small particles such as water, carbon dioxide and
... Small particles such as water, carbon dioxide and oxygen diffuse freely through the cell membrane yet there are other larger particles that the cell needs that cannot be obtained through diffusion. For example cells need glucose for energy. The glucose is present in low concentrations in your blood ...
... Small particles such as water, carbon dioxide and oxygen diffuse freely through the cell membrane yet there are other larger particles that the cell needs that cannot be obtained through diffusion. For example cells need glucose for energy. The glucose is present in low concentrations in your blood ...
exam two_study guide
... What is oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation, how are they similar/different? What is the ATP ase? Dehydrogenase enzymes? Know what takes place in the light reactions and the calvin cycle (in as much detail as presented in class) as well as the three phases of cellular respiratio ...
... What is oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation, how are they similar/different? What is the ATP ase? Dehydrogenase enzymes? Know what takes place in the light reactions and the calvin cycle (in as much detail as presented in class) as well as the three phases of cellular respiratio ...
so what happens to the glucose produced by photosynthesis
... carbon dioxide nitrates oils amino acids cellulose water ...
... carbon dioxide nitrates oils amino acids cellulose water ...
AP Biology Midterm Studyguide 2017
... E. Terms: G3P, lactate, Acetyl CoA, Citric Acid, NAD+, NADPH, RuBisCo…..(this is a sample) F. Enzymes! 1. be sure to understand the enzyme catalyzed reaction graph (see below) 2. Terms: exergonic, endergonic, spontaneous, free energy, catabolism, anabolism 3. Active site, competitive inhibitors, all ...
... E. Terms: G3P, lactate, Acetyl CoA, Citric Acid, NAD+, NADPH, RuBisCo…..(this is a sample) F. Enzymes! 1. be sure to understand the enzyme catalyzed reaction graph (see below) 2. Terms: exergonic, endergonic, spontaneous, free energy, catabolism, anabolism 3. Active site, competitive inhibitors, all ...
Slide 1
... AvrRpm1 or AvrB Induces RPM1-indepentdent Phosphorylation of RIN4, and RPM1 recognizes the phosphorylation to induce HR AvrRpt2 induces disappearance of RIN4, and RPS2 induce HR by the recognization of disappearance ...
... AvrRpm1 or AvrB Induces RPM1-indepentdent Phosphorylation of RIN4, and RPM1 recognizes the phosphorylation to induce HR AvrRpt2 induces disappearance of RIN4, and RPS2 induce HR by the recognization of disappearance ...
1st exam
... 4) Glycolysis is the major pathway for utilizing of glucose and is found in all 5)In ETC, Q (Co Q) serves to shuffle electrons from complexes I, II and III to complex IV 6)Low fat diet and regular exercise can reverse atherosclerotic lesion. 7)Hypercholesterolaemia is almost always due to a raised p ...
... 4) Glycolysis is the major pathway for utilizing of glucose and is found in all 5)In ETC, Q (Co Q) serves to shuffle electrons from complexes I, II and III to complex IV 6)Low fat diet and regular exercise can reverse atherosclerotic lesion. 7)Hypercholesterolaemia is almost always due to a raised p ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 2.) The structural level of a protein in which alpha helixes and beta sheets form are in the A. Primary level B. Secondary level C. Tertiary level D. Quaternary level 3.) Facilitated diffusion transport A. requires membrane channel or carrier protein. B. requires ATP hydrolysis. C. requires H+ cotra ...
... 2.) The structural level of a protein in which alpha helixes and beta sheets form are in the A. Primary level B. Secondary level C. Tertiary level D. Quaternary level 3.) Facilitated diffusion transport A. requires membrane channel or carrier protein. B. requires ATP hydrolysis. C. requires H+ cotra ...
038-Signal Transduction Pathways Activity-V Morris
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
Modifications of redox-active cysteines occurring during sample
... and need them in native form and unoccupied. On the other hand, users who study low-level protein modifications might get interferences from such contaminants. 2) Low pKa cysteine residues are reactive and critical components in redox signaling with sulfenic acid (Cys-SOH) being a versatile reversib ...
... and need them in native form and unoccupied. On the other hand, users who study low-level protein modifications might get interferences from such contaminants. 2) Low pKa cysteine residues are reactive and critical components in redox signaling with sulfenic acid (Cys-SOH) being a versatile reversib ...
CARBOHYDRATES, lipids and proteins handout
... Combinations of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) (usual ratio = 1:2:1)(e.g. glucose is C6H12O6) – sugars and starches Carbohydrate means "hydrated carbon" Primary use = fuel to make energy. The energy molecule of the cell is ATP. Glucose is broken down and the energy released from the ...
... Combinations of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) (usual ratio = 1:2:1)(e.g. glucose is C6H12O6) – sugars and starches Carbohydrate means "hydrated carbon" Primary use = fuel to make energy. The energy molecule of the cell is ATP. Glucose is broken down and the energy released from the ...
Blue Flashcards (CR) - mvhs
... ____________________ (location) to ____________________ (location). This pumping forms a concentration gradient. ______ is the final electron acceptor. ...
... ____________________ (location) to ____________________ (location). This pumping forms a concentration gradient. ______ is the final electron acceptor. ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).