SP600125 Selectively Inhibits Histone H3
... INTRODUCTION. The role played by histone modifications in transcriptional regulation is one recent area of interest in the study of gene expression. These modifications collectively influence a web of regulatory events, and their interconnectedness has led to the hypothesis that there is a “histone ...
... INTRODUCTION. The role played by histone modifications in transcriptional regulation is one recent area of interest in the study of gene expression. These modifications collectively influence a web of regulatory events, and their interconnectedness has led to the hypothesis that there is a “histone ...
6.1 Cellular respiration
... of cellular respiration. Glucose metabolism Cellular respiration = glucose oxidation Glucose 1 oxygen → carbon dioxide 1 water 1 energy (ATP) This reaction does not occur in one simple reaction, but involves over each controlled by specific enzymes. ...
... of cellular respiration. Glucose metabolism Cellular respiration = glucose oxidation Glucose 1 oxygen → carbon dioxide 1 water 1 energy (ATP) This reaction does not occur in one simple reaction, but involves over each controlled by specific enzymes. ...
Organelles and specialized structures
... 6. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants harvest light energy and use it to make glucose. (T/F) 7. Basal bodies are used wherever a flagella or cilia attaches to the cell membrane. (T/F) 8. The nucleolus of the cell is where nuclear protein synthesis is occurri ...
... 6. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants harvest light energy and use it to make glucose. (T/F) 7. Basal bodies are used wherever a flagella or cilia attaches to the cell membrane. (T/F) 8. The nucleolus of the cell is where nuclear protein synthesis is occurri ...
SI Practice Exam / Review Sheet
... 11. The process of glycolysis yields _______ net ATPs. 12. The delta G of digesting one mole of glucose is _____________ kcal/mol. 13. Coupled reactions make __________________ reactions possible under biological conditions. 14. If a molecule contains high free energy its stability is ___________. 1 ...
... 11. The process of glycolysis yields _______ net ATPs. 12. The delta G of digesting one mole of glucose is _____________ kcal/mol. 13. Coupled reactions make __________________ reactions possible under biological conditions. 14. If a molecule contains high free energy its stability is ___________. 1 ...
04b Carbohydrates-student note
... major nutrients for cells; glucose is most common can be produced by __________________________ organisms from CO2, H2O, sunlight store ____________ in chemical bonds, which is released during cellular respiration Characteristics of a sugar: An _____________________ attached to each carbon e ...
... major nutrients for cells; glucose is most common can be produced by __________________________ organisms from CO2, H2O, sunlight store ____________ in chemical bonds, which is released during cellular respiration Characteristics of a sugar: An _____________________ attached to each carbon e ...
Can use more than once
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS – The anabolic reduction of CO2 to form sugar.
... CHAIN – NADH and FADH2 provide the electrons, and O2 ...
... CHAIN – NADH and FADH2 provide the electrons, and O2 ...
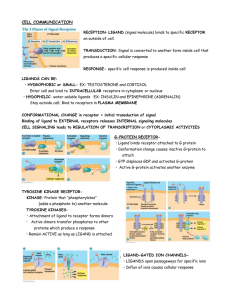
What to know Chap 11
... RECEPTION- LIGAND (signal molecule) binds to specific RECEPTOR on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERON ...
... RECEPTION- LIGAND (signal molecule) binds to specific RECEPTOR on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERON ...
Welcome to the basics lecture on cellular respiration
... In this class, we are not interested in memorizing all of the intermediates and enzymes. There will be time for that in your biochemistry course. Instead, I want you to know the following about glycolysis: 1. It occurs in the cytosol, outside of the mitochondrion. 2. Glucose has some electrons re ...
... In this class, we are not interested in memorizing all of the intermediates and enzymes. There will be time for that in your biochemistry course. Instead, I want you to know the following about glycolysis: 1. It occurs in the cytosol, outside of the mitochondrion. 2. Glucose has some electrons re ...
Enzymes: Principles of Catalysis
... Another way to fine tune enzymatic action is to jam something into another site (not the active site) In oligomeric enzymes, the binding of a ligand may induce a conformational change that affects binding of ligand in other subunits ...
... Another way to fine tune enzymatic action is to jam something into another site (not the active site) In oligomeric enzymes, the binding of a ligand may induce a conformational change that affects binding of ligand in other subunits ...
Energy Production II - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... 1. Energy balance (deficit = more PRO used) 2. CHO available (low = more PRO used) Amino acids derived from body protein can be used to produce: a. energy, via entry into TCA cycle b. glucose, via gluconeogenesis ...
... 1. Energy balance (deficit = more PRO used) 2. CHO available (low = more PRO used) Amino acids derived from body protein can be used to produce: a. energy, via entry into TCA cycle b. glucose, via gluconeogenesis ...
INTRODUCTION to BIOENERGETICS H.R. Kaback
... membranes represents the bridge between biochemistry and physiology. While ATP is the currency of energy exchange in the cytosol, electrochemical ion gradients across energytransducing membranes are involved in a large number of seemingly unrelated processes such as oxidative phosphorylation, active ...
... membranes represents the bridge between biochemistry and physiology. While ATP is the currency of energy exchange in the cytosol, electrochemical ion gradients across energytransducing membranes are involved in a large number of seemingly unrelated processes such as oxidative phosphorylation, active ...
classsssssss
... male who suffers from periodic hemolysis demonstrate a low activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Deficiency of which of the following erythrocyte enzymes has the same pathophysiology as this patient’s condition? • A. bisphosphoglycerate mutase • B. pyruvate kinase • C. hexokinase • D. trans ...
... male who suffers from periodic hemolysis demonstrate a low activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Deficiency of which of the following erythrocyte enzymes has the same pathophysiology as this patient’s condition? • A. bisphosphoglycerate mutase • B. pyruvate kinase • C. hexokinase • D. trans ...
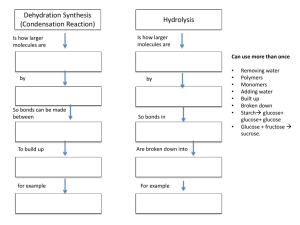
The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence
... These are structural formulas of α and β glucose rings. It’s noticeable that the α and β glucose rings have different structures as in the position of OH atoms. These differences lead to the differences in the polymer chains the α and β glucose rings make. Starch is a polymer made out of α glucose r ...
... These are structural formulas of α and β glucose rings. It’s noticeable that the α and β glucose rings have different structures as in the position of OH atoms. These differences lead to the differences in the polymer chains the α and β glucose rings make. Starch is a polymer made out of α glucose r ...
Biological Molecules- You are What You Eat:
... This worksheet goes Crash Course Biology found on youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8WJ2KENlK0 ...
... This worksheet goes Crash Course Biology found on youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8WJ2KENlK0 ...
Stroma
... 1. Why is ATP important in coupled reactions? 2. Describe the role of NAD+ and FAD. Where do these molecules come from? 3. Explain what is meant by substrate-level phosphorylation and give two examples. 4. Trace the path of glycolysis from glucose through to pyruvate, listing all major intermediates ...
... 1. Why is ATP important in coupled reactions? 2. Describe the role of NAD+ and FAD. Where do these molecules come from? 3. Explain what is meant by substrate-level phosphorylation and give two examples. 4. Trace the path of glycolysis from glucose through to pyruvate, listing all major intermediates ...
Stroma
... Why is ATP important in coupled reactions? Describe the role of NAD+ and FAD. Where do these molecules come from? Explain what is meant by substrate-level phosphorylation and give two examples. Trace the path of glycolysis from glucose through to pyruvate, listing all major intermediates in the corr ...
... Why is ATP important in coupled reactions? Describe the role of NAD+ and FAD. Where do these molecules come from? Explain what is meant by substrate-level phosphorylation and give two examples. Trace the path of glycolysis from glucose through to pyruvate, listing all major intermediates in the corr ...
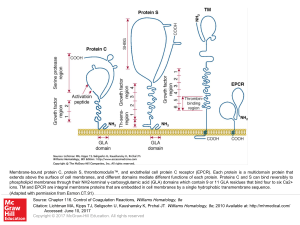
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
REVIEW FOR TEST 3: ENERGETICS
... 1. Define: autotroph, heterotroph, biochemical pathway, aerobic and anaerobic reactions, chemiosmosis, ATP synthase, reduction and oxidation (Redox) 2. Describe the two types of phosphorylation a. substrate-level phosphorylation b. chemiosmotic phosphorylation 1. photophosphorylation (CH 10) 2. oxid ...
... 1. Define: autotroph, heterotroph, biochemical pathway, aerobic and anaerobic reactions, chemiosmosis, ATP synthase, reduction and oxidation (Redox) 2. Describe the two types of phosphorylation a. substrate-level phosphorylation b. chemiosmotic phosphorylation 1. photophosphorylation (CH 10) 2. oxid ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, glucose is broken down completely (citric acid ...
... • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, glucose is broken down completely (citric acid ...
1. Diagram the biosynthetic pathway fiom UMP),
... How does a mutation in the ras gene that leads to formation of a Ras protein with no GTPase activity affect a cell's response to insulin ? (5%) ...
... How does a mutation in the ras gene that leads to formation of a Ras protein with no GTPase activity affect a cell's response to insulin ? (5%) ...
Diagrams to Review 1
... the cell past the G2 checkpoint into M phase - it will also make a proteolytic enzyme that destroys cyclin and thus turn off MPF ...
... the cell past the G2 checkpoint into M phase - it will also make a proteolytic enzyme that destroys cyclin and thus turn off MPF ...
Cell Energy Concept Map
... The Dark Reaction (AKA ___________ Cycle) occurs just after the light reaction in the __________ of the ________________. ______ is “fixed” by the enzyme ______________ as it is added to ________. The ...
... The Dark Reaction (AKA ___________ Cycle) occurs just after the light reaction in the __________ of the ________________. ______ is “fixed” by the enzyme ______________ as it is added to ________. The ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).