Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... modulators, feedback inhibition, Fig 4-11) 3. Different enzymes for reversible rxs, Fig 412) ...
... modulators, feedback inhibition, Fig 4-11) 3. Different enzymes for reversible rxs, Fig 412) ...
Chemical Principles
... Found mainly in plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells. Mycoplasma are the only genus of bacteria that have sterols ...
... Found mainly in plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells. Mycoplasma are the only genus of bacteria that have sterols ...
Name
... Answer in Note book 7.1 Overview of cell respiration 1) Contrast autotrophs with heterotrophs 2) Define cellular respiration 3) Define digestion 4) Define dehydrogenations 5) What are redox reactions? Why are they important in biological systems? 6) What is NADH? How does NAD+ become NADH? 7) Define ...
... Answer in Note book 7.1 Overview of cell respiration 1) Contrast autotrophs with heterotrophs 2) Define cellular respiration 3) Define digestion 4) Define dehydrogenations 5) What are redox reactions? Why are they important in biological systems? 6) What is NADH? How does NAD+ become NADH? 7) Define ...
Cell Resp. Power Point Brief SV
... TWO WAYS TO MAKE ATP 1) ______________________ Phosphorylation: An enzyme transfers a __________ from a substrate (a molecule) to ADP, yielding ATP: ex: 1,3 Bisphosphate glycerate loses a phosphate to ADP-----> ATP 2) ______________________ Phosphorylation: Energy from redox reactions in electrontr ...
... TWO WAYS TO MAKE ATP 1) ______________________ Phosphorylation: An enzyme transfers a __________ from a substrate (a molecule) to ADP, yielding ATP: ex: 1,3 Bisphosphate glycerate loses a phosphate to ADP-----> ATP 2) ______________________ Phosphorylation: Energy from redox reactions in electrontr ...
Chapter 11 Cell Communication
... ○ The ligand (signaling molecule) has bound to the Gprotein-coupled receptor ○ Causes a conformational change in the receptor so it can bind to an inactive G-protein ○ This causes a GTP to displace the GDP ○ This activates the G-protein ...
... ○ The ligand (signaling molecule) has bound to the Gprotein-coupled receptor ○ Causes a conformational change in the receptor so it can bind to an inactive G-protein ○ This causes a GTP to displace the GDP ○ This activates the G-protein ...
Lecture 12
... – Covalently linked to and removed from the regulatory enzyme by separate enzymes ...
... – Covalently linked to and removed from the regulatory enzyme by separate enzymes ...
Biobowl
... 4. The receptor for a polar ligand is found where? 5. The receptor for a non-polar ligand is found where? 6. A non-polar signaling molecule usually acts by doing what in a cell? 7. A protein that binds GTP and is activated by a receptor is known as a 8. What is the benefit of a cascade, when referri ...
... 4. The receptor for a polar ligand is found where? 5. The receptor for a non-polar ligand is found where? 6. A non-polar signaling molecule usually acts by doing what in a cell? 7. A protein that binds GTP and is activated by a receptor is known as a 8. What is the benefit of a cascade, when referri ...
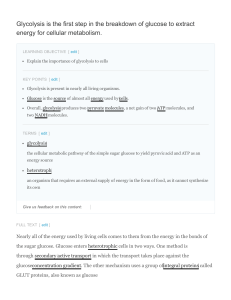
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to
... the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source ...
... the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source ...
2-4_EnergyProd_FabinyiB
... The main energy suppliers of a cell are the mitochondria. They have an outer and an inner membrane that are separated by the intermembrane space and surround the matrix. The inner membrane folds in several times, creating cristae that expands the surface. The outer membrane is more permeable, allows ...
... The main energy suppliers of a cell are the mitochondria. They have an outer and an inner membrane that are separated by the intermembrane space and surround the matrix. The inner membrane folds in several times, creating cristae that expands the surface. The outer membrane is more permeable, allows ...
Chapter 11 Cellular Signaling
... • Important pathway in the regulation of water/salt balance in intestines ...
... • Important pathway in the regulation of water/salt balance in intestines ...
1 - BrainMass
... d. How do you suppose a cell can make these two separate molecules without making errors such as glycogen-cellulose hybrid molecules? 2. Diagram the pathway of Glycolysis from glucose to pyruvate, giving structures and names of all pathway intermediates (enzyme mechanisms are not required) and names ...
... d. How do you suppose a cell can make these two separate molecules without making errors such as glycogen-cellulose hybrid molecules? 2. Diagram the pathway of Glycolysis from glucose to pyruvate, giving structures and names of all pathway intermediates (enzyme mechanisms are not required) and names ...
IB2.14.3 Building a protein
... membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen ...
... membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen ...
biol 3 biomolecules table activity
... simplest is CHOLESTEROL that consists of a 4 ringed carbon structure and has a structural role in the plasma membrane. Other steroids act as HORMONES, eg testosterone and progesterone. SATURATED FATS contain no double bonds between carbons and exist as solids at room temperature. ...
... simplest is CHOLESTEROL that consists of a 4 ringed carbon structure and has a structural role in the plasma membrane. Other steroids act as HORMONES, eg testosterone and progesterone. SATURATED FATS contain no double bonds between carbons and exist as solids at room temperature. ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... Adds the 1 carbon CO2 to RuBP Produces a 6C molecule that immediately splits into 2 PGA Slow rubisco is needed ...
... Adds the 1 carbon CO2 to RuBP Produces a 6C molecule that immediately splits into 2 PGA Slow rubisco is needed ...
powerpoint 29 Aug
... Krebs Cycle stops Pyruvate isn’t converted to Acetyl CoA; instead it goes to lactic acid Lactic acid converted back to pyruvate via liver (Cori Cycle) ...
... Krebs Cycle stops Pyruvate isn’t converted to Acetyl CoA; instead it goes to lactic acid Lactic acid converted back to pyruvate via liver (Cori Cycle) ...
Full size lecture slides (PDF file, 660 kB)
... • e.g. glycogen, plant starch, cellulose (found in plant cell walls), and chitin (a constituent of the shells of insects). • They are all homopolymers meaning they are all made of only one sugar repeated over and over. • Glycogen, plant starch and cellulose are made of glucose only; chitin uses modi ...
... • e.g. glycogen, plant starch, cellulose (found in plant cell walls), and chitin (a constituent of the shells of insects). • They are all homopolymers meaning they are all made of only one sugar repeated over and over. • Glycogen, plant starch and cellulose are made of glucose only; chitin uses modi ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... • Enzymes ____________________ for the electron transport chain are located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Several complexes are called __________________. • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain, ___________________________________________________ ____________ ...
... • Enzymes ____________________ for the electron transport chain are located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Several complexes are called __________________. • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain, ___________________________________________________ ____________ ...
Aerobic Respiration
... In summary, aerobic respiration is: • Glycolysis – the phosphorylation of glucose to 6C hexose phosphate, then splitting into 2 x 3C triose phosphate molecules which are oxidised to form 2 x pyruvate, yielding a little ATP and reduced NAD. In cytoplasm. • Link reaction - pyruvate is decarboxylated ...
... In summary, aerobic respiration is: • Glycolysis – the phosphorylation of glucose to 6C hexose phosphate, then splitting into 2 x 3C triose phosphate molecules which are oxidised to form 2 x pyruvate, yielding a little ATP and reduced NAD. In cytoplasm. • Link reaction - pyruvate is decarboxylated ...
glyoxylate cycle
... other tissues for starch storage. In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
... other tissues for starch storage. In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
6CellCommunication
... • The 3 stages of cell communication. • How G-protein-coupled receptors receive cell signals and start transduction • How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade. • An example of a second messenger and its role in a signal transduction pathway. • How a cell response in the nucleus tu ...
... • The 3 stages of cell communication. • How G-protein-coupled receptors receive cell signals and start transduction • How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade. • An example of a second messenger and its role in a signal transduction pathway. • How a cell response in the nucleus tu ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).