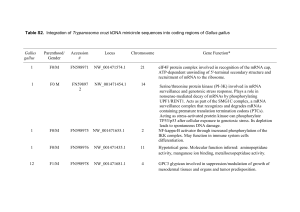
Table S2. Integration of Trypanosoma cruzi kDNA minicircle
... ATP-dependent unwinding of 5'-terminal secondary structure and recruitment of mRNA to the ribosome. ...
... ATP-dependent unwinding of 5'-terminal secondary structure and recruitment of mRNA to the ribosome. ...
Leukaemia Section t(5;11)(q33;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0511q33p13ID1543.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/44691 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2010 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0511q33p13ID1543.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/44691 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2010 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
G protein
... transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA). – The mRNA molecules leave the nucleus and carry information that directs the synthesis (translation) of specific proteins at the ribosome. ...
... transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA). – The mRNA molecules leave the nucleus and carry information that directs the synthesis (translation) of specific proteins at the ribosome. ...
Biology Reading Guide 6 Where all energy ultimately come from Sun
... § DNP all except chemiosmosis in cellular respiration run, so most all energy is lost ...
... § DNP all except chemiosmosis in cellular respiration run, so most all energy is lost ...
Cell signaling - Lectures For UG-5
... SMAD7 competes with other R-SMADs with RI and prevents their phosphorylation. It resides in the nucleus and upon TGF beta receptor activation translocates to the cytoplasm where it binds the RI. SMAD6 binds SMAD4 preventing the binding of R-SMADs with the coSMAD. The levels of I-SMAD increase with T ...
... SMAD7 competes with other R-SMADs with RI and prevents their phosphorylation. It resides in the nucleus and upon TGF beta receptor activation translocates to the cytoplasm where it binds the RI. SMAD6 binds SMAD4 preventing the binding of R-SMADs with the coSMAD. The levels of I-SMAD increase with T ...
Exam 3
... E. glucose-6-phosphatase 13. ______The hormone glucagon will lead to A. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle B. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle C. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver D. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver 14. _ ...
... E. glucose-6-phosphatase 13. ______The hormone glucagon will lead to A. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle B. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle C. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver D. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver 14. _ ...
Master Entrance Exam
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
Extension worksheet – Option C - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... An allosteric, non-competitive inhibitor may combine with an enzyme and cause the shape of the active site to change so that the substrate cannot bind to it. Such inhibitors, if they bind reversibly, can act in end-product inhibition of metabolic reactions. End-product inhibition is an example of ne ...
... An allosteric, non-competitive inhibitor may combine with an enzyme and cause the shape of the active site to change so that the substrate cannot bind to it. Such inhibitors, if they bind reversibly, can act in end-product inhibition of metabolic reactions. End-product inhibition is an example of ne ...
Vragen voor tentamen Protein Engineering (8S080)
... The group of Luc Brunsveld studies nuclear receptor proteins for hormones such as estrogen. Nuclear receptors are transcription factors that consist of a DNA binding domain and a ligand binding domain. The ligand binding domain (LBD) contains a binding site for estrogen. The activity of nuclear rece ...
... The group of Luc Brunsveld studies nuclear receptor proteins for hormones such as estrogen. Nuclear receptors are transcription factors that consist of a DNA binding domain and a ligand binding domain. The ligand binding domain (LBD) contains a binding site for estrogen. The activity of nuclear rece ...
Carbohydrates
... Macromolecule made of lipids and proteins Hydrophilic allows fats to be sheilded from the ...
... Macromolecule made of lipids and proteins Hydrophilic allows fats to be sheilded from the ...
Cell Respiration ch. 9
... pumped into the inner membrane space from the electron transport chain; this enzyme harnesses the flow of H+ back into the matrix to phosphorylate ADP to ATP (oxidative phosphorylation) ...
... pumped into the inner membrane space from the electron transport chain; this enzyme harnesses the flow of H+ back into the matrix to phosphorylate ADP to ATP (oxidative phosphorylation) ...
PowerPoint - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 20 different AA’s used by ribosomes to make proteins The R group is the deciding factor as to what the AA is as all the amino and carboxyl ends are used in bonding the AA’s together There are some modifications to the AA in a polypeptide chain – proline modifies to hydroxyproline when in collagen – ...
... 20 different AA’s used by ribosomes to make proteins The R group is the deciding factor as to what the AA is as all the amino and carboxyl ends are used in bonding the AA’s together There are some modifications to the AA in a polypeptide chain – proline modifies to hydroxyproline when in collagen – ...
M6697 - Sigma
... apoptosis, can be a regulated and programmed mechanism.1 One specific form of programmed necrosis that depends on the serine/threonine kinase activity of RIP kinase proteins was termed necroptosis.2 RIP3 has been identified as a key protein in TNF-induced necroptosis and MLKL (mixed lineage kinase d ...
... apoptosis, can be a regulated and programmed mechanism.1 One specific form of programmed necrosis that depends on the serine/threonine kinase activity of RIP kinase proteins was termed necroptosis.2 RIP3 has been identified as a key protein in TNF-induced necroptosis and MLKL (mixed lineage kinase d ...
Option C - IBperiod5
... competitively inhibits it. Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme somewhere other than the active site and cause a conformational change in the enzyme, inhibiting its function. Example: the enzyme phosphofructokinase ( part of glycolysis) normally has the substrate fructose-6 phosphate, but x ...
... competitively inhibits it. Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme somewhere other than the active site and cause a conformational change in the enzyme, inhibiting its function. Example: the enzyme phosphofructokinase ( part of glycolysis) normally has the substrate fructose-6 phosphate, but x ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 21. What are perturbations? How are they helpful in analyzing flux? 22. Describe Pentose phosphate pathway and its regulation. 23. Give a schematic representation of various types of enzyme inhibition. 24. What are secondary metabolites? Discuss its production in a plant cell. 25. What are the crite ...
... 21. What are perturbations? How are they helpful in analyzing flux? 22. Describe Pentose phosphate pathway and its regulation. 23. Give a schematic representation of various types of enzyme inhibition. 24. What are secondary metabolites? Discuss its production in a plant cell. 25. What are the crite ...
Document
... Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate ...
... Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate ...
Nutrition and metabolism
... • When glucose levels are very low the liver can synthesize glucose – Amino acids + glycerol to produce glucose – Prevents hypoglycemia ...
... • When glucose levels are very low the liver can synthesize glucose – Amino acids + glycerol to produce glucose – Prevents hypoglycemia ...
Exam 2 Study Guide
... a. An agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell b. An agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it c. An agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is unable to be metabolized d. An agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+ 3. In a GPCR signal ...
... a. An agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell b. An agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it c. An agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is unable to be metabolized d. An agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+ 3. In a GPCR signal ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... transfer of the peptidyl tRNA from the A to the P site 20. Beta 2 receptor stimulation will increase aqueous production by: Increasing the activity of the NA/K ATPase via more phosphorylation 21. What is the relationship between the coding DNA strand and RNA transcript produced? The sequence is the ...
... transfer of the peptidyl tRNA from the A to the P site 20. Beta 2 receptor stimulation will increase aqueous production by: Increasing the activity of the NA/K ATPase via more phosphorylation 21. What is the relationship between the coding DNA strand and RNA transcript produced? The sequence is the ...
Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. ... Erika Lacy: Cell Biology & Neuroscience
... Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Protein Interactions in Bacteria Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assay is a complementation-based technique used to study protein interactions. One benefit of this approach is ...
... Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Protein Interactions in Bacteria Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assay is a complementation-based technique used to study protein interactions. One benefit of this approach is ...
doc Midterm 2001. Bio 201
... liver cell membranes has a Km of 5 mM, entry of glucose into liver will a) be saturated at normal blood gluose concentrations b) be faster at normal blood glucose concentrations than in normal people c) be proportional to the concentration of blood glucose d) be slower at normal blood glucose concen ...
... liver cell membranes has a Km of 5 mM, entry of glucose into liver will a) be saturated at normal blood gluose concentrations b) be faster at normal blood glucose concentrations than in normal people c) be proportional to the concentration of blood glucose d) be slower at normal blood glucose concen ...
Slide 1
... (glycogenolysis). Adrenals will release cortisol if levels stay too low to enhance breakdown of protein in muscles to release amino acids so the liver can pick up the amino acids and make them into glucose (gluconeogenesis). ...
... (glycogenolysis). Adrenals will release cortisol if levels stay too low to enhance breakdown of protein in muscles to release amino acids so the liver can pick up the amino acids and make them into glucose (gluconeogenesis). ...
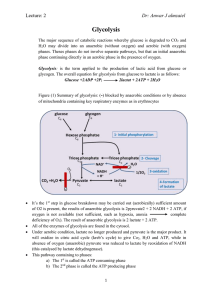
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... concentration of g-6-p inhibits the enzyme and glucose will accumulate and not change to g6-p, but if the g-6-p is removed by anyway the enzyme will act again and glucose will convert to g-6-p, this is the first mechanism of regulation in glycolysis g-6-p is an important compound at the junction of ...
... concentration of g-6-p inhibits the enzyme and glucose will accumulate and not change to g6-p, but if the g-6-p is removed by anyway the enzyme will act again and glucose will convert to g-6-p, this is the first mechanism of regulation in glycolysis g-6-p is an important compound at the junction of ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).