Lecture 11
... 3. The allosteric regulators bind to sites that are not active sites and elicit their effects by causing a Change in Shape of the Catalytic Subunit ...
... 3. The allosteric regulators bind to sites that are not active sites and elicit their effects by causing a Change in Shape of the Catalytic Subunit ...
CHAPTER 8: Cell Respiration Student Notes Definitions and
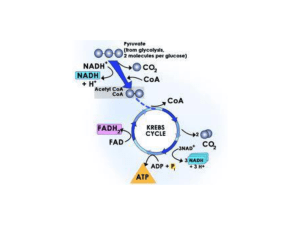
... Pyruvate is decarboxylated and attached to Coenzyme A after glycolysis. What are the final products of that conversion? ...
... Pyruvate is decarboxylated and attached to Coenzyme A after glycolysis. What are the final products of that conversion? ...
Abstract
... Protein kinases mediate most intracellular signal transduction via the reversible phosphorylation on serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue of specific protein/peptide substrates. Such phosphorylation is employed by all eukaryotes in regulation of enzyme activity, protein-protein interaction, subcel ...
... Protein kinases mediate most intracellular signal transduction via the reversible phosphorylation on serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue of specific protein/peptide substrates. Such phosphorylation is employed by all eukaryotes in regulation of enzyme activity, protein-protein interaction, subcel ...
New partners for protein kinases - Journal of Molecular Cell Biology
... The review paper by Dr Delia and Buscemi’s groups systematically reviewed the research progresses of CHK2 kinase, particularly focusing on its responses to DNA damage. CHK2 is well known as a nuclear serine/threonine protein kinase involved in the spreading of DNA damage signal through a phosphoryla ...
... The review paper by Dr Delia and Buscemi’s groups systematically reviewed the research progresses of CHK2 kinase, particularly focusing on its responses to DNA damage. CHK2 is well known as a nuclear serine/threonine protein kinase involved in the spreading of DNA damage signal through a phosphoryla ...
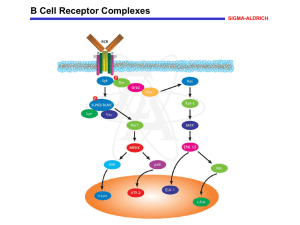
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... B Cell Receptor Complexes Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation plays an important role in regulating B cell function. In particular, binding of antigen to the B cell receptor (BCR) promotes the activation of several protein tyrosine kinases that, in conjunction with protein tyrosine phosphatases, al ...
... B Cell Receptor Complexes Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation plays an important role in regulating B cell function. In particular, binding of antigen to the B cell receptor (BCR) promotes the activation of several protein tyrosine kinases that, in conjunction with protein tyrosine phosphatases, al ...
Krebs and ETC powerpoint
... lactic acid bacteria growing in a water and flour medium. Lactobacilli, especially L. casei and L. brevis, are some of the most common beer spoilage organisms. The species operate by lowering the pH of the fermenting substance by creating the lactic acid, neutralising it to the desired extent. ...
... lactic acid bacteria growing in a water and flour medium. Lactobacilli, especially L. casei and L. brevis, are some of the most common beer spoilage organisms. The species operate by lowering the pH of the fermenting substance by creating the lactic acid, neutralising it to the desired extent. ...
Abstract Document Sample - graduate school of biostudies, kyoto
... FD, a bZIP transcription factor, preferentially expressed in the shoot apical meristem is required for FT protein to promote flowering. FD and FT proteins interact and act as a complex at the shoot apical meristem (SAM) to promote flowering. FD contains a possible phosphorylation sequence in its C-t ...
... FD, a bZIP transcription factor, preferentially expressed in the shoot apical meristem is required for FT protein to promote flowering. FD and FT proteins interact and act as a complex at the shoot apical meristem (SAM) to promote flowering. FD contains a possible phosphorylation sequence in its C-t ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).