chapter_3_study_guide
... __________________________ explains important observations such as the law of constant composition. The main ideas of this theory are: 1. _________________ are made up of tiny particles called ________. 2. All atoms of a given element are ___________. 3. The atoms of a given element are ___________ ...
... __________________________ explains important observations such as the law of constant composition. The main ideas of this theory are: 1. _________________ are made up of tiny particles called ________. 2. All atoms of a given element are ___________. 3. The atoms of a given element are ___________ ...
The Nuclear Atom
... Democritus (460 B.C. – 370 B.C.) • first to suggest the existence of “atoms” ...
... Democritus (460 B.C. – 370 B.C.) • first to suggest the existence of “atoms” ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Review Guide
... 1.1 Atoms are the smallest form of elements Answer each question. You may use your book, reading guides, or reinforcement guides to help you. Answers do not have to be in complete sentences. 1. What does the atomic number tell you? 2. Where are electrons located in an atom and what is their charge? ...
... 1.1 Atoms are the smallest form of elements Answer each question. You may use your book, reading guides, or reinforcement guides to help you. Answers do not have to be in complete sentences. 1. What does the atomic number tell you? 2. Where are electrons located in an atom and what is their charge? ...
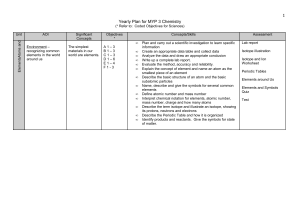
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... environment and that we cannot survive without them - recognizing common chemical reactions in our world - understanding what happens in a chemical change - noticing and identifying common chemicals we use in our everyday lives ...
... environment and that we cannot survive without them - recognizing common chemical reactions in our world - understanding what happens in a chemical change - noticing and identifying common chemicals we use in our everyday lives ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... Most of the mass of the atom and all of its positive charge is contained in a tiny core region called the nucleus The nucleus contains protons and neutrons (Chadwick, 1932) that have approximately the same mass The number of protons is the atomic number (Z) The total number of protons and ne ...
... Most of the mass of the atom and all of its positive charge is contained in a tiny core region called the nucleus The nucleus contains protons and neutrons (Chadwick, 1932) that have approximately the same mass The number of protons is the atomic number (Z) The total number of protons and ne ...
“earth, air, fire and water" matter was composed of small particles
... mass of reactants in the container before a chemical reaction was equal to the mass of the products after the reaction (Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter) Law of Conservation of Mass (Matter)- ...
... mass of reactants in the container before a chemical reaction was equal to the mass of the products after the reaction (Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter) Law of Conservation of Mass (Matter)- ...
Chemistry lecture notes
... of protons), but a different atomic mass number (a different number of neutrons). Isotopes behave the same chemically, because they are the same element. The only difference is that one is heavier than the other, because of the additional neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are both i ...
... of protons), but a different atomic mass number (a different number of neutrons). Isotopes behave the same chemically, because they are the same element. The only difference is that one is heavier than the other, because of the additional neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are both i ...
Physical Science Notes–Ch. 17-Glencoe
... Blue squares are ____________ and are left of the zig zag line. Yellow squares are _____________________and are right of the zig zag line. Green squares are ______________________________________and are along the zig zag line. ...
... Blue squares are ____________ and are left of the zig zag line. Yellow squares are _____________________and are right of the zig zag line. Green squares are ______________________________________and are along the zig zag line. ...
Chemistry- History of the Atom Notes Democritus
... 3. Law of Multiple Proportions(1803)- if two or more different compounds contain the same elements, then the ratio of masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small, whole numbers. (Example: water (H2O) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) both cont ...
... 3. Law of Multiple Proportions(1803)- if two or more different compounds contain the same elements, then the ratio of masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small, whole numbers. (Example: water (H2O) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) both cont ...
File
... 1) Atomic number: Number of protons in the nucleus 2) Chemical symbol: One or two letter symbols that abbreviate an element’s name. 3) Atomic mass: An average of of an element’s protons and neutrons in all of its isotopes. ...
... 1) Atomic number: Number of protons in the nucleus 2) Chemical symbol: One or two letter symbols that abbreviate an element’s name. 3) Atomic mass: An average of of an element’s protons and neutrons in all of its isotopes. ...
Homework 1B1 - 3 - Uddingston Grammar School
... (a) Complete the diagram to show how the electrons are arranged. You may wish to use the data booklet to help you. ...
... (a) Complete the diagram to show how the electrons are arranged. You may wish to use the data booklet to help you. ...
C2.1 Key Terms Atomic number: The number of protons in the
... In chemistry, space around a nucleus that can be occupied by electrons, usually drawn as a circle. Also referred to as shells. Groups: Columns in the periodic table, containing elements with similar properties. Isotopes: Atoms of an element with the same number of protons and electrons but with a di ...
... In chemistry, space around a nucleus that can be occupied by electrons, usually drawn as a circle. Also referred to as shells. Groups: Columns in the periodic table, containing elements with similar properties. Isotopes: Atoms of an element with the same number of protons and electrons but with a di ...
File
... Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. • H2O ...
... Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. • H2O ...
Any substance that cannot be decomposed into
... Classification of Elements in the Periodic Table The periodic table provides an easy way to identify related groups of elements. Those elements on the left of the periodic table are base-forming, while those on the right are acid-forming (see acid and base). Those in between can be either. They for ...
... Classification of Elements in the Periodic Table The periodic table provides an easy way to identify related groups of elements. Those elements on the left of the periodic table are base-forming, while those on the right are acid-forming (see acid and base). Those in between can be either. They for ...
Word format
... Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers are called _________________ Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called ...
... Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers are called _________________ Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called ...
pdf format
... Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers are called _________________ Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called ...
... Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers are called _________________ Example: carbon can exist in 3 forms: _______________________________ The average weight of an atom of any element, taking into account the relative abundances of the different isotopes of that element, is called ...
Chemistry Test Review - Greenslime Home Page
... can’t be broken down; basic part of matter b. Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances containing only 1 type of atom c. Compound – two or more different elements chemically combined d. Molecule – two or more atoms, they can be the same OR different, chemically combin ...
... can’t be broken down; basic part of matter b. Element – a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances containing only 1 type of atom c. Compound – two or more different elements chemically combined d. Molecule – two or more atoms, they can be the same OR different, chemically combin ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... Dalton's atomic theory agrees with modern atomic theory except for what? The deflection of cathode rays in Thomson's experiments was evidence of the ____ nature of electrons. Whose series of experiments identified the nucleus of the atom? What happened to the alpha particles in Rutherford's experime ...
... Dalton's atomic theory agrees with modern atomic theory except for what? The deflection of cathode rays in Thomson's experiments was evidence of the ____ nature of electrons. Whose series of experiments identified the nucleus of the atom? What happened to the alpha particles in Rutherford's experime ...
Atomic Structure and the Elements
... Mendeleev – A Russian chemist, developed a periodic table of elements. He realized that the chemical and physical properties of the elements repeat in an orderly way when elements are organized according to increasing atomic mass. Click here for biography on Mendeleev ...
... Mendeleev – A Russian chemist, developed a periodic table of elements. He realized that the chemical and physical properties of the elements repeat in an orderly way when elements are organized according to increasing atomic mass. Click here for biography on Mendeleev ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.