ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE chapter three
... – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
... – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
Full Text PDF - Science and Education Publishing
... (ii) superheavy elements of the “island of stability” (blue symbols), predicted time ago. The vertical red bar points out the maximum predicted value of Z = 137. The dashed black line corresponds to number of neutrons = number of protons ...
... (ii) superheavy elements of the “island of stability” (blue symbols), predicted time ago. The vertical red bar points out the maximum predicted value of Z = 137. The dashed black line corresponds to number of neutrons = number of protons ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Compare and contrast the evolution of atomic theories, including Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr and quantum mechanics (4.1, 4.2, 5.2) Define and discuss the structure of an atom including the locations, relative masses, and charges of electrons, neutrons and protons (4.3) Use th ...
... Compare and contrast the evolution of atomic theories, including Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr and quantum mechanics (4.1, 4.2, 5.2) Define and discuss the structure of an atom including the locations, relative masses, and charges of electrons, neutrons and protons (4.3) Use th ...
Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
... Example…Cesium has three known isotopes: Cs – 133, Cs – 132, and Cs – 134. Their abundances in nature are 75%, 20%, and 5% respectively. What is the average atomic mass of cesium? Steps #1, #2 and #3 can be performed together: ...
... Example…Cesium has three known isotopes: Cs – 133, Cs – 132, and Cs – 134. Their abundances in nature are 75%, 20%, and 5% respectively. What is the average atomic mass of cesium? Steps #1, #2 and #3 can be performed together: ...
Notes on Atomic Structure Structure of Atoms Atoms are composed
... The periodic table is a list of the elements that make up matter. It is organized by increasing atomic number. The Atomic Number shows the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It identifies the type of atom/element. The atomic number also equals the number of electrons whenever the atom is n ...
... The periodic table is a list of the elements that make up matter. It is organized by increasing atomic number. The Atomic Number shows the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It identifies the type of atom/element. The atomic number also equals the number of electrons whenever the atom is n ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... Draw Carbon Nitrogen atomic number: 7 atomic mass: 14 Carbon atomic number 6 atomic mass: 12 ...
... Draw Carbon Nitrogen atomic number: 7 atomic mass: 14 Carbon atomic number 6 atomic mass: 12 ...
Chapter 4 Review Worksheet. Name
... 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element an arrangement of elements according to similarities in their properties a vertical column of elements in the periodic table a horizontal row of the periodic table stream of electrons produced at the nega ...
... 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element an arrangement of elements according to similarities in their properties a vertical column of elements in the periodic table a horizontal row of the periodic table stream of electrons produced at the nega ...
Atoms - eChalk
... elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or the source of the compound. • 3) The law of multiple proportions- if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combines with a cert ...
... elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or the source of the compound. • 3) The law of multiple proportions- if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combines with a cert ...
Atomic Structure
... 19. Lead has 4 naturally occurring isotopes. Listed below are symbols for these isotopes along with their percent abundance. Using this information, calculate the “average” atomic mass of Pb. (Note: You may complete this calculation on the back of a one of the sheets in this packet). 122 Pb ...
... 19. Lead has 4 naturally occurring isotopes. Listed below are symbols for these isotopes along with their percent abundance. Using this information, calculate the “average” atomic mass of Pb. (Note: You may complete this calculation on the back of a one of the sheets in this packet). 122 Pb ...
Atomic Structure
... •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons and electrons. •To find the most common isotope round the atomic mass to nearest whole number. -Ex: Carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon Which isotope is the ...
... •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons and electrons. •To find the most common isotope round the atomic mass to nearest whole number. -Ex: Carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon Which isotope is the ...
Extension 18.2: Isotopes
... essentially determines its mass (the nucleus’s mass is approximately equal to the mass number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
... essentially determines its mass (the nucleus’s mass is approximately equal to the mass number times the proton’s mass): M nucleus ≈ A x mproton. So different forms of an element may have different mass. ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
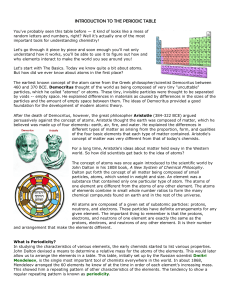
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... After the death of Democritus, however, the great philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BCE) argued persuasively against the concept of atoms. Aristotle thought the earth was composed of matter, which he believed was made up of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. He explained the differences in dif ...
... After the death of Democritus, however, the great philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BCE) argued persuasively against the concept of atoms. Aristotle thought the earth was composed of matter, which he believed was made up of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. He explained the differences in dif ...
Notes matter energy
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
Unit 3 Note Outline
... History of the Atom Democritis - Ancient Greek Philosopher used the word Two discoveries led to the rebirth of the idea of the atom 1. Lavoisier 2. Proust (1799) This led to: ...
... History of the Atom Democritis - Ancient Greek Philosopher used the word Two discoveries led to the rebirth of the idea of the atom 1. Lavoisier 2. Proust (1799) This led to: ...
Atomic Theory NS
... 1. Elements are composed of indivisible particles called _____________________. 2. Atoms of the same element are ____________________________ & atoms of different elements are _______________________________ from one another. 3. Atoms can be physically combined or chemically combined in ____________ ...
... 1. Elements are composed of indivisible particles called _____________________. 2. Atoms of the same element are ____________________________ & atoms of different elements are _______________________________ from one another. 3. Atoms can be physically combined or chemically combined in ____________ ...
Notes#5 Bill nye atoms
... 2. What are atoms? ____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. The word “Atom” comes from a Greek word that means _________________. 4. The heavy particles of an atom are in the _____ ...
... 2. What are atoms? ____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. The word “Atom” comes from a Greek word that means _________________. 4. The heavy particles of an atom are in the _____ ...
John Dalton William Crookes J.J. Thomson Ernest Rutherford
... -Proved that matter is made up of Atoms - Different elements have different masses ...
... -Proved that matter is made up of Atoms - Different elements have different masses ...
PowerPoint
... • He determined that most of the atom was made up of 'empty space'. • Before this, everyone figured atoms were solid mixes of all the different particles. • This is how we know the weight of an atom is all in a small nucleus in the center. ...
... • He determined that most of the atom was made up of 'empty space'. • Before this, everyone figured atoms were solid mixes of all the different particles. • This is how we know the weight of an atom is all in a small nucleus in the center. ...
Atomic Structure Video Guide
... 7. A proton weighs ___ __________________________________. Neutrons also weigh ____ _________________. 8. Neutrons are a subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom and have _______ _______________. 9. Protons and Neutrons take up approximately 1/100,000th of an atom’s ________________. 10. _______ ...
... 7. A proton weighs ___ __________________________________. Neutrons also weigh ____ _________________. 8. Neutrons are a subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom and have _______ _______________. 9. Protons and Neutrons take up approximately 1/100,000th of an atom’s ________________. 10. _______ ...
Chapter 4 notes outline
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
200
... • Q Dalton said all atoms are identical. Right or wrong… explain. • A Wrong, isotopes are the same atom with different numbers of neutrons. ...
... • Q Dalton said all atoms are identical. Right or wrong… explain. • A Wrong, isotopes are the same atom with different numbers of neutrons. ...
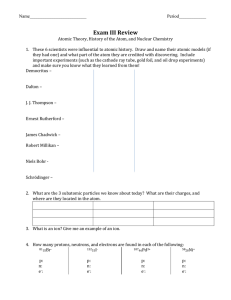
Exam III Review
... 15. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment indicated that a. The nucleus of an atom occupies most of an atom’s volume. b. Positive charges are dispersed throughout the atom. c. Positive charges are concentrated in a very small core at the atom’s center. d. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. ...
... 15. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment indicated that a. The nucleus of an atom occupies most of an atom’s volume. b. Positive charges are dispersed throughout the atom. c. Positive charges are concentrated in a very small core at the atom’s center. d. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. ...
Chapter 4 Review Worksheet
... 3. Use the following information to determine the atomic mass of chlorine. Two isotopes are known: chlorine-35 (mass = 34.97 amu) and chlorine-37 (mass = 36.97 amu). The relative abundance’s are 75.4% and 24. 6%, respectively. ...
... 3. Use the following information to determine the atomic mass of chlorine. Two isotopes are known: chlorine-35 (mass = 34.97 amu) and chlorine-37 (mass = 36.97 amu). The relative abundance’s are 75.4% and 24. 6%, respectively. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.