Ch L14 Atoms Elements the Mole
... This unit is designed to bring the infinitesimally small numbers associated with nuclear particles and single atoms up to something we can work with in the real world A mole is defined as the fundamental SI unit used to measure the amount of a substance, or a collection of 6.022137 x 1023 particles. ...
... This unit is designed to bring the infinitesimally small numbers associated with nuclear particles and single atoms up to something we can work with in the real world A mole is defined as the fundamental SI unit used to measure the amount of a substance, or a collection of 6.022137 x 1023 particles. ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... 5. Isotopes are atoms of an element that have same number of _________ and ____________ but different number of ___________________. ...
... 5. Isotopes are atoms of an element that have same number of _________ and ____________ but different number of ___________________. ...
Chapter 18 section 1
... Conservation of Mass Investigated combustion and cellular respiration in terms of energy and mass ...
... Conservation of Mass Investigated combustion and cellular respiration in terms of energy and mass ...
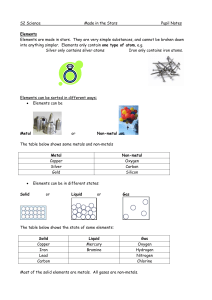
Made in the Stars Notes
... Elements can join together to form compounds. They have to be chemically joined, not just mixed together. A compound is a substance that has more than one kind of atom joined together. For example, if iron joins with oxygen from the air, it forms the compound iron ...
... Elements can join together to form compounds. They have to be chemically joined, not just mixed together. A compound is a substance that has more than one kind of atom joined together. For example, if iron joins with oxygen from the air, it forms the compound iron ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed tog ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed tog ...
Atomic Timeline
... protons & neutrons (an atom is divisible, it is the smallest part of an element) 2. Atoms of on element cannot be converted into atoms of another element by a chemical reaction (nuclear reactions, alter the composition of the nucleus, so convert atoms of one element into ...
... protons & neutrons (an atom is divisible, it is the smallest part of an element) 2. Atoms of on element cannot be converted into atoms of another element by a chemical reaction (nuclear reactions, alter the composition of the nucleus, so convert atoms of one element into ...
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
S1-2-02: What is the basic subatomic structure of an atom?
... S1-2-09: How do you classify matter using: element, compound, atom, molecule, mixture and pure? 6. Find the words from the choices below which match the definitions (One will not be used): Chemistry, Matter, Mass, Volume, Element, Compound, Mixture, Atoms, Molecule a) ...
... S1-2-09: How do you classify matter using: element, compound, atom, molecule, mixture and pure? 6. Find the words from the choices below which match the definitions (One will not be used): Chemistry, Matter, Mass, Volume, Element, Compound, Mixture, Atoms, Molecule a) ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS (also called the LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION): All pure samples of a given compound contain the same proportion of elements by mass ...
... LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS (also called the LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION): All pure samples of a given compound contain the same proportion of elements by mass ...
Development of atomic theory
... energy and spiral into the nucleus. This difficulty was solved by Niels Bohr (1913), who applied the quantum theory developed by Max Planck and Albert Einstein to the problem of atomic structure. Bohr proposed that electrons could circle a nucleus without radiating energy only in orbits for which th ...
... energy and spiral into the nucleus. This difficulty was solved by Niels Bohr (1913), who applied the quantum theory developed by Max Planck and Albert Einstein to the problem of atomic structure. Bohr proposed that electrons could circle a nucleus without radiating energy only in orbits for which th ...
Measuring the Atom
... and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
... and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
CHAPTER 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
section_2_review_set
... creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton +1; neutron 0; electron -1. 6. What two things ...
... creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton +1; neutron 0; electron -1. 6. What two things ...
Atoms and Elements
... More protons than electrons = positive charge. More electrons than protons = negative charge. Same number of protons and electrons = neutral atom. ...
... More protons than electrons = positive charge. More electrons than protons = negative charge. Same number of protons and electrons = neutral atom. ...
Chapter Two - Alfred State College intranet site
... Calculate the atomic mass of an element from the masses and abundances of its isotopes. Determine the number of atoms in a molecule from its chemical formula. Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and explain the usefulness of the table. ...
... Calculate the atomic mass of an element from the masses and abundances of its isotopes. Determine the number of atoms in a molecule from its chemical formula. Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and explain the usefulness of the table. ...
8th Grade Science Notes Chapter 2
... atoms have 6 protons each, oxygen atoms have 8 protons each, etc. Neutral Atoms - most atoms contain the same number of electrons as protons making them electrically neutral. Isotopes - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... atoms have 6 protons each, oxygen atoms have 8 protons each, etc. Neutral Atoms - most atoms contain the same number of electrons as protons making them electrically neutral. Isotopes - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
1 Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of
... suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and _______________________. Dalton's Atomic Theory The modern process of discovery regarding atoms began with John _____________ (1766-1844). By using experimental methods. Dalton transformed Democritus's ideas on atoms ...
... suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and _______________________. Dalton's Atomic Theory The modern process of discovery regarding atoms began with John _____________ (1766-1844). By using experimental methods. Dalton transformed Democritus's ideas on atoms ...
chapter_four
... found outside the nucleus in regions called orbitals Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus of an atom with neutrons, which have no charge There are even smaller particles but we do not study ...
... found outside the nucleus in regions called orbitals Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus of an atom with neutrons, which have no charge There are even smaller particles but we do not study ...
Guided Notes: The Atom
... Millikan-oil drop experiment; found quantity of charge on an _________: carries exactly _____________ of charge, and mass is 1/1840 the mass of a proton Rutherford-1910; __________________ experiment; model of the atom- discovered nucleus and that the atom is mostly empty space ...
... Millikan-oil drop experiment; found quantity of charge on an _________: carries exactly _____________ of charge, and mass is 1/1840 the mass of a proton Rutherford-1910; __________________ experiment; model of the atom- discovered nucleus and that the atom is mostly empty space ...
Ch. 5 notes
... elements at room temperature and normal pressure – Most are solids – Only two are liquids – Gaseous elements are in the top right hand corner except for Hydrogen – The rest are made synthetically (manmade)through nuclear reactions (43, 61, 85, 87, and > 93) ...
... elements at room temperature and normal pressure – Most are solids – Only two are liquids – Gaseous elements are in the top right hand corner except for Hydrogen – The rest are made synthetically (manmade)through nuclear reactions (43, 61, 85, 87, and > 93) ...
Atomic Models
... Democritus (400 BC) - thought that matter was made of particles called ________, but we couldn’t prove this until 2000 years later! Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794) - French chemist - developed.. - his law stated that matter cannot be ___________________________ in a chemical reaction, only changes for ...
... Democritus (400 BC) - thought that matter was made of particles called ________, but we couldn’t prove this until 2000 years later! Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794) - French chemist - developed.. - his law stated that matter cannot be ___________________________ in a chemical reaction, only changes for ...
File
... Vary in mass, but are all atoms of the same element because they have the same number of protons When it is important to distinguish one isotope from another, the mass number will follow the element name o Ex.: Carbon-12 ...
... Vary in mass, but are all atoms of the same element because they have the same number of protons When it is important to distinguish one isotope from another, the mass number will follow the element name o Ex.: Carbon-12 ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Isotopes of an element – Different forms of an element with the same atomic number but with different mass numbers – The atoms of some isotopes are stable – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay ...
... Isotopes of an element – Different forms of an element with the same atomic number but with different mass numbers – The atoms of some isotopes are stable – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.