Prokaryotes
... toxic and the outer membrane protects the pathogens from the defenses of their hosts. Gram-negative bacteria are commonly more resistant than gram-positive species to antibiotics because the outer membrane impedes entry of antibiotics. ...
... toxic and the outer membrane protects the pathogens from the defenses of their hosts. Gram-negative bacteria are commonly more resistant than gram-positive species to antibiotics because the outer membrane impedes entry of antibiotics. ...
Organismal Diversity
... Organisms were once classified into two kingdoms - plants and animals. The organization of some biology curricula still reflects this -- for instance, the Missouri State Legislature's required courses for teacher education in biology specify botany and zoology, but not microbiology or study of fungi ...
... Organisms were once classified into two kingdoms - plants and animals. The organization of some biology curricula still reflects this -- for instance, the Missouri State Legislature's required courses for teacher education in biology specify botany and zoology, but not microbiology or study of fungi ...
PowerPoint
... – Woese and Fox proposed using small subunit (SSU) rRNA nucleotide sequences to assess evolutionary relatedness of organisms ...
... – Woese and Fox proposed using small subunit (SSU) rRNA nucleotide sequences to assess evolutionary relatedness of organisms ...
chapter-1-evaluate-lesson-2-classifying-organisms
... people to classify organisms. He classified animals based on the presence of “red blood”, an animal’s environment, shape, and size. He classified plants according to the structure and size of the plant and whether it was a tree, shrub, or herb. Determining Kingdoms In the 1700’s, Carolus Linnaeu ...
... people to classify organisms. He classified animals based on the presence of “red blood”, an animal’s environment, shape, and size. He classified plants according to the structure and size of the plant and whether it was a tree, shrub, or herb. Determining Kingdoms In the 1700’s, Carolus Linnaeu ...
Infographic: Carbapenemase
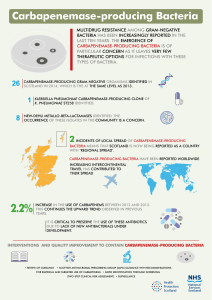
... LAST TEN YEARS. THE EMERGENCE OF CARBAPENEMASE-PRODUCING BACTERIA IS OF PARTICULAR CONCERN AS IT LEAVES VERY FEW THERAPEUTIC OPTIONS FOR INFECTIONS WITH THESE TYPES OF BACTERIA. ...
... LAST TEN YEARS. THE EMERGENCE OF CARBAPENEMASE-PRODUCING BACTERIA IS OF PARTICULAR CONCERN AS IT LEAVES VERY FEW THERAPEUTIC OPTIONS FOR INFECTIONS WITH THESE TYPES OF BACTERIA. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 1. What is the primary criterion in the methodology of cladistics? Common ancestry is the primary criterion used in cladistics. 2. A true clade is: a. monopyletic b. paraphyletic c. polyphyletic 3. Draw an example of a clade: ...
... 1. What is the primary criterion in the methodology of cladistics? Common ancestry is the primary criterion used in cladistics. 2. A true clade is: a. monopyletic b. paraphyletic c. polyphyletic 3. Draw an example of a clade: ...
Domains Kingdom(s)
... Archaea are all prokaryotes (before a nucleus). They have no nucleus. Rather a single circle of DNA. They are unicellular, made of one cell. ...
... Archaea are all prokaryotes (before a nucleus). They have no nucleus. Rather a single circle of DNA. They are unicellular, made of one cell. ...
taxonomy powerpoint
... the first to attempt to classify all living things, and some of his groups are still used today, like the vertebrates and invertebrates, which he called “animals with blood and without blood”. ...
... the first to attempt to classify all living things, and some of his groups are still used today, like the vertebrates and invertebrates, which he called “animals with blood and without blood”. ...
No Slide Title
... • Developed pure culture methods. • Identified cause of anthrax, TB, & cholera. ...
... • Developed pure culture methods. • Identified cause of anthrax, TB, & cholera. ...
Prokaryotes - The first life forms on the planet
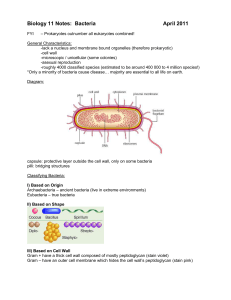
... - Mutualistic symbiotic relations; too numerous to list - Pathogens of animals and plants Structural features - cell wall; peptidiglycan (all Eubacteria); gram positive and gram negative (two variations) - plasma membrane - Shapes of bacteria; cocci = spherical; bacilli = rod-shaped; spirilli = cork ...
... - Mutualistic symbiotic relations; too numerous to list - Pathogens of animals and plants Structural features - cell wall; peptidiglycan (all Eubacteria); gram positive and gram negative (two variations) - plasma membrane - Shapes of bacteria; cocci = spherical; bacilli = rod-shaped; spirilli = cork ...
Paleontology and Life, part 2
... Taxonomic Hierarchy • The Domain is the highest-rank taxon (or taxonomic group) – Within a Domain is the Kingdom – Within a Kingdom is the Phylum, and so on: – Within a Phylum is the Class, followed by the Order, the Family, the Genus and, last, the Species. ...
... Taxonomic Hierarchy • The Domain is the highest-rank taxon (or taxonomic group) – Within a Domain is the Kingdom – Within a Kingdom is the Phylum, and so on: – Within a Phylum is the Class, followed by the Order, the Family, the Genus and, last, the Species. ...
DiscBio_C2 Voc Part 1
... 19. system of biological classification devised by Carolus Linnaeus 20. Archaeans producing methane gas as a by-product of their metabolism 21. the most immediate ancestor that both lineages have in common 22. moment in time when an ancestral group split into 2 separate lineages 23. organelle housin ...
... 19. system of biological classification devised by Carolus Linnaeus 20. Archaeans producing methane gas as a by-product of their metabolism 21. the most immediate ancestor that both lineages have in common 22. moment in time when an ancestral group split into 2 separate lineages 23. organelle housin ...
Bacterial Identification
... • Basic: morphological tests – Gram reaction, size, shape, motility, pigments, etc. – Provide foundational information • But many unrelated bacteria appear similar ...
... • Basic: morphological tests – Gram reaction, size, shape, motility, pigments, etc. – Provide foundational information • But many unrelated bacteria appear similar ...
Chapter 18
... molecules that they engulf & breakdown Some use aerobic respiration and others use fermentation (anaerobic). These processes produce energy ...
... molecules that they engulf & breakdown Some use aerobic respiration and others use fermentation (anaerobic). These processes produce energy ...
ClassificationBacteriaViruses ATA StudyGuide Answers
... 1. Who developed the first classification system that divided organisms into two groups: plants and animals? Aristotle 2. Who developed the binomial nomenclature system of classification that we still use today? Linnaeus 3. How would you write the correct way to write the scientific name of the Nort ...
... 1. Who developed the first classification system that divided organisms into two groups: plants and animals? Aristotle 2. Who developed the binomial nomenclature system of classification that we still use today? Linnaeus 3. How would you write the correct way to write the scientific name of the Nort ...
WISTR Content Teaching Goals: Microbial Life
... 4. Prokaryotic life dominated earth for about 2.5 billion years, during which almost all metabolic cellular functions arose. Eukaryotic cells arose at this time (still unicellular) and multicellular life much later. Humans of course are very recent arrivals. 5. The evolutionary ‘Tree of Life’ consis ...
... 4. Prokaryotic life dominated earth for about 2.5 billion years, during which almost all metabolic cellular functions arose. Eukaryotic cells arose at this time (still unicellular) and multicellular life much later. Humans of course are very recent arrivals. 5. The evolutionary ‘Tree of Life’ consis ...
Lecture 5. Biology A. Taxonomy and Diversity The largest
... most in the domain Bacteria. The third domain is the Eukaryota (eukaryotes: true-nut) and possess internal organelles. [T] Dodson, Figure 3.6, p. 74 The domain Eukaryota is divided into four kingdoms: protists (algae and protozoa; 60,000 named species), fungi (60,000+ named species), plants and anim ...
... most in the domain Bacteria. The third domain is the Eukaryota (eukaryotes: true-nut) and possess internal organelles. [T] Dodson, Figure 3.6, p. 74 The domain Eukaryota is divided into four kingdoms: protists (algae and protozoa; 60,000 named species), fungi (60,000+ named species), plants and anim ...
No Slide Title
... (18th century Swedish naturalist) Classified plants and animals according to similarities in form the more features organisms have in common, the closer the relationship Designed a system in which each organism is given two names. He called this binomial nomenclature His classification system is ...
... (18th century Swedish naturalist) Classified plants and animals according to similarities in form the more features organisms have in common, the closer the relationship Designed a system in which each organism is given two names. He called this binomial nomenclature His classification system is ...
How are bacteria different from viruses?
... acellular entity composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein coat. – Below the resolution of a microscope – Relies on a host – Does not have the properties of cellular life ...
... acellular entity composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein coat. – Below the resolution of a microscope – Relies on a host – Does not have the properties of cellular life ...
File
... (very hot, very salty, in digestive guts) Eubacteria – ‘true’ bacteria – are more common. Both are ‘prokaryotic’ and have a single strand of genetic information floating in the cytoplasm. There is no organized ‘nucleus’. Bacteria – are the oldest and most abundant group of living organisms. Some hav ...
... (very hot, very salty, in digestive guts) Eubacteria – ‘true’ bacteria – are more common. Both are ‘prokaryotic’ and have a single strand of genetic information floating in the cytoplasm. There is no organized ‘nucleus’. Bacteria – are the oldest and most abundant group of living organisms. Some hav ...
Microbial Taxonomy
... جامعة تكريت – كلية طب االسنان “Low G + C gram-positive” bacteria Divided into 3 classes » Class I – Clostridia; includes genera Clostridium Class II – Mollicutes; bacteria in this class cannot make peptidoglycan and lack cell walls; includes genera Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma, and others » Class II ...
... جامعة تكريت – كلية طب االسنان “Low G + C gram-positive” bacteria Divided into 3 classes » Class I – Clostridia; includes genera Clostridium Class II – Mollicutes; bacteria in this class cannot make peptidoglycan and lack cell walls; includes genera Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma, and others » Class II ...