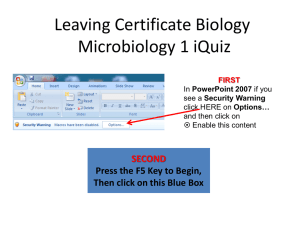
first lecture
... Taxonomy includes: classification – orderly arrangement of organisms into groups nomenclature – assigning names identification – discovering and recording traits of organisms for placement into taxonomic schemes ...
... Taxonomy includes: classification – orderly arrangement of organisms into groups nomenclature – assigning names identification – discovering and recording traits of organisms for placement into taxonomic schemes ...
Bacteria in your life HW
... 10. THINKING QUESTION: Many foods are labeled “vacuum packed.” What does this mean? How can this help to prevent food from spoiling? What does this have to do with bacteria? ...
... 10. THINKING QUESTION: Many foods are labeled “vacuum packed.” What does this mean? How can this help to prevent food from spoiling? What does this have to do with bacteria? ...
What is a Microbe?
... German bacteriologist was the first to cultivate anthrax bacteria outside the body using blood serum at body temperature. Building on pasteur's ...
... German bacteriologist was the first to cultivate anthrax bacteria outside the body using blood serum at body temperature. Building on pasteur's ...
Chapter 17: Classification & Introduction to Taxonomy
... Kingdom largest, most general group Phylum called a division with plants ...
... Kingdom largest, most general group Phylum called a division with plants ...
Bacteria and Germs
... – Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Botulism – improperly canned foods • E. coli – improperly cooked beef • Salmonella – improperly cooked chicken ...
... – Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Botulism – improperly canned foods • E. coli – improperly cooked beef • Salmonella – improperly cooked chicken ...
Bacteria Notes Pre AP Teacher 14-15
... II. Kingdom Eubacteria (true bacteria) text p. 471 Bacteria are located everywhere – air, water, land, on and in living organisms, including people. A. General Characteristics 1. All are – unicellular 2. All are – prokaryotic (no nucleus) 3. Can live in both aerobic (with O2) and anaerobic (without ...
... II. Kingdom Eubacteria (true bacteria) text p. 471 Bacteria are located everywhere – air, water, land, on and in living organisms, including people. A. General Characteristics 1. All are – unicellular 2. All are – prokaryotic (no nucleus) 3. Can live in both aerobic (with O2) and anaerobic (without ...
GHS BIOLOGY SENIOR 1 AUG 2012 TIME
... 1. Which of the following parts of a cell can be used to sort out plants from fungi. A. Cellulose cell wall B. Cytoplasm C. Nucleus D. Vacuole 2. What is a species? A. Living organisms in the same environment. B. A population of many classes of organisms. C. A group of organisms that breed together ...
... 1. Which of the following parts of a cell can be used to sort out plants from fungi. A. Cellulose cell wall B. Cytoplasm C. Nucleus D. Vacuole 2. What is a species? A. Living organisms in the same environment. B. A population of many classes of organisms. C. A group of organisms that breed together ...
Kingdom Monera
... Monerans can get energy in many ways • Autotrophic: can make their own food from the sun • Heterotrophic: can get energy from the matter in their environment (food) ...
... Monerans can get energy in many ways • Autotrophic: can make their own food from the sun • Heterotrophic: can get energy from the matter in their environment (food) ...
Archaea and Bacteria Chapter 27
... a. These prokaryotic organisms of ancient origin discovered first living in extreme environments. b. Archaea lack peptidoglycan in cell wall. c. Like bacteria archaea are prokaryotes, divide by fission and have circular DNA. d. Like Eukarya, some Archaea have histones associated with DNA e. Introns ...
... a. These prokaryotic organisms of ancient origin discovered first living in extreme environments. b. Archaea lack peptidoglycan in cell wall. c. Like bacteria archaea are prokaryotes, divide by fission and have circular DNA. d. Like Eukarya, some Archaea have histones associated with DNA e. Introns ...
Chapter 20 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea
... The viruses are a biological enigma. They have a DNA or RNA genome, but they can reproduce only by using the metabolic machinery of a host cell. Viruses are noncellular, and therefore cannot be assigned a two-part binomial name, as are organisms. In 1884, Pasteur suspected something smaller than bac ...
... The viruses are a biological enigma. They have a DNA or RNA genome, but they can reproduce only by using the metabolic machinery of a host cell. Viruses are noncellular, and therefore cannot be assigned a two-part binomial name, as are organisms. In 1884, Pasteur suspected something smaller than bac ...
Unit 7 NOTES: The Classification of Living Things
... Taxonomy—the science of classifying living things. Somebody who does this for a living is called a taxonomist. Binomial System—Using the Genus and the species name to classify an organism. Ex: Homo sapiens = *Note: The Genus name is capitalized, the species name is lower-case. Order of Classificatio ...
... Taxonomy—the science of classifying living things. Somebody who does this for a living is called a taxonomist. Binomial System—Using the Genus and the species name to classify an organism. Ex: Homo sapiens = *Note: The Genus name is capitalized, the species name is lower-case. Order of Classificatio ...
1. List unique characteristics that distinguish archaea from bacteria.
... organic carbon source (unique to some prokaryotes) Chemoheterotrophs must obtain organic molecules for energy and as a carbon source - examples: most bacteria and most eukaryotes ...
... organic carbon source (unique to some prokaryotes) Chemoheterotrophs must obtain organic molecules for energy and as a carbon source - examples: most bacteria and most eukaryotes ...
PN-II-RU-TE-2012-3 “Retrieving new bacterial isolates for potential
... analysis of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene. These strains shared 92-100% similarity values with the type strains of bacterial species with validly published names. Pure cultures of several potential new genera and species were obtained, mainly belonging to the bacterial phyla Proteobacteria and Bacterio ...
... analysis of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene. These strains shared 92-100% similarity values with the type strains of bacterial species with validly published names. Pure cultures of several potential new genera and species were obtained, mainly belonging to the bacterial phyla Proteobacteria and Bacterio ...
Prokaryotes represent a broad group of organisms that for many
... proposed in 1968, has become a popular standard and with some refinement is still used in many works, or forms the basis for newer multi-kingdom systems. The Monerans include all of the prokaryotic cells and reflects collectively close to 4 billion years of evolution. Until recently (the last 10 – 2 ...
... proposed in 1968, has become a popular standard and with some refinement is still used in many works, or forms the basis for newer multi-kingdom systems. The Monerans include all of the prokaryotic cells and reflects collectively close to 4 billion years of evolution. Until recently (the last 10 – 2 ...
Prokaryotes
... 4. Bacterial cell wall is composed of ______________. Gram positive bacteria have _______ peptidoglycan while Gram negative bacteria have ____________ peptidoglycan. 5. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which ...
... 4. Bacterial cell wall is composed of ______________. Gram positive bacteria have _______ peptidoglycan while Gram negative bacteria have ____________ peptidoglycan. 5. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which ...
Characteristics of pathogenic bacteria
... variety of lifestyles. Some of them are free living, not requiring other organisms for their survival, and existing in everything from the soil and fresh water to extreme environments such as deep ocean volcanic vents and radioactive waste, for example. Some bacteria can be beneficial to other organ ...
... variety of lifestyles. Some of them are free living, not requiring other organisms for their survival, and existing in everything from the soil and fresh water to extreme environments such as deep ocean volcanic vents and radioactive waste, for example. Some bacteria can be beneficial to other organ ...