Classification Systems Change as Scientists Learn More
... • Usually 3 groups: mushroom, yeast, & molds. Fungi take in nutrients from their surroundings instead of eating or using sunlight. • Stay rooted in 1 place (like plants), most have cell walls too. • Many act as decomposers (break down dead/decaying material into simpler parts that can be absorbed or ...
... • Usually 3 groups: mushroom, yeast, & molds. Fungi take in nutrients from their surroundings instead of eating or using sunlight. • Stay rooted in 1 place (like plants), most have cell walls too. • Many act as decomposers (break down dead/decaying material into simpler parts that can be absorbed or ...
Classification of All Living Things
... This two part system is called binomial nomenclature Remember the rules Capitalize the genus Lower case species Underline or italics both Use Latin terms to describe ...
... This two part system is called binomial nomenclature Remember the rules Capitalize the genus Lower case species Underline or italics both Use Latin terms to describe ...
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISMS
... CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISMS NOTES 1. There are _____ billion species that have been named. This only accounts for _____% of all the organisms that have lived on Earth! 2. ________________________________ is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities (how they ...
... CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISMS NOTES 1. There are _____ billion species that have been named. This only accounts for _____% of all the organisms that have lived on Earth! 2. ________________________________ is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities (how they ...
Document
... • 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil • 1 million in a milliliter of freshwater • Approximately 10x as many bacterial cells as human cells in the human body – most on skin & digestive tract ...
... • 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil • 1 million in a milliliter of freshwater • Approximately 10x as many bacterial cells as human cells in the human body – most on skin & digestive tract ...
Classification of Organisms Chapter 17
... • The science & process of classifying living things. • Categorized into groups; subdivide these into smaller ...
... • The science & process of classifying living things. • Categorized into groups; subdivide these into smaller ...
Scientific American, February 2010, p
... Most bacteria are well-behaved companions. Indeed, if you are ever feeling lonely, remember that the trillions of microbes living in and on the average human body outnumber the human cells by a ratio of 10 to one. Of all the tens of thousands of known bacterial species, only about 100 are renegades ...
... Most bacteria are well-behaved companions. Indeed, if you are ever feeling lonely, remember that the trillions of microbes living in and on the average human body outnumber the human cells by a ratio of 10 to one. Of all the tens of thousands of known bacterial species, only about 100 are renegades ...
Bacteria - Part One
... Chapter #20 : Bacteria and Viruses I. Bacteria A. Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote – a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus/major organelles. -All prokaryotes used to belong to the Kingdom Monera. -They’re now divided into 2 groups : 1. Kingdom Eubacteria – larger group that is found almost ...
... Chapter #20 : Bacteria and Viruses I. Bacteria A. Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote – a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus/major organelles. -All prokaryotes used to belong to the Kingdom Monera. -They’re now divided into 2 groups : 1. Kingdom Eubacteria – larger group that is found almost ...
bacteria
... Bacteria Prokaryotes Lack nucleus and membrane bound organelles Evolving on Earth for last 2.5 billion years Exist in variety of environments First organisms ...
... Bacteria Prokaryotes Lack nucleus and membrane bound organelles Evolving on Earth for last 2.5 billion years Exist in variety of environments First organisms ...
Bacteria and Viruses
... Work with your shoulder partner to complete the “Classifying Bacteria : Shapes of Bacteria” worksheet. ...
... Work with your shoulder partner to complete the “Classifying Bacteria : Shapes of Bacteria” worksheet. ...
Taxonomy Basics Homework
... 7. Classify the following organisms into one of the three domains (Archaea, Bacteria, & Eukarya) on the lines below after reading their descriptions: a. ______________ Lactobacillus acidophilus is found in yogurt, can only be seen under a microscope and is known to help humans digest food ...
... 7. Classify the following organisms into one of the three domains (Archaea, Bacteria, & Eukarya) on the lines below after reading their descriptions: a. ______________ Lactobacillus acidophilus is found in yogurt, can only be seen under a microscope and is known to help humans digest food ...
Biology 11 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Grouping Species The
... § The broadest category in the classification used by most biologists is the domain. § The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms and three domains. § The three domains are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. § The six kingdoms are Bacteria, Archaea, Protists, Fungi, Plan ...
... § The broadest category in the classification used by most biologists is the domain. § The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms and three domains. § The three domains are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. § The six kingdoms are Bacteria, Archaea, Protists, Fungi, Plan ...
Bacterial Growth Metabolism - King George`s Medical University
... Bacterial Taxonomy Bacterial growth curve Fastidious /non fastidious bacteria ...
... Bacterial Taxonomy Bacterial growth curve Fastidious /non fastidious bacteria ...
Fill in the table with the characteristics and roles/examples for each
... Facultative Anaerobes ...
... Facultative Anaerobes ...
Bacteria and Viruses (SE).
... every 5 minutes. If one bacterium invades the human body, how many bacteria will be present in the body after 3 hours? ...
... every 5 minutes. If one bacterium invades the human body, how many bacteria will be present in the body after 3 hours? ...
Lecture 1 Introduction, History and Microscopy
... have now been prepared for all the major prokaryotic and eukaryotic groups. • A huge database of rRNA sequences exists. For example, the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) contains a large collection of such sequences, now numbering over 100,000. • The universal phylogenetic tree is the road map of li ...
... have now been prepared for all the major prokaryotic and eukaryotic groups. • A huge database of rRNA sequences exists. For example, the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) contains a large collection of such sequences, now numbering over 100,000. • The universal phylogenetic tree is the road map of li ...
Ch. 20 - Organizing Life Notes
... Category 5: Original – Strawberry, Peach, Banana, Vanilla 1. Classification: The grouping of objects or information based on similarities 2. Taxonomy: The branch of biology concerned with the grouping and naming of organisms 3. Taxonomists: ...
... Category 5: Original – Strawberry, Peach, Banana, Vanilla 1. Classification: The grouping of objects or information based on similarities 2. Taxonomy: The branch of biology concerned with the grouping and naming of organisms 3. Taxonomists: ...
Microbiology Chapter 1
... were caused by tiny invisible “wee animalcules” Diseases, they thought, were caused by: ...
... were caused by tiny invisible “wee animalcules” Diseases, they thought, were caused by: ...
Gram positive - Cloudfront.net
... chromosome • Endospore: “cocoon” to protect DNA in harsh timescell wall plasmid ...
... chromosome • Endospore: “cocoon” to protect DNA in harsh timescell wall plasmid ...
Bell Pettigrew Museum of Natural History - synergy
... of carbon dioxide, into larger organic compounds on which the worms feed. There are around 140 species in 2 classes. The relatively small (< 85cm in length) perviatan worms live in soft sediments in shallower waters, while the deepwater vestimentiferans can reach lengths in excess of 2m. Recent mole ...
... of carbon dioxide, into larger organic compounds on which the worms feed. There are around 140 species in 2 classes. The relatively small (< 85cm in length) perviatan worms live in soft sediments in shallower waters, while the deepwater vestimentiferans can reach lengths in excess of 2m. Recent mole ...
Bell Ringer - Effingham County Schools
... a mass of information. c. several variables. d. a single variable. 2. The set of skills or steps that scientists use to answer questions is the a. scientific method c. taxonomy b. controlled experiment d. binomial nomenclature 3. A set of related hypotheses that are supported by evidence may become ...
... a mass of information. c. several variables. d. a single variable. 2. The set of skills or steps that scientists use to answer questions is the a. scientific method c. taxonomy b. controlled experiment d. binomial nomenclature 3. A set of related hypotheses that are supported by evidence may become ...
The Five Kingdoms
... cyanobacteria, and ancient bacteria (archaebacteria). All of these organisms are prokaryotes—which means that they are single-celled and lack distinct unicellular nuclei and membrane-bound organelles Bacteria are the most diverse and abundant organisms on Earth 2. Kingdom Protista—according to W ...
... cyanobacteria, and ancient bacteria (archaebacteria). All of these organisms are prokaryotes—which means that they are single-celled and lack distinct unicellular nuclei and membrane-bound organelles Bacteria are the most diverse and abundant organisms on Earth 2. Kingdom Protista—according to W ...
1409161760.
... A. Crustacea. B. Platyhelminthes. C. Annelida. D. Monera. 20.Which of the following suits an antelope? A. Chordata. B. Nematoda. C. Annelida. D.Coelenterata 21.In the classification of organisms which of the following is the correct hierarchy of the taxonomic groups? A. family genus kingdom class or ...
... A. Crustacea. B. Platyhelminthes. C. Annelida. D. Monera. 20.Which of the following suits an antelope? A. Chordata. B. Nematoda. C. Annelida. D.Coelenterata 21.In the classification of organisms which of the following is the correct hierarchy of the taxonomic groups? A. family genus kingdom class or ...
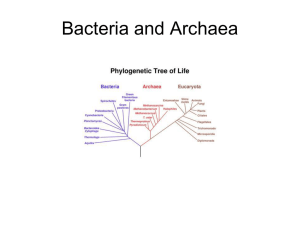
Bacteria and Archaea
... The World of Prokaryotes • They are everywhere, estimated to be 400,000 to be 4 million species • Differ from eukaryotic cells, how? • Pathogens, decomposers, symbiotes ...
... The World of Prokaryotes • They are everywhere, estimated to be 400,000 to be 4 million species • Differ from eukaryotic cells, how? • Pathogens, decomposers, symbiotes ...
4 The dominant form of life on Earth
... Let’s consider the relative biomass of humans and bacteria on Earth. With 6 billion people on Earth, with an average mass of 50 kg, the biomass of humans is 6 × 109 people × 50 kg/person = 3 × 1011 kg. What about bacteria? Let’s consider bacteria in oceans. A rough estimate, which certainly varies w ...
... Let’s consider the relative biomass of humans and bacteria on Earth. With 6 billion people on Earth, with an average mass of 50 kg, the biomass of humans is 6 × 109 people × 50 kg/person = 3 × 1011 kg. What about bacteria? Let’s consider bacteria in oceans. A rough estimate, which certainly varies w ...