Kingdom Monera - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Most bacteria display one of the following basic shapes: ...
... Most bacteria display one of the following basic shapes: ...
Prokaryotes
... A. can cause disease in humans and animals. B. live in unusual habitats or generate unusual metabolic byproducts. C. have the same cell wall composition as other prokaryotes. D. are classified in one phylum. ...
... A. can cause disease in humans and animals. B. live in unusual habitats or generate unusual metabolic byproducts. C. have the same cell wall composition as other prokaryotes. D. are classified in one phylum. ...
Bacteria Poster Questions
... (c) Give one example of each type of bacteria. 3. Some bacteria are said to be Gram negative (G-), and others are said to be Gram positive (G+). (a) Is there a difference in colour between G- and G+ bacteria? If so what is the colour difference? (b) Using the internet write a definition for G- and G ...
... (c) Give one example of each type of bacteria. 3. Some bacteria are said to be Gram negative (G-), and others are said to be Gram positive (G+). (a) Is there a difference in colour between G- and G+ bacteria? If so what is the colour difference? (b) Using the internet write a definition for G- and G ...
Chapter Notes - schallesbiology
... Phylogeny • organizes the diversity of living organisms in the context of evolution. • are based on several types of evidence: 1. Fossil Record 2. Morphology 3. Embryology 4. Chromosomes & Macromolecules ...
... Phylogeny • organizes the diversity of living organisms in the context of evolution. • are based on several types of evidence: 1. Fossil Record 2. Morphology 3. Embryology 4. Chromosomes & Macromolecules ...
Chapter 1 ppt
... •Consist of DNA or RNA and may contain protein for replication and pathogenesis; components are then enclosed in a protein coat with or without a lipid membrane coat. •Parasites- requiring host cell to replicate •The cells they infect and the host response to the infectious dictate the nature of the ...
... •Consist of DNA or RNA and may contain protein for replication and pathogenesis; components are then enclosed in a protein coat with or without a lipid membrane coat. •Parasites- requiring host cell to replicate •The cells they infect and the host response to the infectious dictate the nature of the ...
Board Bulletin Offical Notice
... identify the role of this organism in its ecosystem: - Archaea - Eubacteria - Cyanobacteria, including those that form stromatolites - nitrogen fixing bacteria - methanogens - deep-sea bacteria ...
... identify the role of this organism in its ecosystem: - Archaea - Eubacteria - Cyanobacteria, including those that form stromatolites - nitrogen fixing bacteria - methanogens - deep-sea bacteria ...
Bacterial Taxonomy
... determined by valid publication, legitimacy of the name with regard to the rules of nomenclature, and priority of publication. ...
... determined by valid publication, legitimacy of the name with regard to the rules of nomenclature, and priority of publication. ...
Microbiology Homework # 1 Prof. Santos 1
... 9- Two general categories that all cells fall under are a- Unicellular and multicellular b- Eukaryote and prokaryote c- Gram positive and gram negative d- Cocci and bacilli 10- The area in a prokaryote cell where the genetic material is found is called the a- Nucleus b- Mitochondria c- Nucleoid d- C ...
... 9- Two general categories that all cells fall under are a- Unicellular and multicellular b- Eukaryote and prokaryote c- Gram positive and gram negative d- Cocci and bacilli 10- The area in a prokaryote cell where the genetic material is found is called the a- Nucleus b- Mitochondria c- Nucleoid d- C ...
Bacteria
... What are the basic characteristics of bacteria? What are the 2 kingdoms of prokaryotes & what differentiates the 2. 3 basic shapes. Identify the basic structure of a prokaryote as well as the additional structures that can be found in certain species. Understand several impacts of bacterial processe ...
... What are the basic characteristics of bacteria? What are the 2 kingdoms of prokaryotes & what differentiates the 2. 3 basic shapes. Identify the basic structure of a prokaryote as well as the additional structures that can be found in certain species. Understand several impacts of bacterial processe ...
5echap10n16guidedreading
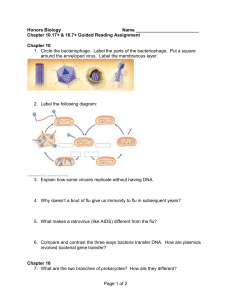
... 4. Why doesn’t a bout of flu give us immunity to flu in subsequent years? ...
... 4. Why doesn’t a bout of flu give us immunity to flu in subsequent years? ...
Lecture 11
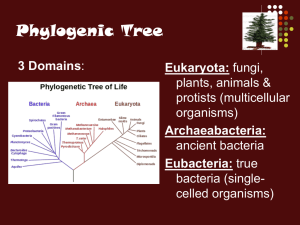
... • A cladogram is a diagram much like a family tree showing the phylogenic tree of different species and demonstrating where they evolved from common ancestors. – Once taxonomists based cladograms on physical, easily-observed characteristics; – Today, they can use more reliable information like genet ...
... • A cladogram is a diagram much like a family tree showing the phylogenic tree of different species and demonstrating where they evolved from common ancestors. – Once taxonomists based cladograms on physical, easily-observed characteristics; – Today, they can use more reliable information like genet ...
Bacterial Classification (The second lecture)
... identifies the species within the genus. For example, humans belong to the genus Homo and within this genus to the species Homo sapiens. The binomial names of species are usually typeset in italics; for example, Staphylococcus aureus . Generally, the binomial should be printed in a font style differ ...
... identifies the species within the genus. For example, humans belong to the genus Homo and within this genus to the species Homo sapiens. The binomial names of species are usually typeset in italics; for example, Staphylococcus aureus . Generally, the binomial should be printed in a font style differ ...
Microbe Math
... 3. Divide the class into groups of four. Give each group a fist-sized piece of clay that represents a single bacterium. Every 30 to 60 seconds, have each group divide its “bacteria”: first two, then four, then eight, then 16, then 32. Track the bacterial growth of the class on a class graph sheet or ...
... 3. Divide the class into groups of four. Give each group a fist-sized piece of clay that represents a single bacterium. Every 30 to 60 seconds, have each group divide its “bacteria”: first two, then four, then eight, then 16, then 32. Track the bacterial growth of the class on a class graph sheet or ...
Taxonomy and Dichotomous Key Notes
... Monera, Protista, and Fungi kingdoms added to the 2 established kingdoms Kingdoms defined based on 2 main characteristics Possession of a true nucleus (prokaryote or eukaryote) How it gets food Heterotroph Autotroph Decomposer ...
... Monera, Protista, and Fungi kingdoms added to the 2 established kingdoms Kingdoms defined based on 2 main characteristics Possession of a true nucleus (prokaryote or eukaryote) How it gets food Heterotroph Autotroph Decomposer ...
KINGDOM MONERA Examples : bacteria, blue
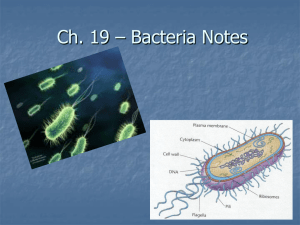
... Refer to diagrams of bacteria in your textbook: Recognise the 3 shapes of bacteria coccus, bacillus and spirillus. Also take note that bacteria have no nuclear membrane. ♦ Cell wall is not made of the same chemical as plant cell walls. Monerans can be identified by whether their cell walls can be st ...
... Refer to diagrams of bacteria in your textbook: Recognise the 3 shapes of bacteria coccus, bacillus and spirillus. Also take note that bacteria have no nuclear membrane. ♦ Cell wall is not made of the same chemical as plant cell walls. Monerans can be identified by whether their cell walls can be st ...