* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Currenty we have three DOMAINS Who are these organisms
Lyme disease microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
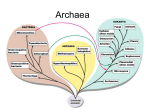
Currenty we have three DOMAINS Who are these organisms? Prokaryotes here are….? Bacteria Archaea Common ancestor of all species living today Eukarya We are going to be very bad biologists and lump Archaea and Bacteria together and talk about them as if they are very similar. Figure 24.18 Euryarchaeotes Crenarchaeotes UNIVERSAL ANCESTOR Nanoarchaeotes Proteobacteria Bacteria Spirochetes Cyanobacteria Gram-positive bacteria Domain Bacteria Chlamydias Prokaryotes Archaea Domain Archaea Korarchaeotes Domain Eukarya Eukaryotes Figure 24.18 Euryarchaeotes Crenarchaeotes UNIVERSAL ANCESTOR Nanoarchaeotes Domain Archaea Korarchaeotes Domain Eukarya Eukaryotes Proteobacteria Spirochetes Cyanobacteria Gram-positive bacteria Domain Bacteria Chlamydias 3 Domains? 2 Domains? Proceedings National Academy of Sciences 2015 May 26;112(21):6670-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420858112. Epub 2015 May 11. The two-domain tree of life is linked to a new root for the Archaea. root of the Archaea that lies within the Euryarchaeota, challenging the traditional topology of the archaeal tree. Therefore, if we are to embrace an archaeal origin for eukaryotes, our view of the evolution of the third domain of life will have to be profoundly reconsidered, as will many areas of investigation aimed at inferring ancestral characteristics of early life and Earth. Precambrian (Evolution of life to 500mya) Paleozoic (500-250mya) Mesozoic (250-about 65mya) Cenozoic (65mya-present) Precambrian (Evolution of life to 500mya) Evolution of Prokaryotes (when?) TODAY we will talk about diversity of Prokaryotes around on earth today! Evolution of Eukaryotes Paleozoic Evolution of lots of bigger things… Mesozoic Dinosaurs and lots of other things… Cenozoic Evolution of many seed plants and flowering plants Evolution of mammals PROKARYOTES are Everywhere! (Remember we are loosely grouping Bacteria and Archaea here) 500 species in mouth (300 described and named) Total number of bacterial cells in/on the human host out-number host cells by at least 100-fold. In the gut alone, the bacterial population is ~ 100 trillion and is composed of between 500 and 1,000 different species (http://www.nature.com/ajgsup/journal/v1/n1/pdf/ajgsup20126a.pdf) 8-13km=Upper Troposphere Microbiome of the upper troposphere: Species composition and prevalence, effects of tropical storms, and atmospheric implications ( Science Magazine-January 2013) ……airborne microorganisms above the oceans remain essentially uncharacterized, as most work to date is restricted to samples taken near the Earth’s surface. Here we report on the microbiome of low- and high-altitude air masses sampled ……before, during, and after two major tropical hurricanes, Earl and Karl. Quantitative PCR and microscopy revealed that viable bacterial cells represented on average around 20% of the total …... The samples from the two hurricanes were characterized by significantly different bacterial communities, revealing that hurricanes aerosolize a large amount of new cells. Nonetheless, 17 bacterial taxa, ….were found in all samples, indicating that these organisms possess traits that allow survival in the troposphere. The findings presented here suggest that the microbiome is a dynamic and underappreciated aspect of the upper troposphere with potentially important impacts on the hydrological cycle, clouds, and Extremely important! Some nasty… • During 14th c Black Death or Bubonic plague killed 25% of population.. (other diseases tuberculosis, cholera, Lyme etc ) But most are beneficial….. • Mutualisms- generate nutrients that we need in our gut • Nutrient cycling-decomposers.. Archaea Thermophiles Halophiles Methanogens https://www.uni-due.de/biofilm-centre/archaea/ Thermophiles.. • The current record is …..Pyrodictium occultum, survived 121 C (250 F) for an hour. • Some living at 170 C (338 F) around volcanic vents in ocean (J. Parkes). • Early life on Earth –hyperthermophile? Extreme Halophiles • Tolerate salt concentrations exceeding 15% • Most are photosynthetic autotrophs but not using chlorophyll • Use bacteriorhodopsin (which uses all light except for purple, making the cells appear purple). Methanogens-common in many areas Release methane Why do we hear about methane these days? Anaerobic Wetland soils, bottom of lakes In gut of cattle, termites and humans… In sewage treatment facilities Methanogens in Human Health and Disease Mark Pimentel MD1, et al. (2012)1GI Motility Program, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, USA There is growing evidence that host/microbial interactions within the gut can have a profound impact on human health and disease; in fact, the intestinal microflora have been shown to influence the innate physiology, biochemistry, immunology, maturation of the vasculature, and gene expression in a host. Although most research has focused on gut bacteria, current evidence suggests that the Archaea—an ancient domain of single-celled organisms—are resident within the gut in high numbers, and have direct and indirect effects on the host. In particular, the methanogens are an essential component of luminal intestinal microbial ecosystems. Methanogens oxidize hydrogen to produce methane and ensure more complete fermentation of carbohydrate substrates, leading to higher production and adsorption of shortchain fatty acids, which may lead to obesity. Methane, the key product of carbohydrate fermentation by the methanogens, has long been thought to produce no ill effects in humans aside from gaseous distention. However, recent evidence has linked methane production to the pathogenesis of constipation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), as well as obesity. In particular, a significant percentage of patients with IBS and constipation excrete methane, suggesting an overabundance of methanogenic archaea in their gut. Methane by itself may influence intestinal transit and pH and facilitate development of constipation. If methane has a direct or indirect effect on intestinal transit, attempting to manipulate methanogenic flora may serve as a novel therapeutic option. Thus, understanding methanogens and their role in gut function/dysfunction is vital to our understanding of human health and disease. Behavior 1. Getting around.. Flagellum or flagella Analogous or homologous? Secrete mucous (chemicals-ooze around) Figure 24.10 Flagellum Filament Hook Motor Cell wall Plasma membrane Rod Peptidoglycan layer 20 nm Fimbriae? Gonorrhea bacterium uses these 2. Show photo, chemo, geotaxis. 3. Endospores-packages chromosome in tough coat (Anthrax) 4. Bacteriocins chemical “weapons” that kill or inhibit other bacteria Galvez A, Lopez RL, Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Omar NB. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2008;28(2):125-52. Area de Microbiologia, Facultad de Ciencias Experimentales, Universidad de Jaén, Jaén, Spain. [email protected] Bacteriocins are antimicrobial peptides or proteins produced by strains of diverse bacterial species. The antimicrobial activity of this group of natural substances against foodborne pathogenic, as well as spoilage bacteria, has raised considerable interest for their application in food preservation. Application of bacteriocins may help reduce the use of chemical preservatives and/or the intensity of heat and other physical treatments, satisfying the demands of consumers for foods that are fresh tasting, ready to eat, and lightly preserved. In recent years, considerable effort has been made to develop food applications for many different bacteriocins and bacteriocinogenic strains. Depending on the raw materials, processing conditions, distribution, and consumption, the different types of foods offer a great variety of scenarios where food poisoning, pathogenic, or spoilage bacteria may proliferate. Therefore, the effectiveness of bacteriocins requires careful testing in the food systems for which they are intended to be applied against the selected target bacteria. This and other issues on application of bacteriocins in foods of dairy, meat, seafood, and vegetable origins are addressed in this review. 5. Quorum sensing Release and detect chemical pheromones to gauge their population density When lots of neighbors (a quorum) a group behavior is triggered ….. bioluminesce attack Bacterium that causes Cholera does this 6. Individually, in strings, small clumps and in colonies-Biofilms! Typically multispecies mats stuck to a solid surface. Harmful in some cases (Cystic fibrosis). Kolenbrander, P. Andersen, R. Blehert, D. Palmer, R. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002 September; 66(3): 486–505. Communication among Oral Bacteria Development of the oral microbial community involves competition as well as cooperation among the 500 species that compose this community. Sequential changes in populations of bacteria associated with tooth eruption as well as with caries development and periodontal disease states are known. Temporal changes in populations of bacteria on tooth surfaces after professional cleaning are ordered and sequential. Such sequential changes must occur through attachment and growth of different bacterial species. With the attachment of each new cell type, a nascent surface is presented for the attachment of other kinds of bacteria, resulting in a progression of nascent surfaces and concomitant changes in species diversity . Such coordination indicates communication. In the absence of communication, these orderly changes would be random. Due to the dynamics of growth and adherence, the bacterial populations in the oral cavity are constantly changing, even during the intervals between normal daily oral hygiene treatments. It is unlikely that the various species within oral biofilms function as independent, discrete constituents; rather, these organisms function as a coordinated community that uses intra- and interspecies communication. 7. Reproduction Binary fission-what is that? No sexual reproduction (a Eukaryotic thing) So where does new genetic variation come from? mutation (obviously Eukaryotes experience mutations too) In addition to mutation there are other “styles” of recombination (mixing genomes) Conjugation-use pili to pull each other together Get together share a plasmid Transformation Pick up “naked DNA” Transduction Phage infection (bacteriophages) All of these processes are… Lateral Gene Transfer… Also called Horizontal gene transfer… So this is not like us…… we have vertical transmission! 8. Genome 1/1000 as much DNA as eukaryotes • One double stranded circular DNA molecule • Additional PLASMIDS • These two parts replicate (make copies of themselves) independently Figure 24.12 Chromosome Plasmids Ruptured E. coli 1 µm 9. Nutrition (focus on energy source) Actually just know that they are photosynthetic (autotrophs), able to extract energy from inorganic deep sea vent gasses (like hydrogen sulfide) and eat things (heterotrophic like us)! There are some cool things in this table but probably too much for us right now! 10. Nutrient Cycling Elements move between biological and physical parts of ecosystems “Legumes add nitrogen to the soil” Rhizobium species fix nitrogen (each legume may have its own). Uptake of K by plants (mg) Even non-legumes do better in soils with some strains of bacteria added 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Figure 24.22 Seedlings growing in the lab No Strain 1 Strain 2 Strain 3 bacteria Soil treatment 11. Humans….. • Many are mutualistic (vitamins in gut) • Many are commensal (neither hurt nor harm us) • Others are parasitic (neg. effects on us-Lyme disease, Salmonella-”food poisoning”) Normal flora-keep out disease causing bacteria What about E. coli…. Text- strain 0157:H7 About ¼ of its genes came in through transduction as compared to non pathogenic strain. Which is? (phage) These genes code for adhesive fimbraie that help it stick to your gut wall. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O26 Random addition #1 Gram staining.. Purple positive (have larger quantities of peptidoglycan in cell wall-considered simpler) Gram negative pink (more complex outer membrane-more dangerous -more resistant to antibiotics) Random addition #2 The largest prokaryote, next to a fruit fly-almost 1mm in diameter. Sulfur Pearl (Thiomargarita namibiensis) from Namibia, inhabits the sediments along the west coast of Africa. (microbe garden website) Random addition #3 Bloom of cyanobacteria MN Pollution Control Agency Severe blue-green algal blooms typically occur on lakes with poor water quality (high in nutrients), and look like green paint, pea soup, or a thick green cake (see photo gallery below for examples). HAB often result in extremely low water clarity (less than 1 foot). There is no visual way to predict the toxicity of an algal bloom Random addition #4 We use these organisms-Bioremediation! Random addition #5 Mutualism: bacterial “headlights” Random addition #6 tubeworms ! • no mouths, no stomachs, and no intestines • bodies house billions of bacteria that feed them (convert hydrogen sulfide from the hydrothermal vents into molecules that serve as usable nutrients) • eight feet long