* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title - Iowa State University
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
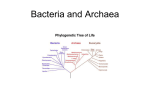
Week 2, Session 1 Chapters 26-27 Important text sections: 26.1, 26.3, 26.6, 27.1, 27.2, Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Kelsey Course: Bio 211 Instructor: Dr. Holscher Date: 8-31-09 Phylogeny 1. Who first developed the binomial nomenclature system? Carolus Linneaus a. What are the two components of the binomial nomenclature format? genus and species b. Give an example of this format: homo sapiens Cladistics 1. What is the primary criterion in the methodology of cladistics? Common ancestry is the primary criterion used in cladistics. 2. A true clade is: a. monopyletic b. paraphyletic c. polyphyletic 3. Draw an example of a clade: Three Domain System 1. What are the domains are found in the three-domain system? Eukarya Bacteria Archaea Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu Characteristics of Prokaryotes 1. List four characteristics of prokaryotes: able to live in extreme environments first organism on earth unicellular have a diameter of around 0.5-5 micrometers 2. Name and draw the three common shapes of prokaryotes: Cocci (spherical) Bacilli (rod-shaped) Spriochetes (spiral) 3. A gram-positive__ bacteria has a thick cell wall made of peptidoglycan that causes it to appear purple_ during gram staining. 4. A gram-negative bacteria has a thin layer of peptidoglycan sandwiched between two membranes that causes it to appear _pink/red_ during gram staining. 5. Match the following prokaryotic cell structures with their function: 1. capsule __a__ a. a sticky layer that allows prokaryotes to adhere to other things 2. fimbriae __c__ b. a structure that enables motility by propulsion c. hair-like appendages that aid the cell in sticking to 3. sex pili __d__ other things d. an appendage used to pull two cells together for 4. flagellum __b__ DNA transfer e. resistant cells that form when nutrients are lacking 5. endospores __e__ 6. List and describe the three ways in which prokaryotes perform genetic recombination: Transformation A prokaryotic cell takes up foreign DNA from its surroundings. Transduction Conjugation Bacteriophages move bacterial Two bacterial cells genes from one host to a temporarily join and transfer different host. the material between them. 7. Describe the four modes of nutrition in prokaryotes: Photoautotrophs Use light energy to drive synthesis of organic compounds. Chemoautotrophs Oxidize inorganic substances to use as a carbon source. Photoheterotrophs Use light energy and must obtain carbon in organic form. Chemoheterotrophs Must consume organic molecules for energy and carbon. 8. Write in the name of the oxygen-use type that matches the given definitions: Obligate aerobe Require oxygen for cellular respiration, cannot grow without oxygen. Obligate anaerobe Are poisoned by oxygen, cannot grow in the presence of oxygen. Facultative anaerobe Use oxygen if it is present but can also grow without oxygen. 9. What is the most important role that prokaryotes play in the biosphere? Decomposers- break down corpses, waste, and dead plants which releases carbon and nitrogen. 10. Describe the four types of ecological interactions that exist between prokaryotes and other organisms: Symbiosis: a relationship in which two species live in close contact o Mutualism: both species benefit o Commensalism: one species benefits, the other is neither harmed nor helped o Parasitism: a parasite eats the tissues or fluids of its host, which harms the host Archaea 1. Name the three types of extremophiles, and describe their living conditions/preferences: Halophiles Either tolerate or prefer highly saline environments. Thermophiles Thrive in extremely hot environments. Methanogens Obtain energy by using carbon dioxide to oxidize hydrogen gas, releasing methane as a waste product. Bacteria 1. True or false: All bacteria are pathogenic (harmful). _False a. If this is false, give an example of a non-pathogenic (beneficial) type of bacteria: Many are found in human intestines. We have a mutualistic relationship with these bacteria and depend on them to help digest some foods we eat. 2. __Exotoxins___ are poisonous illness-causing proteins secreted by bacteria and other organisms. An example of this type of toxin is _cholera_. 3. _Endotoxins______ are components of the outer membrane of some types of bacteria that are released when the cell walls break down. An example of this type of toxin is _salmonella_. 4. List four ways in which bacteria and/or archaea are being used in research, technology, and industry today: Food production- cheese and yogurt Bioremediation- use of organisms to remove pollutants from soil, air, and water Production of natural plastics Modification of vitamins, antibiotics, and hormones