cell_assignment
... careful not to pull blood when you do it!! Draw the animal and plant cells in the boxes. ...
... careful not to pull blood when you do it!! Draw the animal and plant cells in the boxes. ...
NAME - SchoolNotes
... 20. Diffusion = Movement of other materials like salt and sugar from where there is much to where there is less. 21. Mitosis = When a single cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. 22. Prophase = The tangled mass of DNA condenses ...
... 20. Diffusion = Movement of other materials like salt and sugar from where there is much to where there is less. 21. Mitosis = When a single cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. 22. Prophase = The tangled mass of DNA condenses ...
Structures and Organelles
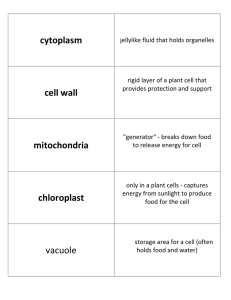
... Cytoplasm-semifluid material prokaryotes- Chemical process occur eukaryotes- Where organelles are found Cytoskeleton- Support “net” for organelles microtubules and microfilaments ...
... Cytoplasm-semifluid material prokaryotes- Chemical process occur eukaryotes- Where organelles are found Cytoskeleton- Support “net” for organelles microtubules and microfilaments ...
Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell
... proceeds in both directions. • Entire genome is replicated once - further replication is blocked • involves DNA polymerase and other proteins that function to unwind and stabilize the DNA and “prime” DNA replication of the “lagging” strand. ...
... proceeds in both directions. • Entire genome is replicated once - further replication is blocked • involves DNA polymerase and other proteins that function to unwind and stabilize the DNA and “prime” DNA replication of the “lagging” strand. ...
cell reproduction
... Cell increases in size Cell prepares to copy its DNA and organelles increase in number Cells spend most of their time in this phase. ...
... Cell increases in size Cell prepares to copy its DNA and organelles increase in number Cells spend most of their time in this phase. ...
cell theory
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
Lesson 12-Mitosis - Northern Highlands
... • Chromatin (DNA strands) coil up into visible chromosomes • They look kind of hairy! • Each chromosome is made of two identical halves called SISTER CHROMATIDS • These halves are held together by a CENTROMERE ...
... • Chromatin (DNA strands) coil up into visible chromosomes • They look kind of hairy! • Each chromosome is made of two identical halves called SISTER CHROMATIDS • These halves are held together by a CENTROMERE ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound compounds that contain
... the longest stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows, 13 interphase copies its DNA, and prepares to divide the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its 14 replication / replicates nucleus the stage of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides 15 mitosis into two new nuclei ...
... the longest stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows, 13 interphase copies its DNA, and prepares to divide the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its 14 replication / replicates nucleus the stage of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides 15 mitosis into two new nuclei ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound
... the longest stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows, 13 interphase copies its DNA, and prepares to divide the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its 14 replication / replicates nucleus the stage of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides 15 mitosis into two new nuclei fi ...
... the longest stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows, 13 interphase copies its DNA, and prepares to divide the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its 14 replication / replicates nucleus the stage of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides 15 mitosis into two new nuclei fi ...
2/23/10 Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce
... for DNA synthesis Gap 0: There are times when a cell will leave the cycle and quit dividing. This may be a temporary resting period i.e. liver cell, or more permanent, i.e. a cell that has reached an end stage of development and will no longer divide (e.g. nerve cells in the brain). Gap 2: The cell ...
... for DNA synthesis Gap 0: There are times when a cell will leave the cycle and quit dividing. This may be a temporary resting period i.e. liver cell, or more permanent, i.e. a cell that has reached an end stage of development and will no longer divide (e.g. nerve cells in the brain). Gap 2: The cell ...
Cell Cycle/Reproduction Notes
... until they are over-ridden by go ahead signals. Three checkpoints exists in G1, G2, and M. Cells also have a predetermined lifespan. Timing is controlled by regulatory proteins – cyclins and kinases. These proteins selectively access, activate and silence information in DNA. Contact Inhibition – ...
... until they are over-ridden by go ahead signals. Three checkpoints exists in G1, G2, and M. Cells also have a predetermined lifespan. Timing is controlled by regulatory proteins – cyclins and kinases. These proteins selectively access, activate and silence information in DNA. Contact Inhibition – ...
a. What kind of cell – diploid or haploid – are the body
... Through what process do these body cells reproduce as the animal grows? Mitosis b. What is the animal’s diploid number? 40 What is the animal’s haploid number? 20 c. How many chromosomes do the sex cells of the insect contain? 20 Are these cells haploid or diploid? Haploid d. Through what process ar ...
... Through what process do these body cells reproduce as the animal grows? Mitosis b. What is the animal’s diploid number? 40 What is the animal’s haploid number? 20 c. How many chromosomes do the sex cells of the insect contain? 20 Are these cells haploid or diploid? Haploid d. Through what process ar ...
Study Guide for Science Test
... Organ System: Organs that work together to perform a function. Mitosis: The process in which a cell divides into two exact copies of itself. Cell differentiation: The specialization of cells. Cell develops into different type of cell that does a specific job. Cell respiration: Process of using oxyge ...
... Organ System: Organs that work together to perform a function. Mitosis: The process in which a cell divides into two exact copies of itself. Cell differentiation: The specialization of cells. Cell develops into different type of cell that does a specific job. Cell respiration: Process of using oxyge ...
Sep 52:43 PM Sep 81:29 PM Sep 52:53 PM Sep 53:37 PM Sep 54
... organize the spindle, a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes. During prophase, the condensed chromosomes becomes attached to fibers in the spindle at a point near the centromere of each chromatid. Interestingly, plant cells do not have centrioles, but still organiz ...
... organize the spindle, a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes. During prophase, the condensed chromosomes becomes attached to fibers in the spindle at a point near the centromere of each chromatid. Interestingly, plant cells do not have centrioles, but still organiz ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Questions The following questions closely
... List 2 things that happen to cells during anaphase. a. Sister chromatids split at the centromere b. Kinetichore fibers shorten Sketch and label the mitotic spindle and attached chromosomes. ...
... List 2 things that happen to cells during anaphase. a. Sister chromatids split at the centromere b. Kinetichore fibers shorten Sketch and label the mitotic spindle and attached chromosomes. ...
p. 208
... Prophase: The first phase of mitosis (p. 206-208) 22. Prophase is the _______________ and ___________________ phase of mitosis. 23. What happens to the chromatin during prophase? ...
... Prophase: The first phase of mitosis (p. 206-208) 22. Prophase is the _______________ and ___________________ phase of mitosis. 23. What happens to the chromatin during prophase? ...
Online Mitosis Lab - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Or click on the link called “Mitosis Online Lab Activity” on Ms. Maier’s webpage under Grade 9 Science. Step 1: Read the introduction. Step 2: Click “Begin Assignment” Step 3: Follow the directions on the page. Answer all questions on this assignment sheet as you complete each section. Part 1 1) Can ...
... Or click on the link called “Mitosis Online Lab Activity” on Ms. Maier’s webpage under Grade 9 Science. Step 1: Read the introduction. Step 2: Click “Begin Assignment” Step 3: Follow the directions on the page. Answer all questions on this assignment sheet as you complete each section. Part 1 1) Can ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.