Why do cells divide?
... G1 (Gap 1) is when the cell grows and functions normally and during this time, protein synthesis occurs and the cell grows producing more organelles, increasing the volume of the cytoplasm. Synthesis (S) is when the cell duplicates its DNA G2 (Gap 2) is where the cell resumes its growth in prepa ...
... G1 (Gap 1) is when the cell grows and functions normally and during this time, protein synthesis occurs and the cell grows producing more organelles, increasing the volume of the cytoplasm. Synthesis (S) is when the cell duplicates its DNA G2 (Gap 2) is where the cell resumes its growth in prepa ...
Study Guide for Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis, and Sexual and
... Study Guide for Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis, and Sexual and Asexual Reproduction 11. a.Name the four stages of mitosis. Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 ...
... Study Guide for Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis, and Sexual and Asexual Reproduction 11. a.Name the four stages of mitosis. Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 ...
6 - Mitosis and Cytokinesis Reading
... Mitosis and Cytokinesis – Reading During mitosis , when the nucleus divides, the two chromatids that make up each chromosome separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the cell. This is shown in Figure below . You can watch an animation of the process at the following link: http://www.bi ...
... Mitosis and Cytokinesis – Reading During mitosis , when the nucleus divides, the two chromatids that make up each chromosome separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the cell. This is shown in Figure below . You can watch an animation of the process at the following link: http://www.bi ...
Cell Cycle Card Sort Lab
... B. Locate the pictures of the cell going through the cell cycle. 4. Place the pictures in the correct order under the name cards. Have your teacher check that you have them in the correct order. Then sketch and label the 6 pictures of the cell cycle. Include the terms parent cell, daughter cells, ch ...
... B. Locate the pictures of the cell going through the cell cycle. 4. Place the pictures in the correct order under the name cards. Have your teacher check that you have them in the correct order. Then sketch and label the 6 pictures of the cell cycle. Include the terms parent cell, daughter cells, ch ...
Exam III Sample Questions
... 16. Proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix of animal tissues: A) Provide Tensile Strength B) Are linked to microtubules through the plasma membrane C) Are polysaccharides composed of glucose subunits D) Provide resistance to compression E) None of the Above 17. Any blastomere removed from an 8 ce ...
... 16. Proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix of animal tissues: A) Provide Tensile Strength B) Are linked to microtubules through the plasma membrane C) Are polysaccharides composed of glucose subunits D) Provide resistance to compression E) None of the Above 17. Any blastomere removed from an 8 ce ...
Regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo
... Copying DNA: Cells make an extra copy of the DNA in its nucleus in a Process called replication. Replication is important because each new cell, called a daughter cell, must have a complete set of DNA to survive (46 chromosomes) Preparing for Division: Cells produce structures that it will use to di ...
... Copying DNA: Cells make an extra copy of the DNA in its nucleus in a Process called replication. Replication is important because each new cell, called a daughter cell, must have a complete set of DNA to survive (46 chromosomes) Preparing for Division: Cells produce structures that it will use to di ...
Daily Power point and warm up
... Skin cancer - the abnormal growth of skin cells - most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. Cell that reproduce by asexual reproduction reproduce constantly. ...
... Skin cancer - the abnormal growth of skin cells - most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. Cell that reproduce by asexual reproduction reproduce constantly. ...
Mitosis and Meiosis
... –The cell just finished dividing so in Gap 1 the cell is recovering from mitosis ...
... –The cell just finished dividing so in Gap 1 the cell is recovering from mitosis ...
notes File - selu moodle
... Chromosomes reach opposite poles of the cell Undoing prophase Nuclear membranes reform Golgi and ER reform Spindle breaks down Chromosomes uncoil rRNA genes can be expressed Cytokinesis – Cytoplasmic division Animals (actin filaments form cleavage furrow) Plants (cell plate filled in with cellulose) ...
... Chromosomes reach opposite poles of the cell Undoing prophase Nuclear membranes reform Golgi and ER reform Spindle breaks down Chromosomes uncoil rRNA genes can be expressed Cytokinesis – Cytoplasmic division Animals (actin filaments form cleavage furrow) Plants (cell plate filled in with cellulose) ...
Mitosis and Cancer - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
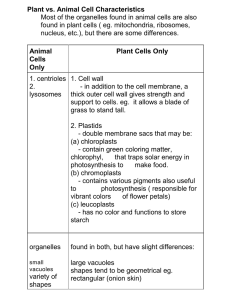
Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in
... Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
... Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
The Continuity of Life
... What cell parts migrate to the poles during prophase? __________________. ...
... What cell parts migrate to the poles during prophase? __________________. ...
cp biology final exam review sheet
... process of photosynthesis – light reaction and Calvin cycle hydrogen acceptor – what is it, give an example of one found in aerobic respiration ...
... process of photosynthesis – light reaction and Calvin cycle hydrogen acceptor – what is it, give an example of one found in aerobic respiration ...
Mitosis ppt
... S (synthesis) = cell is continuing to grow & duplicates its DNA (i.e. chromosomes) in preparation for making duplicate cells during mitosis G2 (2nd gap) = cell keeps growing & making proteins; it grows too big…solution = divide in 2 ...
... S (synthesis) = cell is continuing to grow & duplicates its DNA (i.e. chromosomes) in preparation for making duplicate cells during mitosis G2 (2nd gap) = cell keeps growing & making proteins; it grows too big…solution = divide in 2 ...
3/10/15- Phases of Meiosis WS
... Meiosis I results in two haploid daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. ...
... Meiosis I results in two haploid daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. ...
Why do Cells Divide?
... Reminder from cell theory • All cells come from pre-existing cells!! -Cell Division follows this b/c it’s the process where new cells are made from 1 cell • Cell Division makes 2 new daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell ...
... Reminder from cell theory • All cells come from pre-existing cells!! -Cell Division follows this b/c it’s the process where new cells are made from 1 cell • Cell Division makes 2 new daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell ...
BIOL 100 Quiz 3 1. What is a sister chromatid? A) a chromosome in
... 6. Animal cells undergo cytokinesis by way of a cleavage furrow. Plant cells cannot do this and grow a structure called the cell plate instead. Why can’t plant cells form a cleavage furrow? A) plant cells don’t have a cytoskeleton B) plant cells have cells walls that are too rigid to form a cleavage ...
... 6. Animal cells undergo cytokinesis by way of a cleavage furrow. Plant cells cannot do this and grow a structure called the cell plate instead. Why can’t plant cells form a cleavage furrow? A) plant cells don’t have a cytoskeleton B) plant cells have cells walls that are too rigid to form a cleavage ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Pre-Test
... B. Divides the nucleus. C. Divides the cytoplasm. D. Produces a new cell. 2012 FL Holt McDougal Biology 7. Why do cells lining the stomach divide more quickly than those in the liver? A. They are much smaller cells. B. They have fewer chromosomes. C. They need much more surface area. D. They undergo ...
... B. Divides the nucleus. C. Divides the cytoplasm. D. Produces a new cell. 2012 FL Holt McDougal Biology 7. Why do cells lining the stomach divide more quickly than those in the liver? A. They are much smaller cells. B. They have fewer chromosomes. C. They need much more surface area. D. They undergo ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... cell cycle) with special emphasis on the two ways that cells divide (mitosis and meiosis). Special attention will be paid to: whether the products are haploid or diploid what happens in each stage of each cell cycle recognizing each stage of each type of cell division in plant and animal cells ...
... cell cycle) with special emphasis on the two ways that cells divide (mitosis and meiosis). Special attention will be paid to: whether the products are haploid or diploid what happens in each stage of each cell cycle recognizing each stage of each type of cell division in plant and animal cells ...
Cell Cycle SOL Q
... What significant event occurs during metaphase? ...chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell ...spindle fibers connect the centrioles to the spindle poles ...
... What significant event occurs during metaphase? ...chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell ...spindle fibers connect the centrioles to the spindle poles ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.