chromosomes
... How is DNA organized? Usually in a cell, DNA is wrapped histone proteins in long around ________ ...
... How is DNA organized? Usually in a cell, DNA is wrapped histone proteins in long around ________ ...
10-2 - Kleins
... During this phase DNA is replicated so that when division occurs, there is a complete set of DNA for each daughter cell ...
... During this phase DNA is replicated so that when division occurs, there is a complete set of DNA for each daughter cell ...
Mitosis and Meiosis
... –The cell just finished dividing so in Gap 1 the cell is recovering from mitosis ...
... –The cell just finished dividing so in Gap 1 the cell is recovering from mitosis ...
Unit 9 obj. Mitosis and Meiosis
... vary from organism to organism but one characteristic of each organism is that each of their body (somatic) cells always maintains the same number of chromosomes. The Cell Theory states that cells come from other cells; meaning that cells divide to produce two new cells called daughter cells. These ...
... vary from organism to organism but one characteristic of each organism is that each of their body (somatic) cells always maintains the same number of chromosomes. The Cell Theory states that cells come from other cells; meaning that cells divide to produce two new cells called daughter cells. These ...
Biology and you - properties of life and the scientific method
... 2. Mitosis (which is broken into four phases) a. Prophase – first stage of mitosis. Nuclear envelope begins to disappear; chromatin coils up and becomes X-shaped chromosomes. b. Metaphase – chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Spindle fibers attach the centromere on the chromosome. Spindle ...
... 2. Mitosis (which is broken into four phases) a. Prophase – first stage of mitosis. Nuclear envelope begins to disappear; chromatin coils up and becomes X-shaped chromosomes. b. Metaphase – chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Spindle fibers attach the centromere on the chromosome. Spindle ...
Cell Division
... Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) • Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome and its copy(sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase ...
... Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) • Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome and its copy(sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase ...
Review ANSWER KEY File
... List the steps in DNA replication. 1. Unzipping of the DNA to separate the base pairs 2. New bases pair with those on the parent DNA strands 3. 2 identical DNA molecules are produced What happens during mitosis? Sister chromatids become separated to produce daughter chromosomes, which will split int ...
... List the steps in DNA replication. 1. Unzipping of the DNA to separate the base pairs 2. New bases pair with those on the parent DNA strands 3. 2 identical DNA molecules are produced What happens during mitosis? Sister chromatids become separated to produce daughter chromosomes, which will split int ...
END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONS
... production, and metabolic activities; the S phase, during which DNA is replicated prior to cell division and growth activities continue; and the G2 phase, characterized by completion of centriole replication, organelle production, and synthesis of proteins needed for cellular division. ...
... production, and metabolic activities; the S phase, during which DNA is replicated prior to cell division and growth activities continue; and the G2 phase, characterized by completion of centriole replication, organelle production, and synthesis of proteins needed for cellular division. ...
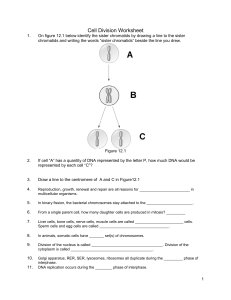
Cell Division Worksheet PDF
... 2. Division of cytoplasm and organelles _______________ 3. Cell grows in size following division ______________ 4. Cell has twice as much DNA as parent cell _________ 5. Division of chromosomes _________________ ...
... 2. Division of cytoplasm and organelles _______________ 3. Cell grows in size following division ______________ 4. Cell has twice as much DNA as parent cell _________ 5. Division of chromosomes _________________ ...
The Cell Cycle - HomeworkNOW.com
... • Parent Cell: Original cell in interphase, before division occurs. • Daughter Cell: Cells produced from parent cell at the end of the cell cycle. ...
... • Parent Cell: Original cell in interphase, before division occurs. • Daughter Cell: Cells produced from parent cell at the end of the cell cycle. ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
Cell Division Mitosis
... pinches in around the middle of the cell. The result is a new daughter cell that is identical to the parent cell. It should have the same number of ...
... pinches in around the middle of the cell. The result is a new daughter cell that is identical to the parent cell. It should have the same number of ...
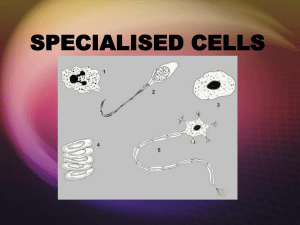
Muscle Cells
... A. Unicellular Organisms- Single cell organisms including yeast, algae, bacteria and protozoa (Kingdom – Protista) B. Multicellular Organisms- organisms made of more than one cell 1. Cell specialization- the ways different cells have evolved to perform different tasks 2. Specialized Animal and Plant ...
... A. Unicellular Organisms- Single cell organisms including yeast, algae, bacteria and protozoa (Kingdom – Protista) B. Multicellular Organisms- organisms made of more than one cell 1. Cell specialization- the ways different cells have evolved to perform different tasks 2. Specialized Animal and Plant ...
Human Body Ch 1
... Stage 3: Cytokinesis 17. During cytokinesis the _________________ divides. The _________________ are _____________________ into each of the two new cells. 18. What happens during cytokinesis in animal cells? 19. What happens during cytokinesis in plant cells? Structure and Replication of DNA 20. Why ...
... Stage 3: Cytokinesis 17. During cytokinesis the _________________ divides. The _________________ are _____________________ into each of the two new cells. 18. What happens during cytokinesis in animal cells? 19. What happens during cytokinesis in plant cells? Structure and Replication of DNA 20. Why ...
Meiosis Coloring
... composite nucleus, it became obvious that at some point there must be a mechanism by which the cell reduces the number of chromosomes by half when such gametes are produced. Otherwise the number of chromosomes would double with each generation, and cells would soon have to double in size with each g ...
... composite nucleus, it became obvious that at some point there must be a mechanism by which the cell reduces the number of chromosomes by half when such gametes are produced. Otherwise the number of chromosomes would double with each generation, and cells would soon have to double in size with each g ...
CelI/DNA Review 6-
... 13.What type of bond hold the two strands of a DNA molecule together? lX°,oOÿ-Jÿ 14.The backbone of the DNA helix is composed of alternating ? and ? ,.ÿOOtO.X' ÿ ÿOf:'l2:r-aÿ'X'O--ÿ 15. In the DNA, each nucleotide is composed of (3 things) Ak)ÿXOo.g") ÿ'ÿkÿkÿa.ÿ"- --ÿ_ÿ','ÿA--xk,(ÿ.ÿ, 16. The strand ...
... 13.What type of bond hold the two strands of a DNA molecule together? lX°,oOÿ-Jÿ 14.The backbone of the DNA helix is composed of alternating ? and ? ,.ÿOOtO.X' ÿ ÿOf:'l2:r-aÿ'X'O--ÿ 15. In the DNA, each nucleotide is composed of (3 things) Ak)ÿXOo.g") ÿ'ÿkÿkÿa.ÿ"- --ÿ_ÿ','ÿA--xk,(ÿ.ÿ, 16. The strand ...
100 pt - Mahtomedi Middle School
... The cytoplasm divides, distributing the organelles into each of the two new cells. ...
... The cytoplasm divides, distributing the organelles into each of the two new cells. ...
10.1 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
... 4. The information crisis in a cell is solved by the replication of the DNA before cell division. 5. VISUAL ANALOGY In the visual analogy of the growing town, what does the library represent? Identify two characteristics that make it a good choice for this analogy. ...
... 4. The information crisis in a cell is solved by the replication of the DNA before cell division. 5. VISUAL ANALOGY In the visual analogy of the growing town, what does the library represent? Identify two characteristics that make it a good choice for this analogy. ...
answers - Biology Resources
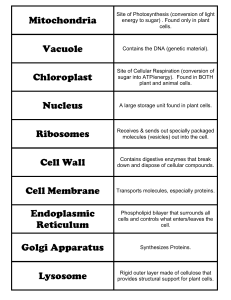
... 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
... 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.