Mitosis vs Meiosis Chart
... number of chromosomes with an exact copy of information from the parent cell ...
... number of chromosomes with an exact copy of information from the parent cell ...
Mitosis
... for the same thing (two sisters and a homologous), a condition known as trisomy, and the latter cell having only one chromosome (the homologous chromosome), a condition known as monosomy. These cells are considered aneuploidic cells. ...
... for the same thing (two sisters and a homologous), a condition known as trisomy, and the latter cell having only one chromosome (the homologous chromosome), a condition known as monosomy. These cells are considered aneuploidic cells. ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... I regulate activities from day to day. ...
... I regulate activities from day to day. ...
Mitosis
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. Spindle fibers form between the poles. ...
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. Spindle fibers form between the poles. ...
Mitosis Meiosis
... • Meiosis is the type of cell division which only occurs for the formation of sex cells (gametes) like eggs and sperm for sexual reproduction. • The mother cell is a diploid cell and the DNA replicates, as in mitosis, but following this, there are two divisions resulting in four haploid (half the nu ...
... • Meiosis is the type of cell division which only occurs for the formation of sex cells (gametes) like eggs and sperm for sexual reproduction. • The mother cell is a diploid cell and the DNA replicates, as in mitosis, but following this, there are two divisions resulting in four haploid (half the nu ...
SQUASH PREPARATION OF ONION ROOT TIP FOR MITOTIC
... 8. Squash the slide with your thumb using a firm and even pressure. (Avoid squashing with such force that the cover slip breaks or slides). 9. Observe it under a compound microscope in 10x objective. Scan and narrow down to a region containing dividing cells and switch to 40x for a better view. The ...
... 8. Squash the slide with your thumb using a firm and even pressure. (Avoid squashing with such force that the cover slip breaks or slides). 9. Observe it under a compound microscope in 10x objective. Scan and narrow down to a region containing dividing cells and switch to 40x for a better view. The ...
Cell Organelle Card Sort
... Gives the cell membrane added support. Gives plant cells their box-like shape. ...
... Gives the cell membrane added support. Gives plant cells their box-like shape. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... a) Protein b) RNA c) DNA d) Carbohydrate e) Lipid 5. Chromosomes are __________ during interphase and _________during karyokinesis. a) Condensed, Extended b) Extended, Condensed c) Straight, Bent d) Bent, Straight 6. What are the five phases of mitosis and briefly describe what occurs at each phase? ...
... a) Protein b) RNA c) DNA d) Carbohydrate e) Lipid 5. Chromosomes are __________ during interphase and _________during karyokinesis. a) Condensed, Extended b) Extended, Condensed c) Straight, Bent d) Bent, Straight 6. What are the five phases of mitosis and briefly describe what occurs at each phase? ...
Slide 1
... Spindle fibers shorten, breaking sister chromatids apart to form separate chromosomes. The chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell -Chromosomes begin to unwind back to chromatin. -The nuclear envelope and nucleolus reappear in each daughter cell -The spindle disappears ...
... Spindle fibers shorten, breaking sister chromatids apart to form separate chromosomes. The chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell -Chromosomes begin to unwind back to chromatin. -The nuclear envelope and nucleolus reappear in each daughter cell -The spindle disappears ...
The Onion`s Tip
... Interphase - In interphase, the chromosomes are not condensed yet, and individual chromosomes cannot be distinguished. ...
... Interphase - In interphase, the chromosomes are not condensed yet, and individual chromosomes cannot be distinguished. ...
Control of Cell Cycle 2013/14
... the process of mitosis by coding for proteins that promote cell division e.g. MPF • These are dominant genes therefore a single mutation would convert them into the mutant type ‘oncogenes’, starting uncontrolled cell division • Oncogenes are mutated genes where there is a ‘gain-offunction’ • Oncogen ...
... the process of mitosis by coding for proteins that promote cell division e.g. MPF • These are dominant genes therefore a single mutation would convert them into the mutant type ‘oncogenes’, starting uncontrolled cell division • Oncogenes are mutated genes where there is a ‘gain-offunction’ • Oncogen ...
Ch 9 Study Guide How Cells Divide_HB
... 8. Regions of DNA uncoil in between cell division so they can be read and so information can be used to direct the activities of the cell. This less tightly coiled DNA protein complex is called _________________. 9. DNA in most prokaryotes are made of only __________________ which is attached to the ...
... 8. Regions of DNA uncoil in between cell division so they can be read and so information can be used to direct the activities of the cell. This less tightly coiled DNA protein complex is called _________________. 9. DNA in most prokaryotes are made of only __________________ which is attached to the ...
Meiosis - SchoolNotes
... • In the S stage of Interphase: – Each DNA Strand makes an exact copy of itself • The two identical strands are joined together by a centomere. • The joined strands are called sister chromatids ...
... • In the S stage of Interphase: – Each DNA Strand makes an exact copy of itself • The two identical strands are joined together by a centomere. • The joined strands are called sister chromatids ...
Mitosis
... In order for the body to grow and to repair damaged or old tissue cells, the cells must reproduce. During the process of mitosis, cells identical to the original cell are created. This allows tissues to produce more of the same kinds of cells to either increase the number of cells in the tissue or t ...
... In order for the body to grow and to repair damaged or old tissue cells, the cells must reproduce. During the process of mitosis, cells identical to the original cell are created. This allows tissues to produce more of the same kinds of cells to either increase the number of cells in the tissue or t ...
The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... – A series of stages through which most eukaryotic cells pass during some time in their development – In single-celled eukaryotes, the cell cycle often represents the major mechanism for asexual reproduction of the species – In multicellular eukaryotes, the cell cycle is used for cellular reproducti ...
... – A series of stages through which most eukaryotic cells pass during some time in their development – In single-celled eukaryotes, the cell cycle often represents the major mechanism for asexual reproduction of the species – In multicellular eukaryotes, the cell cycle is used for cellular reproducti ...
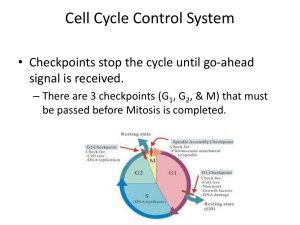
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
... peaks during M phase and initiates Mitosis aids in the disassembly of the nuclear lamina switched off during Anaphase ...
... peaks during M phase and initiates Mitosis aids in the disassembly of the nuclear lamina switched off during Anaphase ...
Word Bank:
... 2) A centromere is a protein disk that attaches two chromatids to each other in a chromosome. 3) You can study a karyotype to learn about the chromosomes present in a somatic cell. 4) A diploid cell is one that is designated by the symbol 2n, has chromosomes found in pairs, and has two homologues of ...
... 2) A centromere is a protein disk that attaches two chromatids to each other in a chromosome. 3) You can study a karyotype to learn about the chromosomes present in a somatic cell. 4) A diploid cell is one that is designated by the symbol 2n, has chromosomes found in pairs, and has two homologues of ...
Product Information
... The required dose of G 418-BC for the selection of resistant cells varies in dependence of the cell type and the current phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active ce ...
... The required dose of G 418-BC for the selection of resistant cells varies in dependence of the cell type and the current phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active ce ...
03-Mitosis student HO - Alexmac
... 1. During which stage of the cell cycle does replication of the DNA occur? ...
... 1. During which stage of the cell cycle does replication of the DNA occur? ...
Chapter 7 test review 2015
... 12. Know what it means for a solution to be hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic and how it affects cells. Draw what cells look like after being in each solution and where the water is moving. ...
... 12. Know what it means for a solution to be hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic and how it affects cells. Draw what cells look like after being in each solution and where the water is moving. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.