Space ppt
... What is a Galaxy? • Galaxy: A giant structure that contains hundreds of billions of stars bound together by gravity. • Spiral Galaxy: A galaxy whose arms curve outward in a pinwheel pattern. Contains solar systems and nebulae (gas, new stars, and dust). • Irregular Galaxy: A galaxy that does not ha ...
... What is a Galaxy? • Galaxy: A giant structure that contains hundreds of billions of stars bound together by gravity. • Spiral Galaxy: A galaxy whose arms curve outward in a pinwheel pattern. Contains solar systems and nebulae (gas, new stars, and dust). • Irregular Galaxy: A galaxy that does not ha ...
PHYSICS 015
... For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, about 10 km in diameter, it already inside its Schwarzschild radius and is doomed to collapse! Stars can’t ‘know’ that they should shed ...
... For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, about 10 km in diameter, it already inside its Schwarzschild radius and is doomed to collapse! Stars can’t ‘know’ that they should shed ...
Manual - Test Equipment Depot
... This is called astrology; the word is from the Greek meaning the “Science of the Stars”. Thousands of years ago astrology was used to determine when to plant and harvest crops. At a later date this developed into the idea that you may be able to tell the future by the position of the stars and plane ...
... This is called astrology; the word is from the Greek meaning the “Science of the Stars”. Thousands of years ago astrology was used to determine when to plant and harvest crops. At a later date this developed into the idea that you may be able to tell the future by the position of the stars and plane ...
Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature)
... Light-year: distance light travels in one year Speed of light is ~300,000km/s (186,000mi/s) or 9.5 trillion km in one year Easier to use light year than km/s North Star is 431 light years away, or 4,080,000,000,000,000km ...
... Light-year: distance light travels in one year Speed of light is ~300,000km/s (186,000mi/s) or 9.5 trillion km in one year Easier to use light year than km/s North Star is 431 light years away, or 4,080,000,000,000,000km ...
Name: Notes – #6 Our Sky Through Binoculars and Telescopes 1
... 7. M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, is ___________________________ light years away. ...
... 7. M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, is ___________________________ light years away. ...
CelestialSphere
... causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. The “S” shape is due to the fact that the orbital planes aren’t quite aligned. ...
... causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. The “S” shape is due to the fact that the orbital planes aren’t quite aligned. ...
Galaxy Powerpoint
... 1. The cluster that the Milky Way is located in is called the Local Group. ...
... 1. The cluster that the Milky Way is located in is called the Local Group. ...
tire
... 10. A plot of the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of stars versus their surface temp (or spectral type). 11. A very compact dense star composed almost entirely of neutrons. 12. The force with which all matter attracts all other matter. ...
... 10. A plot of the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of stars versus their surface temp (or spectral type). 11. A very compact dense star composed almost entirely of neutrons. 12. The force with which all matter attracts all other matter. ...
less than 1 million years
... 1. Today, scientists have _________ about how stars evolve, what makes them different from one another, and how they _____. 2. When __________ fuel is depleted , a star loses its _________ ___________ status. (2 words) 3. This (depletion of star’s hydrogen) can take less than 1 million years for the ...
... 1. Today, scientists have _________ about how stars evolve, what makes them different from one another, and how they _____. 2. When __________ fuel is depleted , a star loses its _________ ___________ status. (2 words) 3. This (depletion of star’s hydrogen) can take less than 1 million years for the ...
Slayt 1
... However, as a gas temperature goes up, the average speed of the particles goes up and the protons get closer before repelling one another. If the proton get very close, the short-range nuclear force ...
... However, as a gas temperature goes up, the average speed of the particles goes up and the protons get closer before repelling one another. If the proton get very close, the short-range nuclear force ...
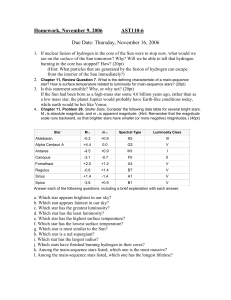
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... star? How is surface temperature related to luminosity for main-sequence stars? (20pt) ...
... star? How is surface temperature related to luminosity for main-sequence stars? (20pt) ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Finally we come to a stage in the stars life where most of the fuel for fusion is used up 1. the temperature and pressure of the core can no longer support the weight of its ...
... Finally we come to a stage in the stars life where most of the fuel for fusion is used up 1. the temperature and pressure of the core can no longer support the weight of its ...
SECTION 8: STARS- OBSERVING CONSTELLATIONS INTRODUCTION
... A light year is a unit of measure for distance in space and equals the distance light travels in 1 year. Light travels 300,000 km (186,000 miles) per second. It takes 8 ½ minutes for light to reach us from our Sun and 4.5 light years for light to reach us from the next closest star, Centauri Proxima ...
... A light year is a unit of measure for distance in space and equals the distance light travels in 1 year. Light travels 300,000 km (186,000 miles) per second. It takes 8 ½ minutes for light to reach us from our Sun and 4.5 light years for light to reach us from the next closest star, Centauri Proxima ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Theoretical Modeling of Massive Stars Mr. Russell University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
What are stars? - Manhasset Schools
... A giant’s core will continue to contract and become hotter. When it uses up all its helium, it contracts even more. When the temperature reaches 100 million K, helium fuses, forming carbon. Now the star is enormous and its surface is much cooler. Its outer layers escape into space leaving behind a ...
... A giant’s core will continue to contract and become hotter. When it uses up all its helium, it contracts even more. When the temperature reaches 100 million K, helium fuses, forming carbon. Now the star is enormous and its surface is much cooler. Its outer layers escape into space leaving behind a ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.