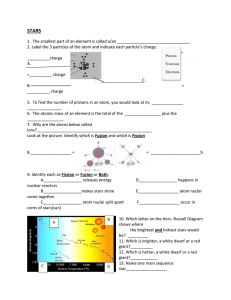
galaxies
... • young stars! only a few million years old • may still be surrounded by nebula from which they formed • located in the spiral arms of a galaxy • example: Pleiades ...
... • young stars! only a few million years old • may still be surrounded by nebula from which they formed • located in the spiral arms of a galaxy • example: Pleiades ...
Star Life Cycles
... A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size; such a star is near its final stage of life. White dwarfs eventually become black dwarfs, which is a white dwarf that has cooled down enough that it no longer emits light. Interes ...
... A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size; such a star is near its final stage of life. White dwarfs eventually become black dwarfs, which is a white dwarf that has cooled down enough that it no longer emits light. Interes ...
Ch 29 Sun and Solar Activity
... gravitationally bound together • orbit a common center of mass • More than ½ the stars in the sky are either binary stars or are part of a multiple-star system • Most binary stars appear to be a single star to the human eye + with tele. too close and one is brighter ...
... gravitationally bound together • orbit a common center of mass • More than ½ the stars in the sky are either binary stars or are part of a multiple-star system • Most binary stars appear to be a single star to the human eye + with tele. too close and one is brighter ...
- MrKowalik.com
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
... 4. If Earth and another celestial object were coming closer together, the electromagnetic waves are bunched together resulting in _____________________________________ 5. If Earth and another celestial object were moving apart, the electromagnetic waves are spread out causing a _____________________ ...
Mon Oct 22, 2012 MOON IN CAPRICORNUS The moon is waxing
... In the constellation Perseus the hero, there is a star named Algol; it’s over in the northeastern sky this evening. Algol is not a particularly bright star – if you didn’t know just where to look for it, you’d probably not even notice it. But it is quite an unusual star – three stars, actually. The ...
... In the constellation Perseus the hero, there is a star named Algol; it’s over in the northeastern sky this evening. Algol is not a particularly bright star – if you didn’t know just where to look for it, you’d probably not even notice it. But it is quite an unusual star – three stars, actually. The ...
CONSTELLATION CASSIOPEIA named after the
... the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to th ...
... the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to th ...
Science Astronomy Name
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
stars
... • They were used but early explorers to navigate the sea at night • All together there are 88 constellations in the night sky. ...
... • They were used but early explorers to navigate the sea at night • All together there are 88 constellations in the night sky. ...
Science Astronomy Name
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2005
... NGC2903 (8.9) sg. A spiral galaxy inclined to our line of sight. One of the brightest galaxies in Leo it is surprisingly not a Messier object. NGC3190 (11.0) sg and NGC3193 (10.9) eg. Pair of galaxies located mid-way between and . NGC3226 (11.4) and NGC3227 (10.8) about 1o east of form a close ...
... NGC2903 (8.9) sg. A spiral galaxy inclined to our line of sight. One of the brightest galaxies in Leo it is surprisingly not a Messier object. NGC3190 (11.0) sg and NGC3193 (10.9) eg. Pair of galaxies located mid-way between and . NGC3226 (11.4) and NGC3227 (10.8) about 1o east of form a close ...
Testing Your Sky
... The darkness of the sky as seen from your favorite observing site can be either a help or a hindrance when it comes to observing the night. Under brightly lit conditions you'll not be able to view the fainter objects of the night. What follows is an exercise for determining darkness of the sky, a co ...
... The darkness of the sky as seen from your favorite observing site can be either a help or a hindrance when it comes to observing the night. Under brightly lit conditions you'll not be able to view the fainter objects of the night. What follows is an exercise for determining darkness of the sky, a co ...
May 2017 - Museums Wellington
... Our evening skies this month are dominated by Jupiter and Saturn, along with some of our brightest stars. Jupiter will be one of the first objects to appear, visible in the north east shortly after the Sun has set. Just to the right of Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in the constellation of Vir ...
... Our evening skies this month are dominated by Jupiter and Saturn, along with some of our brightest stars. Jupiter will be one of the first objects to appear, visible in the north east shortly after the Sun has set. Just to the right of Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in the constellation of Vir ...
Night Sky Checklist October–November
... 2.1, it dims to about 1/3 that brightness for about 10 hours in a cycle of slightly less than 3 days. If you watch it regularly, sooner or later you will catch it at its dimmest. Algol is a binary star, one relatively bright and the other relatively dim. As they orbit each other they happen to be or ...
... 2.1, it dims to about 1/3 that brightness for about 10 hours in a cycle of slightly less than 3 days. If you watch it regularly, sooner or later you will catch it at its dimmest. Algol is a binary star, one relatively bright and the other relatively dim. As they orbit each other they happen to be or ...
Notes- Stars
... will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
... will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
Exploration of the Universe
... model? Who first proposed the heliocentric model? Who discovered that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses? 6. Describe two features of the Sun. 7. Define asteroids, comets, meteors and meteorites. 8. Name three types of electromagnetic radiation. 9. What two factors affect the brightness of a star? 10 ...
... model? Who first proposed the heliocentric model? Who discovered that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses? 6. Describe two features of the Sun. 7. Define asteroids, comets, meteors and meteorites. 8. Name three types of electromagnetic radiation. 9. What two factors affect the brightness of a star? 10 ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... 1. a ball of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of electromagnetic energy 2. From Earth, stars appear as tiny specs of white light, but they actually vary in color. 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. D 7. C 8. A 9. the elements that make up the star 10. hydrogen; helium 11. A 12. C 13. B 14. the surface temper ...
... 1. a ball of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of electromagnetic energy 2. From Earth, stars appear as tiny specs of white light, but they actually vary in color. 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. D 7. C 8. A 9. the elements that make up the star 10. hydrogen; helium 11. A 12. C 13. B 14. the surface temper ...
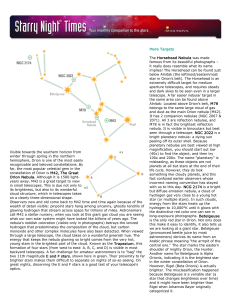
Characteristics of Stars
... Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... converted to helium by nuclear fusion. -> helium-rich core->less hydrogen to burn->core begins to contract->heats the core->fusion restart in the outer layer->outer layers of the star expand and then cool->become a red giant. In about 5 billion years, our Sun will become a red giant. Star with a mas ...
... converted to helium by nuclear fusion. -> helium-rich core->less hydrogen to burn->core begins to contract->heats the core->fusion restart in the outer layer->outer layers of the star expand and then cool->become a red giant. In about 5 billion years, our Sun will become a red giant. Star with a mas ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.